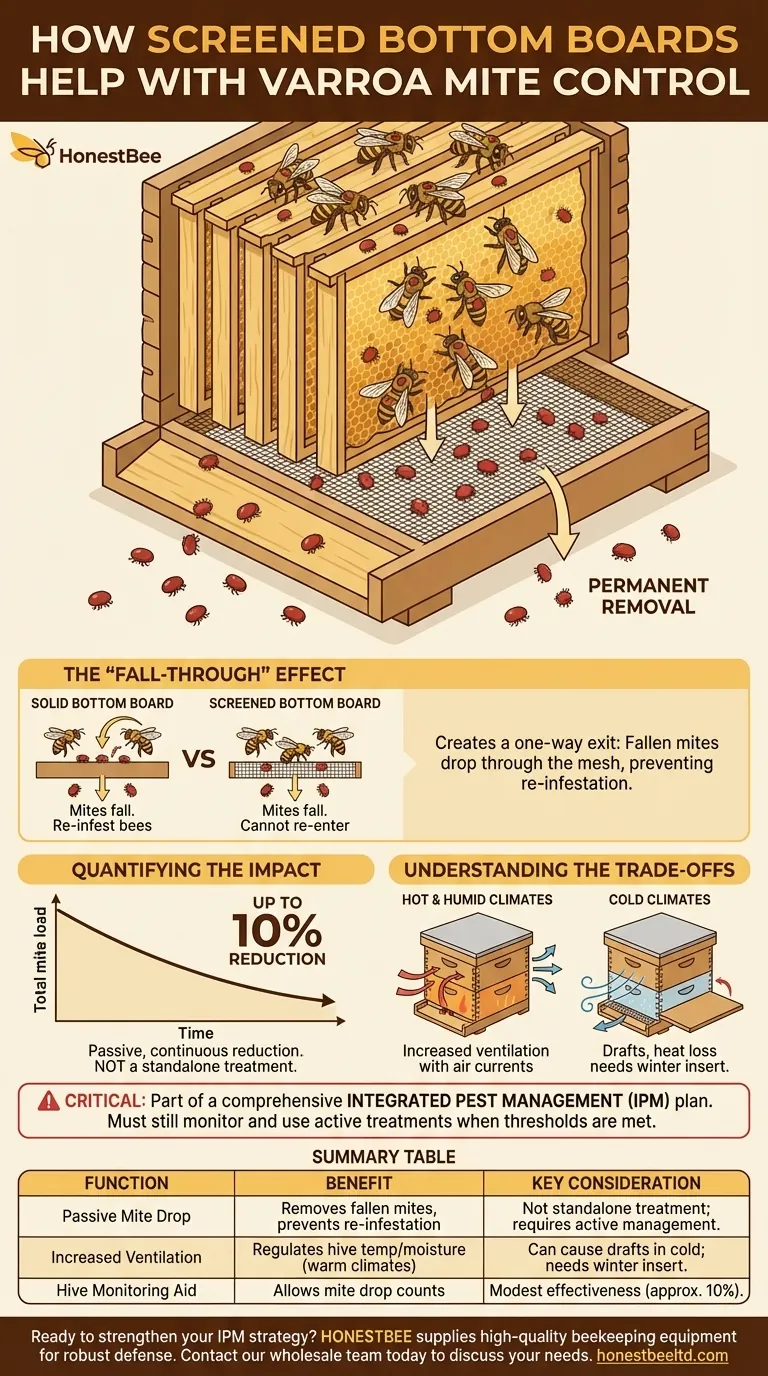
In short, a screened bottom board helps control Varroa mites by creating a one-way exit. When mites naturally fall off honey bees during grooming or movement, they drop through the mesh screen and out of the hive. This prevents them from climbing back onto another bee and re-entering the colony's brood cycle, thus providing a passive, continuous reduction in the overall mite population.
A screened bottom board is a valuable tool for passive mite reduction and hive monitoring, but it is not a standalone treatment. Its effectiveness lies in being one part of a comprehensive Integrated Pest Management (IPM) plan, not a replacement for active mite treatments when thresholds are met.
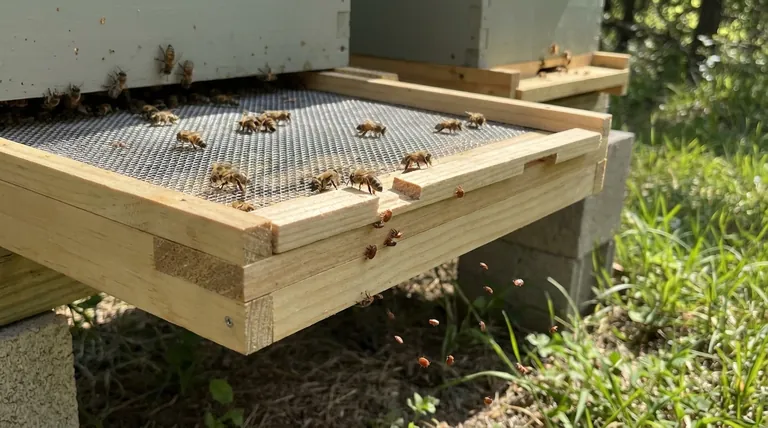

The Mechanics of Passive Mite Reduction
To truly understand the value of a screened bottom board, you must see it as a component that subtly alters the hive environment in your favor, rather than an active weapon against mites.
