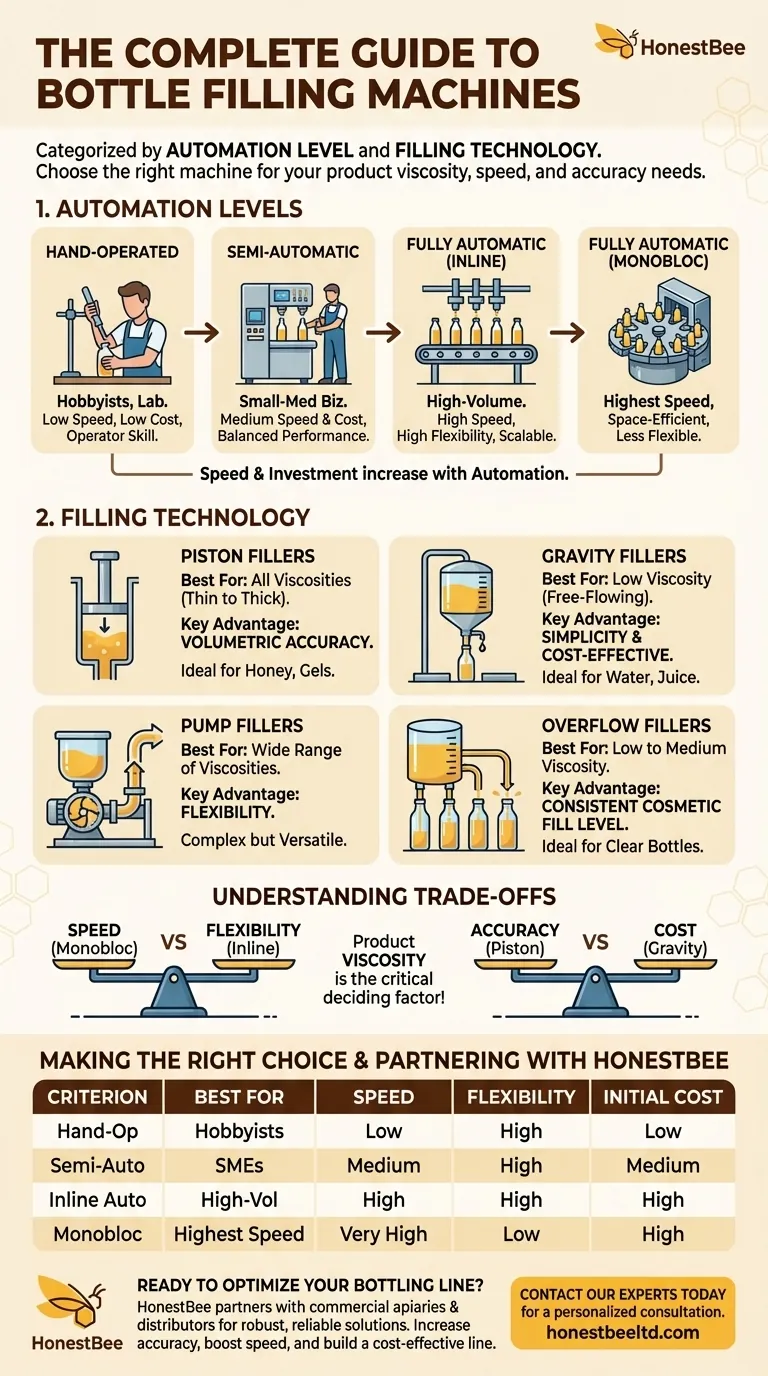
In essence, bottle filling machines are primarily categorized along two key dimensions: their level of automation and the specific filling technology they employ. Automation levels range from simple hand-operated devices to fully integrated, high-speed automatic systems, while the technology—such as piston, gravity, or pump fillers—is chosen based on the liquid's characteristics and desired fill accuracy.
The challenge isn't knowing the types of fillers, but understanding how to match the right machine to your specific product and production goals. The viscosity of your liquid, your required speed, and your need for accuracy will ultimately determine the ideal solution.

The First Dimension: Level of Automation
The level of automation directly correlates with production volume, labor requirements, and initial investment. It is the first major decision point in selecting a machine.
Hand-Operated Solutions
For hobbyists, lab work, or very small-scale startups, hand-operated fillers are the entry point. The operator manually controls every aspect of the fill.
These are the least expensive options but offer the lowest speed and consistency, relying entirely on operator skill.
Semi-Automatic Fillers
Semi-automatic machines are the workhorse for many small to medium-sized businesses. An operator is still required to place bottles and initiate the fill cycle, but the machine handles the dispensing of the liquid automatically.
This represents a significant step up in speed and accuracy from manual filling, providing a good balance between cost and performance for growing operations.
Fully Automatic Fillers: Inline Systems
Inline automatic fillers use a conveyor to move containers in a straight line through the filling station, where multiple heads fill the bottles simultaneously.
These systems are highly scalable and flexible, making them one of the most common configurations for high-volume production lines that may require future modifications.
Fully Automatic Fillers: Monobloc Systems
A monobloc system integrates multiple packaging functions—typically filling and capping—onto a single, rotary chassis. Bottles are fed onto a star wheel that moves them in a circle to each station.
These machines are incredibly fast and space-efficient but are generally less flexible than inline systems, often being optimized for a specific bottle and cap combination.
The Second Dimension: Filling Technology
The filling technology is the heart of the machine. The choice here is dictated almost entirely by the physical properties of your product, especially its viscosity.
