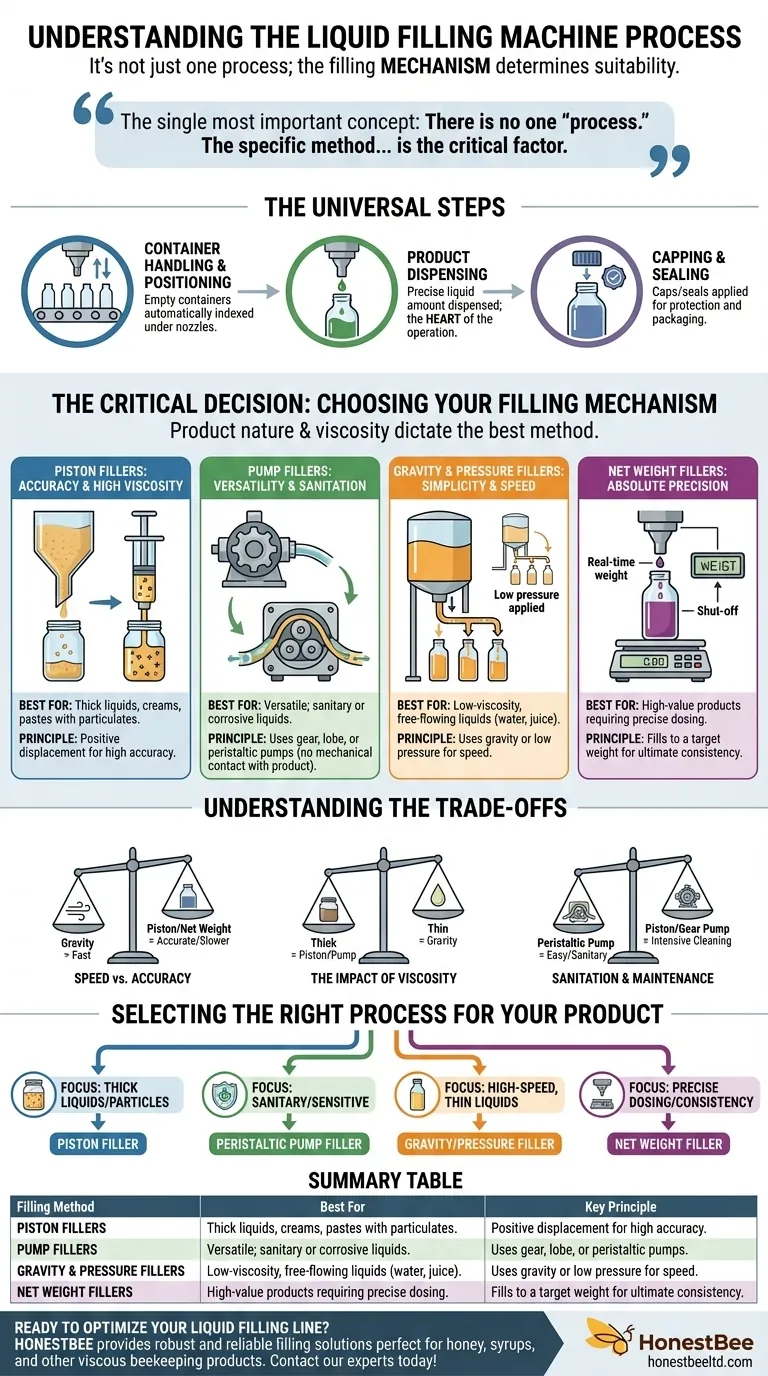
At its core, the liquid filling machine process involves a sequence of automated steps to fill and seal containers accurately. This typically includes feeding the product into the machine's reservoir, positioning empty containers under filling nozzles, dispensing a precise amount of liquid, and then capping or sealing the filled containers for distribution.
The single most important concept to understand is that there is no one "process." The specific method of dispensing the liquid—whether by piston, pump, gravity, or weight—is the critical factor that determines the machine's suitability for your specific product.

The Universal Steps of Liquid Filling
While the filling technology varies, the overall workflow follows a consistent, logical progression. Each stage is designed to ensure efficiency and product integrity.
Container Handling and Positioning
The process begins with empty containers being fed onto a conveyor system. These containers are then automatically indexed and precisely positioned directly beneath the filling nozzles to prevent spillage and ensure a clean fill.
Product Dispensing
This is the heart of the operation. The machine's chosen mechanism—piston, pump, or other—is activated to dispense the liquid product from a holding tank or hopper into the waiting containers. The goal is to deliver a consistent and accurate amount into every single container.
Capping and Sealing
Once filled, the containers move along the conveyor to a capping or sealing station. Here, caps are applied and tightened, or a seal is applied to protect the product from contamination and leakage, making it ready for final packaging.
