Choosing the right mechanical seal is a critical engineering decision that hinges on a systematic evaluation of your specific operating conditions. The selection process is driven by four key parameters: the chemical and physical properties of the fluid being sealed, the operating temperature and pressure within the equipment, the presence of any abrasive solids, and the physical constraints of the machinery itself.
The goal is not merely to pick a part from a catalog, but to select a complete sealing system whose design and materials are perfectly matched to the application's demands, ensuring reliability, safety, and operational efficiency.
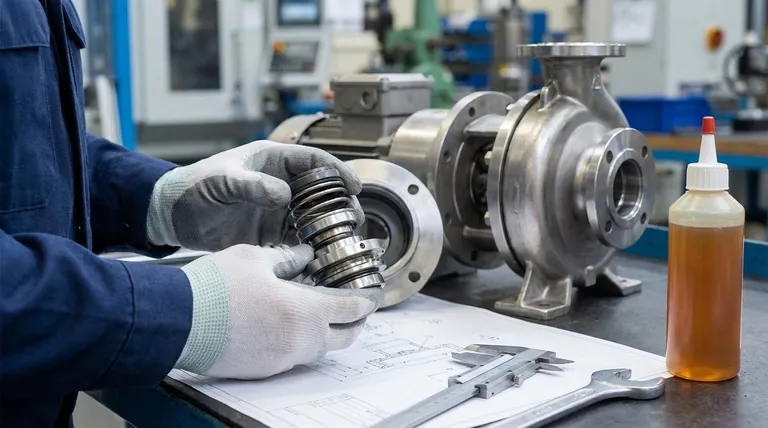

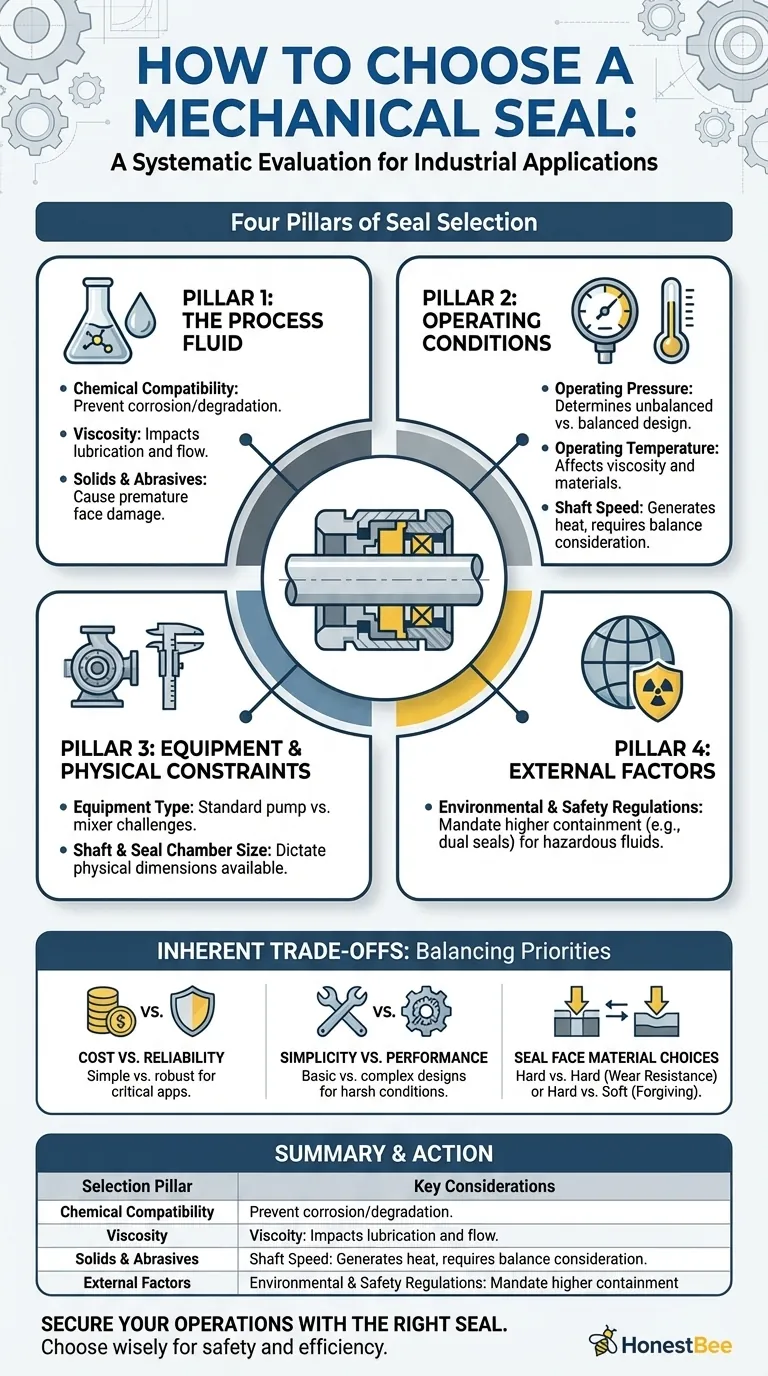
The Four Pillars of Seal Selection
A mechanical seal's success or failure is determined by its ability to maintain a microscopic, stable fluid film between its two primary faces. Every selection criterion is aimed at achieving and preserving this film under specific operational stresses.
Pillar 1: The Process Fluid
The fluid you are sealing is the single most important factor. Its properties dictate the fundamental material choices for the entire seal.
Chemical Compatibility You must identify the exact process fluid and its concentration. This information is critical for selecting elastomers (like O-rings) and seal faces that will not corrode, dissolve, or otherwise degrade when in contact with the fluid.
