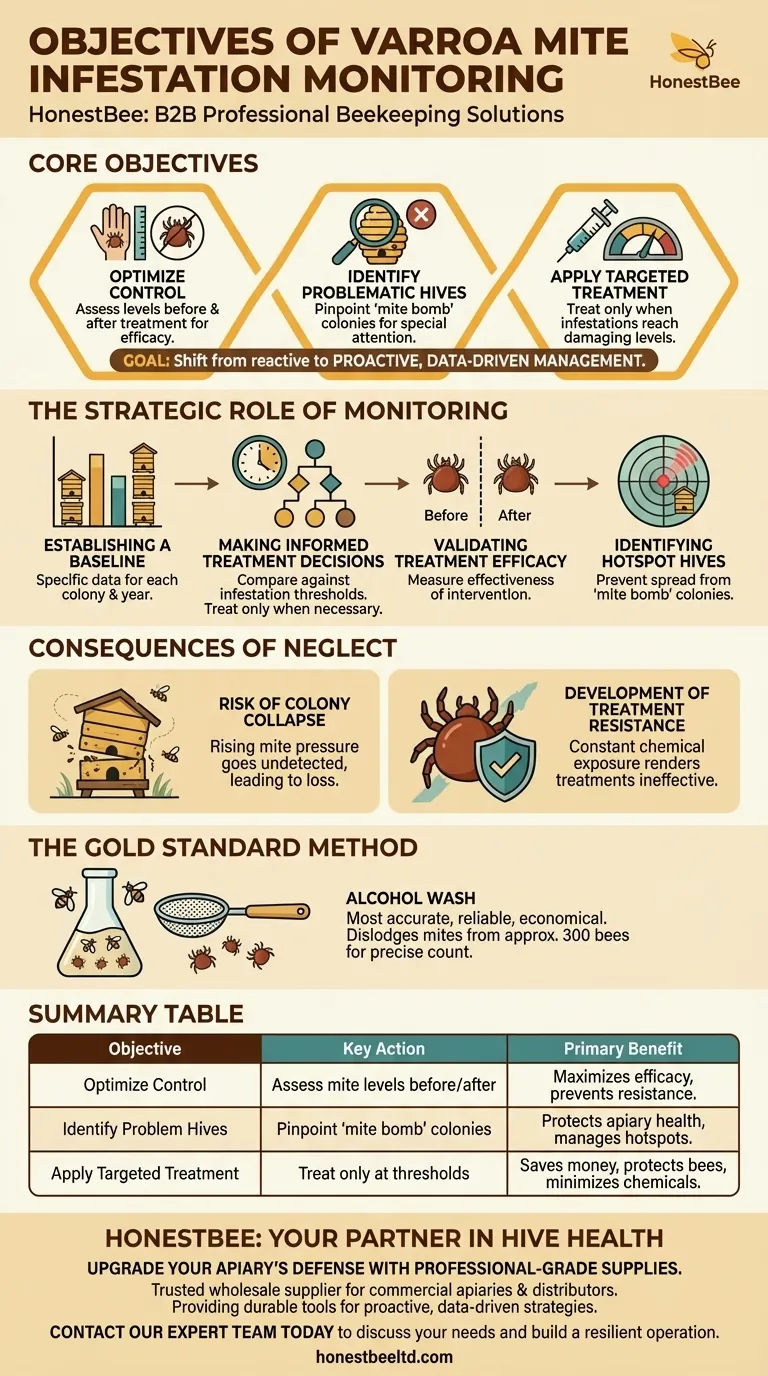
At its core, monitoring for varroa mites serves three primary objectives. It allows beekeepers to optimize control strategies by assessing mite levels before and after treatment, to identify problematic hives that require special attention, and to ensure that treatments are only applied when infestations reach an unacceptable, damaging level.
The fundamental goal of varroa monitoring is to shift from reactive, calendar-based chemical treatments to a proactive, data-driven management strategy. This protects bee health, prevents colony loss, and minimizes the development of treatment-resistant mites.

The Strategic Role of Monitoring in Hive Health
Effective varroa management is not about guesswork; it is about precise, timely intervention. Monitoring provides the critical data needed to make sound decisions for the health of your apiary.
Establishing a Baseline
Varroa infestations can vary significantly from one hive to another and from one year to the next. Monitoring establishes a specific baseline for each colony.