The "Fall-Through" Effect
Varroa mites spend a portion of their lives on the bodies of adult bees. During this "phoretic" stage, they can be dislodged by the bees' own grooming behaviors or simply lose their grip.
In a hive with a solid bottom board, these fallen mites can survive for a time on the floor. They can then easily climb back onto a passing bee, re-infesting the colony.
A screened bottom board, typically a #8 hardware cloth, creates a gap too large for a mite to cross. Any mite that falls is permanently removed from the hive's ecosystem.
Quantifying the Impact
Studies and field observations suggest this passive "mite drop" can reduce the in-hive mite population by a modest amount.
While estimates vary, a common figure is that a screened bottom board alone may account for up to a 10% reduction in the total mite load. This is a helpful contribution but is not sufficient to keep mite levels below the damaging economic threshold for a healthy colony.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Like any piece of beekeeping equipment, a screened bottom board is not without its considerations. Its benefits in mite control and ventilation must be weighed against potential downsides, particularly concerning climate.
Ventilation vs. Insulation
The primary secondary benefit of a screened bottom is increased ventilation. This is especially valuable in hot and humid climates, as it helps the bees regulate temperature and manage moisture, reducing stress and potentially preventing chalkbrood.
However, this same feature is a significant drawback in cold climates. An open screen during winter can create a draft and make it much harder for the colony to maintain its crucial winter cluster temperature, leading to increased honey consumption and potential winter losses. Most screened bottom boards come with a removable solid insert for this exact reason.
Not a Substitute for Monitoring or Treatment
Perhaps the most common mistake is assuming a screened bottom board absolves the beekeeper of mite management duties. This is a dangerous misconception.
It is a passive tool, not an active treatment. Relying on it exclusively will almost certainly lead to a catastrophic mite buildup. It works best when combined with regular mite monitoring (like an alcohol wash or sugar roll) and appropriate, timely treatments when mite counts exceed established thresholds.
Making the Right Choice for Your Apiary
A screened bottom board is a strategic choice, and its use should align with your specific goals and environmental conditions.
- If your primary focus is Integrated Pest Management (IPM): A screened bottom board is an excellent component for passive mite reduction and for conducting "mite drop" counts on a sticky board insert.
- If your primary focus is maximum hive survivability: Use the screened bottom board during the active season and switch to a solid insert or a solid bottom board for the winter, especially in colder climates.
- If your primary focus is low-intervention beekeeping: A screened bottom board provides a baseline level of mite control, but you must still monitor colony health and be prepared to intervene if the mite load becomes unsustainable.
By understanding its role as a helpful but limited tool, you can effectively integrate a screened bottom board into a robust and successful hive health strategy.
Summary Table:
| Function | Benefit | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Passive Mite Drop | Removes fallen mites from hive, preventing re-infestation. | Not a standalone treatment; requires active management. |
| Increased Ventilation | Helps regulate hive temperature and moisture in warm climates. | Can cause drafts in cold climates; requires a solid insert for winter. |
| Hive Monitoring Aid | Allows for mite drop counts on a sticky board. | Effectiveness is modest (approx. 10% mite reduction). |
Ready to strengthen your Integrated Pest Management (IPM) strategy? For commercial apiaries and distributors, effective mite control is non-negotiable for colony health and productivity. HONESTBEE supplies the durable, high-quality beekeeping equipment you need to build a robust defense. Let us help you equip your operation for success. Contact our wholesale team today to discuss your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Langstroth Screen Bottom Board for Beekeeping Wholesale
- Australian Pine Wood Langstroth Screen Bottom Board for Wholesale
- HONESTBEE Wooden Bee Escape Board with Triangle Mesh Design for Beekeeping
- Wholesales Dadant Size Wooden Bee Hives for Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE Multi Exit Plastic Bee Escape Board for Efficient Honey Harvesting
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of using screened bottom boards? Improve Hive Health & Control Varroa Mites
- What are the benefits of using a screened bottom board in warm or humid climates? Boost Hive Health & Control Pests
- How does a screened bottom board affect hive cleanliness? Improve Hive Health with Passive Cleaning
- What is the 3-in-1 functionality of the Screened Bottom Board? Master Hive Ventilation, Pest Control, and Insulation
- What is the primary function of a screened bottom board on a beehive? Enhance Hive Ventilation & Pest Control



