Viscosity A fluid's viscosity, or its resistance to flow, directly impacts the lubrication of the seal faces. Highly viscous fluids can be difficult to establish a film with, while very thin, non-lubricating fluids can make it difficult to maintain one.
Solids and Abrasives The presence of any solids, abrasives, or slurries in the process fluid is a primary cause of seal failure. These particles can damage the precision-lapped seal faces, leading to premature leakage and wear.
Pillar 2: The Operating Conditions
Once you understand the fluid, you must define the environment in which the seal will operate. These conditions determine the required strength, heat tolerance, and overall design of the seal.
Operating Pressure The pressure in the seal chamber tries to force the seal faces apart or, more commonly, force them together. This pressure determines whether a simple unbalanced seal is sufficient or if a more robust balanced seal design is needed to reduce face-loading and heat generation.
Operating Temperature Temperature affects fluid viscosity, can cause chemical changes in the fluid, and has a significant impact on material selection. Elastomers, in particular, have strict temperature limits, and high temperatures can cause the fluid film at the seal faces to vaporize, leading to face damage.
Shaft Speed The rotational speed of the shaft is a critical factor. Higher speeds generate more heat at the seal faces and require careful consideration of balance and seal face materials to manage that thermal energy.
Pillar 3: The Equipment and Physical Constraints
The seal does not operate in a vacuum. It must fit and function within the physical confines of the pump, mixer, or other rotating equipment.
Equipment Type The type of machine influences the seal choice. A standard centrifugal pump presents a different set of challenges than a high-vibration mixer or a large-shaft-deflection agitator.
Shaft and Seal Chamber Size The physical dimensions, such as the shaft diameter and the available space in the seal chamber (or stuffing box), dictate the size and type of seal that can be physically installed.
Pillar 4: External Factors
Finally, external requirements can override other choices, often mandating more complex and robust sealing solutions.
Environmental and Safety Regulations If the process fluid is toxic, flammable, or otherwise hazardous, regulations will almost certainly require a higher level of containment. This often necessitates the use of dual seals (also called double seals) to provide redundant sealing and prevent any emissions to the atmosphere.
Understanding the Inherent Trade-offs
Selecting a mechanical seal is always an exercise in balancing competing priorities. Understanding these trade-offs is key to making an informed decision.
Cost vs. Reliability
A simple, inexpensive component seal may be perfectly adequate for a non-critical water pump. However, using that same seal in a hazardous chemical application is a recipe for failure, where the cost of downtime, product loss, and safety risks far outweighs the initial savings.
Simplicity vs. Performance
Basic pusher-type seals are common and easy to install but may struggle with abrasive fluids or pressure fluctuations. More complex designs, like stationary metal bellows seals, offer superior performance in harsh conditions but come at a higher cost and require more care during installation.
Seal Face Material Choices
The combination of seal face materials is a critical trade-off. A "hard vs. hard" combination (e.g., Silicon Carbide vs. Silicon Carbide) offers exceptional wear resistance for abrasive services but is less forgiving of misalignment. A "hard vs. soft" combination (e.g., Silicon Carbide vs. Carbon) is more forgiving but the soft face will wear more quickly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use your operational data to guide your final decision, focusing on the most critical requirement for your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is sealing a non-hazardous, low-pressure fluid (like water): A basic, single-spring component seal with standard materials (Carbon/Ceramic faces, Buna elastomers) is likely the most cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is reliability in a demanding process with abrasives: Prioritize hard seal faces (like Silicon Carbide vs. Silicon Carbide) and consider a robust design, potentially supported by an external flush plan.
- If your primary focus is safety and environmental compliance with a hazardous fluid: A dual seal arrangement (either pressurized or unpressurized) is almost always the necessary choice to ensure absolute containment.
- If your primary focus is managing high temperatures or aggressive chemicals: Your selection will be driven by exotic materials, such as perfluoroelastomers (FFKM) for the O-rings and carefully selected seal face materials.
A methodical evaluation of the fluid, the operating conditions, and the equipment transforms seal selection from a guess into a strategic engineering decision.
Summary Table:
| Selection Pillar | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Process Fluid | Chemical compatibility, viscosity, presence of abrasives/solids |
| Operating Conditions | Pressure, temperature, shaft speed |
| Equipment & Constraints | Machine type, shaft diameter, seal chamber size |
| External Factors | Safety regulations, environmental requirements (e.g., dual seals for hazardous fluids) |
Secure Your Operations with the Right Seal
Choosing the correct mechanical seal is critical for preventing downtime, ensuring safety, and protecting your equipment investment. HONESTBEE supplies high-performance beekeeping supplies and equipment to commercial apiaries and distributors through wholesale-focused operations, ensuring you have access to durable, reliable components.
Let our expertise guide you to the optimal sealing solution for your specific application. Contact HONESTBEE today for a consultation and discover how our wholesale solutions can enhance your operational efficiency and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Honey Wax Separating Wax Press with Metal Screw Wax Separator Machine
- HONESTBEE Heavy Duty All Metal Frame Wire Crimper Tool
- Langstroth Screen Bottom Board for Beekeeping Wholesale
- High Performance Plastic Queen Excluder for Beekeeping and Apiary Management
- Australian Pine Wood Langstroth Screen Bottom Board for Wholesale
People Also Ask
- What happens to the remaining wax in the Wax Screw Presses set? A Guide to Efficient Honey & Wax Separation
- What are the main benefits of using a honey-wax separating screw press? Boost Yield and Efficiency for Your Apiary
- What are the benefits of a Honey-Wax Separating Screw Press? Boost Honey Yield & Efficiency
- What is the primary function of a honey screw press? Maximize Yield with Advanced Cold Press Separation Technology
- What is the purpose of the Wax Screw Presses set? Maximize Honey & Wax Yield Efficiently