This case-by-case data is essential for devising a control strategy that is tailored to the actual threat level in each hive, rather than applying a blanket solution.
Making Informed Treatment Decisions
The most crucial function of monitoring is to determine if and when treatment is necessary. Beekeepers compare mite counts against established infestation thresholds.
Treating only when a threshold is crossed prevents the overuse of chemicals, which can harm honey bee larvae, reduce the lifespan of adult bees, and waste time and money.
Validating Treatment Efficacy
Monitoring should be conducted both before and after a treatment is applied. This is the only way to measure how effective the intervention actually was.
If post-treatment mite levels remain high, it signals that the treatment may have failed or was not applied correctly, allowing the beekeeper to take further action.
Identifying "Hotspot" Hives
Regular assessments help you quickly identify "mite bomb" colonies with exceptionally high infestation levels.
These hives can be targeted for special attention or culling, which prevents them from collapsing and spreading mites to healthier colonies in the apiary.
The Consequences of Neglect
Failing to monitor is not a neutral act; it introduces significant risks to your colonies and the long-term viability of your pest management plan.
The Risk of Colony Collapse
Without regular data, a beekeeper has no visibility into the rising mite pressure within a hive.
An unmonitored infestation can quickly spiral out of control, weakening the colony and often leading to its collapse, especially as it prepares for winter.
The Development of Treatment Resistance
Applying treatments on a fixed schedule, regardless of mite levels, exposes mites to chemicals unnecessarily.
This constant pressure accelerates the mites' ability to develop resistance, rendering treatments less effective over time for everyone.
The Gold Standard Method
The alcohol wash is widely considered the most accurate, reliable, and economical method for assessing varroa mite levels. It involves shaking a sample of approximately 300 bees in alcohol to dislodge the mites for an easy and precise count.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your monitoring strategy should align directly with your primary beekeeping objectives.
- If your primary focus is maximizing colony survival: Regularly monitor throughout the season, especially in late summer, to ensure mite levels are well below the damaging threshold before winter.
- If your primary focus is minimizing chemical use: Adhere strictly to treatment thresholds, applying controls only when mite counts prove it is absolutely necessary.
- If your primary focus is improving apiary-wide health: Use monitoring data to identify and manage high-mite colonies before they can re-infest their neighbors.
Ultimately, consistent monitoring transforms beekeeping from a reactive guessing game into proactive, evidence-based hive management.
Summary Table:
| Objective | Key Action | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Optimize Control | Assess mite levels before/after treatment | Maximizes treatment efficacy and prevents resistance |
| Identify Problem Hives | Pinpoint 'mite bomb' colonies | Protects overall apiary health by managing hotspots |
| Apply Targeted Treatment | Treat only when thresholds are crossed | Saves money, protects bees, and minimizes chemical use |
Upgrade your apiary's defense with professional-grade monitoring and control supplies from HONESTBEE.
As a trusted wholesale supplier to commercial apiaries and equipment distributors, we provide the durable, reliable tools you need—from alcohol wash kits to integrated pest management solutions—to implement a proactive, data-driven strategy that protects your investment and ensures colony health.
Contact our expert team today to discuss your specific needs and build a more resilient, profitable beekeeping operation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Varroa Easy Check Mite Tester Kit Counter Alcohol Wash Jar
- Adjustable Formic and Acetic Acid Dispenser for Bee Mite Treatment
- Professional Galvanized Hive Strap with Secure Locking Buckle for Beekeeping
- Full Set Beekeeping Electronic Bee Venom Collector Machine Device for Bee Venom Collecting
- Versatile Ratchet Hive Strap with S-Hooks for Secure Fastening
People Also Ask
- How is the powdered sugar shake method performed to detect Varroa mite levels? Protect Your Bees with This Guide
- How does the alcohol wash method function in a specialized varroa monitoring tool? Precise Mite Monitoring Explained
- How does a shake jar containing 70% alcohol facilitate assessment of Varroa mite infestation rates? Industry Insights
- What is the alcohol wash method for assessing Varroa mite infestations? The Industry Standard for Mite Control
- Why are Alcohol Washing Kits precise for Varroa monitoring? The Gold Standard for Accurate Mite Infestation Rates



















