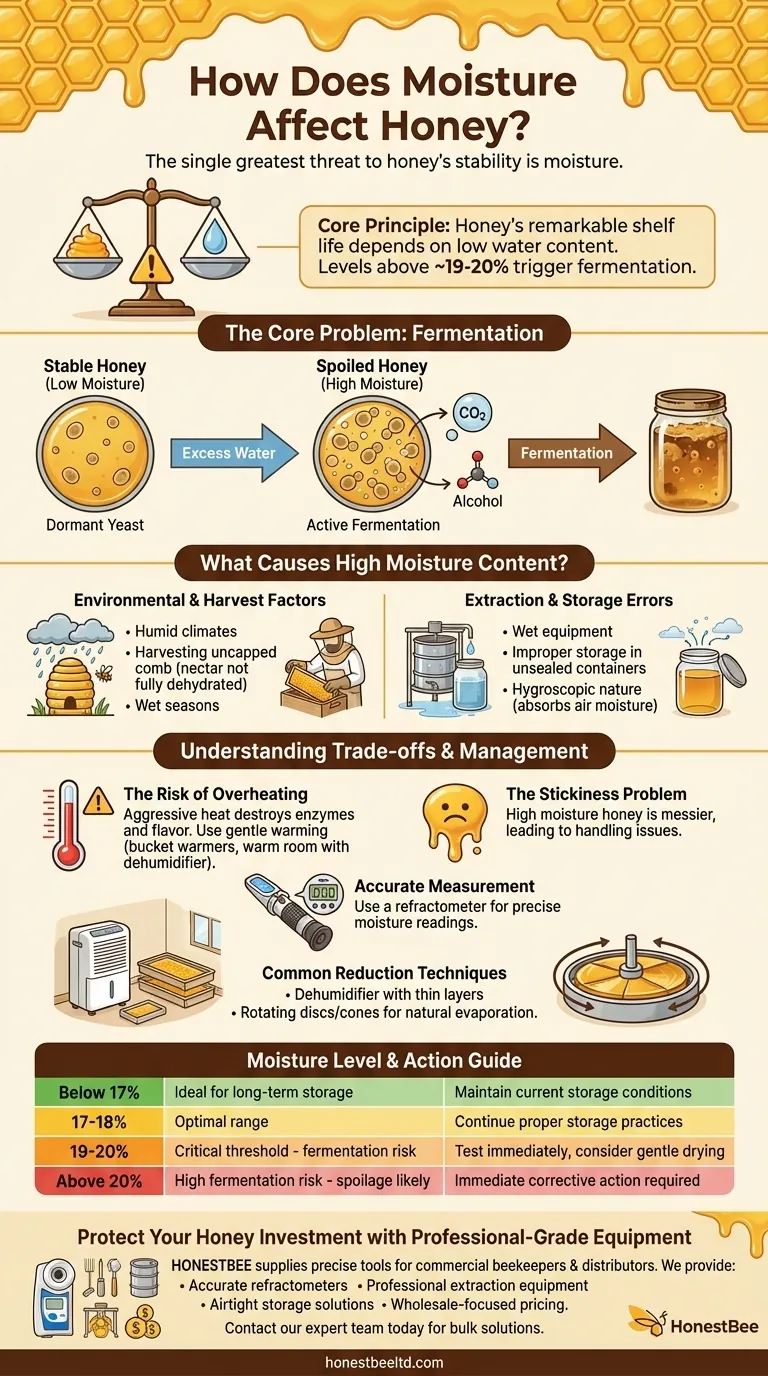
The single greatest threat to honey's stability is moisture. Excess water disrupts honey's natural balance of sugars, awakening dormant yeast cells and triggering a fermentation process that lowers its quality and leads to spoilage. This process is functionally identical to the one used to create mead, but in this context, it ruins the honey.
The core principle to understand is that honey's remarkable shelf life depends on its low water content. When moisture levels rise above a critical threshold of approximately 19-20%, naturally present yeasts begin to multiply, causing the honey to ferment and spoil.

The Core Problem: Fermentation
Why Honey is Naturally Stable
Honey is a supersaturated solution of sugars, primarily fructose and glucose, with a very low water content. This creates a high osmotic pressure environment where there is simply not enough available water for microorganisms like yeast and bacteria to survive and multiply.
This low water activity is the primary reason raw, properly harvested honey can last for decades, or even centuries, without spoiling.
The Tipping Point: How Moisture Fuels Yeast
Wild yeasts are naturally present in honey, but they remain dormant and harmless in its low-moisture state. When excess water is introduced, it dilutes the sugars and provides these yeast cells with the hydration they need to become active.
Once activated, the yeasts begin to consume the sugars in the honey, converting them into alcohol and carbon dioxide. This is the process of fermentation, and it permanently alters the honey's flavor, aroma, and chemical composition.
What Causes High Moisture Content?
Environmental and Harvest Factors
High moisture can be introduced before the honey is even harvested. Bees naturally dehydrate nectar, but harvesting honey from uncapped or partially capped comb means you are collecting it before this process is complete.