Piston Fillers
A piston filler uses a cylinder to pull in a precise volume of product and then push it into the container. The fill volume is highly accurate and easily adjustable.
This technology is extremely versatile, capable of handling everything from thin, watery liquids to thick, viscous products like honey, gels, and creams. It is the go-to choice for volumetric accuracy.
Gravity Fillers
Gravity fillers hold the product in an overhead tank, allowing the liquid to flow into the bottles via gravity. The fill cycle is typically controlled by time.
This method is simple, reliable, and cost-effective, but it is only suitable for low-viscosity, free-flowing liquids like water, juice, or wine.
Pump Fillers
Pump fillers use a gear, lobe, or other type of pump to move product from a bulk source into the containers. The fill volume can be controlled by timing the pump's operation or by counting its rotations.
This technology is exceptionally flexible and can handle a vast range of product viscosities, making it a powerful but often more complex solution.
Overflow Fillers
Overflow fillers are designed for a specific purpose: to fill every container to the same cosmetic level, regardless of minor inconsistencies in bottle volume.
This machine fills the bottle until the liquid reaches an overflow port, with the excess product being returned to the supply tank. It is ideal for transparent containers where visual appeal is critical and is best used with low to medium-viscosity liquids.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a filling machine involves balancing competing priorities. There is no single "best" machine, only the best fit for your application.
Speed vs. Flexibility
Monobloc systems deliver maximum speed in a small footprint but are often "hard-tooled" for one bottle type, making changeovers difficult. Inline systems may not reach the same peak speeds but offer far greater flexibility to run different products and containers on the same line.
Accuracy vs. Cost
A highly accurate piston filler is more mechanically complex and expensive than a simple gravity filler. If your product is low-cost and sold by volume (e.g., a beverage), a less precise fill is acceptable. If your product is high-value or regulated (e.g., pharmaceuticals), volumetric accuracy is non-negotiable.
Product Viscosity is a Deciding Factor
This is the most critical technical constraint. Attempting to run a thick paste through a gravity filler will fail. Conversely, using a sophisticated pump filler for a simple, water-thin liquid might be an unnecessary expense. The product's characteristics must guide the technology choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Product
Use your primary goal to guide your initial search and narrow down your options.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, consistent production: A fully automatic inline or monobloc system is your necessary starting point.
- If your primary focus is product accuracy with thick or viscous liquids: A piston filler is the most reliable and proven technology for your needs.
- If your primary focus is a consistent cosmetic fill level in clear bottles: An overflow filler is specifically designed to solve this exact problem.
- If you are a small business or starting with a modest budget: A semi-automatic machine provides the best balance of increased output for your investment.
By matching the machine's automation and filling principle to your product and goals, you can build a reliable and efficient packaging line.
Summary Table:
| Criterion | Hand-Operated | Semi-Automatic | Fully Automatic (Inline) | Fully Automatic (Monobloc) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Best For | Hobbyists, Labs, Startups | Small-Medium Businesses | High-Volume, Flexible Lines | High-Speed, Space-Efficient Lines |
| Speed | Low | Medium | High | Very High |
| Flexibility | High | High | High | Low |
| Initial Cost | Low | Medium | High | High |
| Filling Technology | Best For Viscosity | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Piston Filler | All (Thin to Thick) | Volumetric Accuracy |
| Gravity Filler | Low (Free-Flowing) | Simplicity & Cost-Effectiveness |
| Pump Filler | Wide Range | Flexibility |
| Overflow Filler | Low to Medium | Consistent Cosmetic Fill Level |
Ready to Optimize Your Bottling Line?
Choosing the right bottle filling machine is critical for the efficiency and profitability of your operation. Whether you are a commercial apiary packaging honey or a distributor supplying beekeeping equipment, the wrong machine can lead to product waste, downtime, and lost revenue.
HONESTBEE partners with commercial apiaries and distributors to provide the right bottling solutions. We understand the unique challenges of handling products like honey, and our wholesale-focused operations ensure you get robust, reliable equipment at competitive prices.
Let us help you:
- Increase accuracy and reduce product giveaway with the right filling technology.
- Boost your production speed with automation that matches your scale.
- Build a reliable, cost-effective packaging line that grows with your business.
Don't leave your packaging efficiency to chance. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation and discover how HONESTBEE can equip your operation for success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Semi Automatic Small Honey Bottle Filling Machine Honey Filler
- Double Nozzle Small Honey Filling Machine Honey Sachet Packing Packaging Equipment
- Pneumatic Double Nozzle Honey Filling Bottling Packaging Machine
- Automatic Honey Filling and Filtering Machine for Beekeeping Bottle Filling
- Pneumatic Paste Filling Machine Bottling Packaging Machine Single Nozzle
People Also Ask
- What is the best use case for piston filling machines? Master Viscous & Chunky Product Filling
- What is the best use case for gravity filling machines? Bottle Thin Liquids with Unmatched Simplicity
- What contribution does automatic honey filling and processing machinery make to the honey industry's value enhancement?
- What are the key steps in the working of a honey filling machine? Optimize Your Packaging Line for Efficiency
- What is the function of industrial-grade plastic funnels in honey bottling? Essential Tools for Precision & Hygiene
- What are the technical advantages of industrial-grade honey filling machines? Optimize Your Commercial Production
- What is the purpose of a shaped honey stick machine? Boost Brand Appeal & Sales
- What is the role of automated honey-filling machines in the post-processing of honey products? Boost Brand & Quality



