The Critical Decision: Choosing Your Filling Mechanism
The "process" is truly defined by how the liquid is moved. The nature of your product, especially its viscosity (thickness), dictates the best mechanism.
Piston Fillers: For Accuracy and High Viscosity
A piston filler operates like a large syringe. A valve opens, allowing product to flow from a hopper into a precisely sized cylinder. The valve then shifts, and the piston pushes forward, dispensing the exact volume of product out through a nozzle.
This method uses positive displacement, making it extremely accurate and powerful enough to handle thick products like creams, pastes, and sauces, even those with large particulates like salsa.
Pump Fillers: For Versatility and Sanitation
Pump fillers use various types of pumps to transfer product from a bulk tank into containers. The type of pump is matched to the product.
Gear or lobe pumps are also positive displacement pumps, ideal for moving higher-viscosity liquids. Peristaltic pumps, however, use rollers to squeeze a flexible tube, moving the product without it ever touching the mechanical parts. This makes them perfect for sensitive, sterile, or corrosive liquids, as the tube can be easily replaced for sanitation.
Gravity and Pressure Fillers: For Simplicity and Speed
This is the most straightforward method. The liquid is held in a tank above the filling nozzles, and it flows into the containers using the simple force of gravity. For slightly thicker liquids or faster fill speeds, low air pressure can be added to the tank to assist the flow.
This process is best suited for low-viscosity (thin), free-flowing liquids like water, juice, or oils.
Net Weight Fillers: For Absolute Precision
Unlike the other methods that fill by volume, a net weight filler dispenses product until the container reaches a specific target weight. A scale under the container provides real-time feedback to the filling nozzle, which shuts off once the correct weight is achieved.
This process ensures unparalleled uniformity and is ideal for high-value products where precise dosing is critical for cost control and quality assurance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a filling process involves balancing competing priorities. There is no single "best" method; there is only the best method for your specific application.
Speed vs. Accuracy
Generally, simple gravity fillers offer the highest speeds for thin liquids. Piston and net weight fillers provide superior accuracy but may operate at a slightly slower pace due to their more complex, deliberate mechanics.
The Impact of Viscosity
This is often the deciding factor. Trying to fill a thick paste with a gravity filler will fail. You must use a positive displacement system like a piston or gear pump that can physically force the product through the nozzle.
Sanitation and Maintenance
Peristaltic pumps are the clear winners for sanitary applications, as the product is completely contained within a disposable tube. Piston and gear pumps are highly effective but require more intensive disassembly and cleaning between production runs.
Selecting the Right Process for Your Product
Your product's characteristics and your business goals should guide your decision.
- If your primary focus is handling thick, viscous liquids or products with particles: A piston filler provides the necessary power and volumetric accuracy.
- If your primary focus is sanitary processing or handling sensitive/corrosive liquids: A peristaltic pump filler offers the best product isolation and easiest cleanup.
- If your primary focus is high-speed filling of low-viscosity, free-flowing liquids: A gravity or pressure filler is the most efficient and straightforward solution.
- If your primary focus is maximizing product consistency and minimizing giveaway: A net weight filler ensures every package contains the exact amount required.
By matching the filling mechanism to the product's needs, you ensure a process that is efficient, accurate, and reliable.
Summary Table:
| Filling Method | Best For | Key Principle |
|---|---|---|
| Piston Filler | Thick liquids, creams, pastes with particulates | Positive displacement for high accuracy |
| Pump Filler | Versatile; sanitary or corrosive liquids | Uses gear, lobe, or peristaltic pumps |
| Gravity/Pressure Filler | Low-viscosity, free-flowing liquids like water or juice | Uses gravity or low pressure for speed |
| Net Weight Filler | High-value products requiring precise dosing | Fills to a target weight for ultimate consistency |
Ready to optimize your liquid filling line? As a trusted wholesale supplier to commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors, HONESTBEE provides robust and reliable filling solutions perfect for honey, syrups, and other viscous beekeeping products. Our equipment ensures accuracy and efficiency, helping you scale your production. Contact our experts today to discuss the ideal filling machine for your operation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Semi-Automatic Pneumatic Bottle Capping Machine by HONESTBEE
- 10L Stainless Steel Electric Honey Press Machine
- Automatic Honey Frame Uncapper Machine for Beekeeping
- Honey Convey Pump Screw Honey Pump for Viscous Liquid
- Stainless Steel Manual Honey Press with Guard for Pressing Honey and Wax
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of bottle capping equipment and what types are available? Professional Sealing Solutions
- What is the purpose of a bottle capping machine? Boost Efficiency and Ensure Product Integrity
- What is the purpose of the capping and sealing process in filling machines? Ensure Product Integrity & Shelf Life
- Why is integrated packaging and labeling equipment important? Elevate Your Brand for Mainstream Retail Success
- What is the role of a capping scratcher in the uncapping process? The Essential Tool for Maximum Honey Yield

