Humid climates and exceptionally wet seasons can also make it more difficult for bees to reduce the nectar's moisture content to the ideal level, which is between 17% and 18%.
Extraction and Storage Errors
Water can also be introduced accidentally during the extraction and bottling process. Using wet equipment or storing honey in a damp environment can lead to moisture absorption.
Because honey is hygroscopic, meaning it attracts and absorbs water from the air, improper storage in unsealed containers can easily increase its moisture content over time.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Overheating
While controlled heating is a method used to reduce moisture, it comes with a significant risk. Aggressive or excessive heat can destroy the delicate enzymes and aromatic compounds that give honey its unique flavor and beneficial properties.
The goal is to gently encourage evaporation, not to cook the honey. Methods like using bucket warmers or placing the honey in a warm room with a dehumidifier are often safer than direct, high-heat applications.
The Physical Stickiness Problem
Beyond fermentation, a less critical but still notable issue is handling. Honey with a high moisture content is less viscous and can be much stickier and messier.
This makes it difficult to handle and dispense, especially in commercial packaging, leading to waste and consumer frustration.
How to Manage Moisture Levels
The First Step: Accurate Measurement
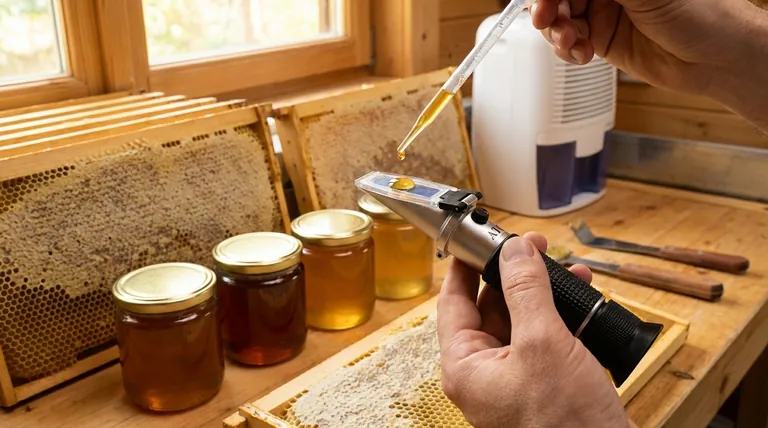
You cannot manage what you don't measure. The standard tool for measuring the moisture content in honey is a refractometer. This simple device provides an immediate and accurate reading, allowing you to know for certain if your honey is within the safe range.
Common Reduction Techniques
If your honey's moisture is too high, several methods can be used to reduce it. Spreading the honey in thin layers on trays and placing it in a sealed room with a dehumidifier is a common and gentle approach.
Other techniques include using rotating discs or cones to increase the honey's surface area, which speeds up natural evaporation without requiring high heat.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is harvesting quality honey: Prioritize pulling frames that are at least 80% capped, as this is the bees' signal that the honey is dehydrated and ready.
- If your primary focus is long-term storage: Use airtight, sealed containers and store them in a cool, dry location to prevent the honey from absorbing atmospheric moisture.
- If you suspect your honey has high moisture: Test it with a refractometer immediately. If it's above 19%, take gentle corrective action before fermentation has a chance to begin.
By understanding and controlling moisture, you preserve the natural perfection and remarkable longevity of your honey.
Summary Table:
| Moisture Level | Impact on Honey | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Below 17% | Ideal for long-term storage | Maintain current storage conditions |
| 17-18% | Optimal range | Continue proper storage practices |
| 19-20% | Critical threshold - fermentation risk | Test immediately, consider gentle drying |
| Above 20% | High fermentation risk - spoilage likely | Immediate corrective action required |
Protect Your Honey Investment with Professional-Grade Equipment
As commercial beekeepers and distributors, maintaining honey quality is critical to your business success. HONESTBEE supplies the precise tools you need to monitor and control moisture levels effectively.
We provide:
- Accurate refractometers for instant moisture testing
- Professional extraction equipment that prevents contamination
- Airtight storage solutions designed for commercial-scale operations
- Wholesale-focused pricing that supports your bottom line
Don't let moisture compromise your honey's quality and market value. Contact our expert team today to discuss bulk equipment solutions tailored to your commercial apiary or distribution needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Precision Honey Refractometer Instrument for Quality Assessment
- Professional Thermostatic Conical Honey Melter
- Honey Concentrating Vacuum Heating Thickening Machine Dehumidifier for Honey
- 0.5T Capacity Honey Dehumidifier Dryer with Vacuum Heating and Thickening Filtering Machine
- 8-Frame Electric Self-Reversing Honey Extractor Spinner for Commercial Honey Extraction Equipment
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-precision refractometer considered essential for honey quality? Master Moisture Control for Stability
- What should be considered regarding the measurement range of a honey refractometer? Ensure Peak Honey Quality
- What is the principle and importance of using a refractometer for honey moisture? Ensure Quality & Prevent Fermentation
- Why is a refractometer necessary for determining the moisture content and quality grade of honey? Ensure Market Success
- What is the primary function of a desktop refractometer? Ensure Honey Quality and Prevent Fermentation



















