After completing a varroa mite treatment, your immediate priority is to verify its effectiveness and assess the colony's recovery. This involves more than simply removing the treatment strips or trays; it requires a deliberate inspection to confirm the mite load is under control and that the treatment itself hasn't caused unintended harm to the queen or brood.
The goal of a varroa treatment is not just to kill mites, but to restore the colony to a state of health. Therefore, your post-treatment actions must focus on two things: confirming the treatment worked and evaluating the overall condition of the hive.
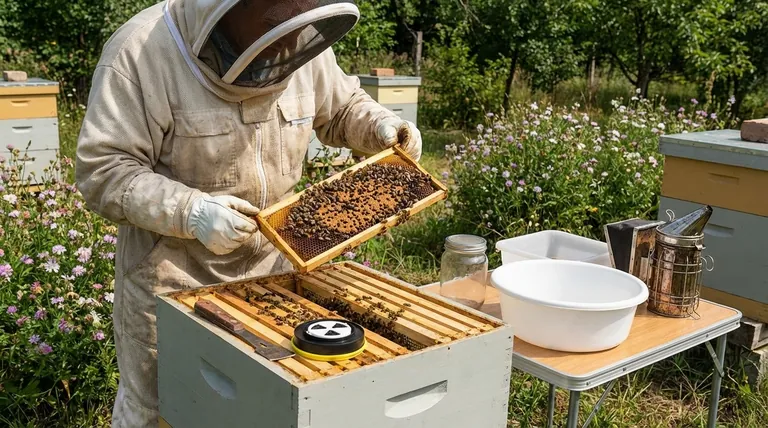

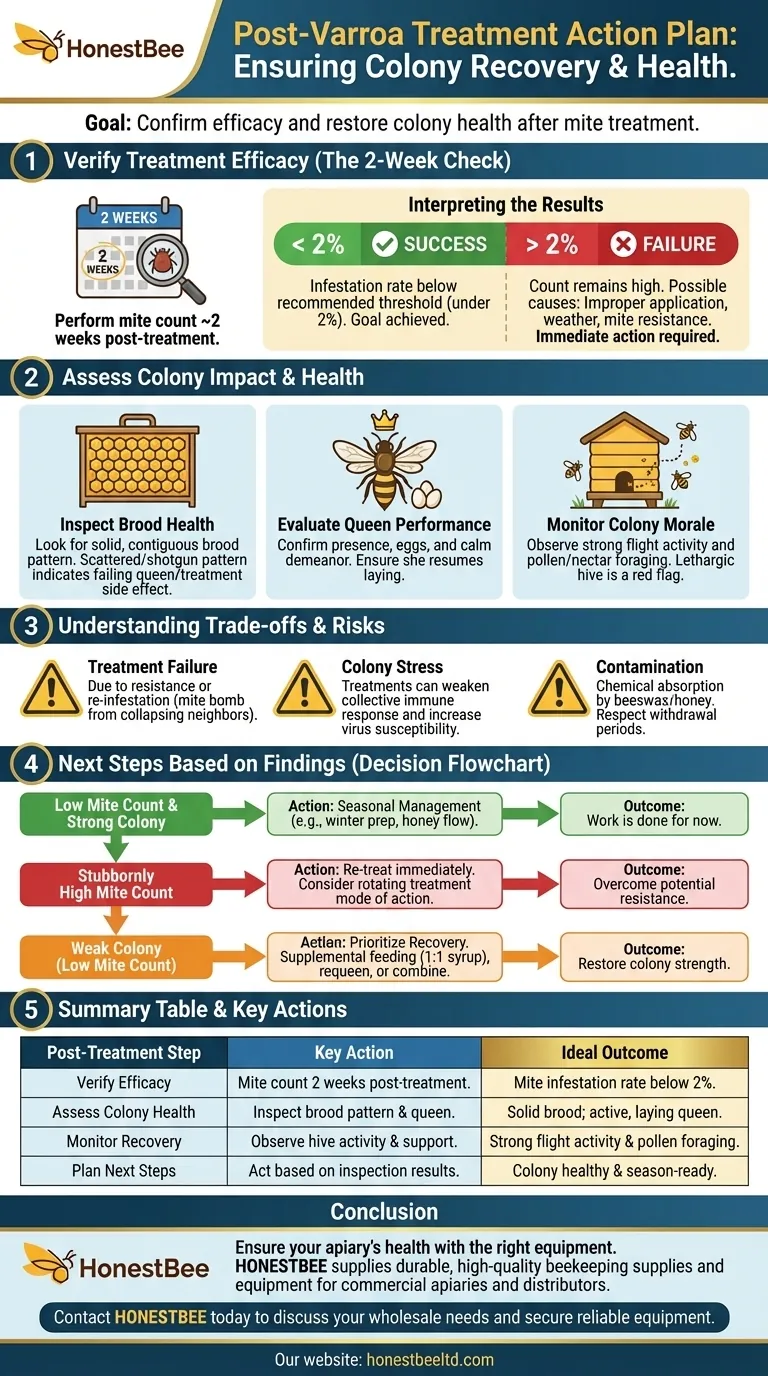
Verifying Treatment Efficacy
The only way to know if your efforts were successful is to measure the results. Assuming a treatment worked without verification is a common and often costly mistake.
The Post-Treatment Mite Count
A follow-up mite count is the most critical step after treatment. This step confirms whether the intervention successfully reduced the mite population to a manageable level.
Perform this check approximately two weeks after the treatment period has ended. This timing allows for the treatment's full effect to manifest and provides a more accurate picture of the remaining phoretic mite load.
Interpreting the Results
Your goal is an infestation rate below the recommended threshold, typically under 2% (fewer than 2 mites per 100 bees).
If your count remains high, the treatment has failed. This could be due to improper application, weather conditions, or, increasingly, mite resistance to the chemical used. A high count requires immediate action.
Assessing the Impact on Your Colony
Varroa treatments are a necessary stressor on a honey bee colony. Even "soft" or organic treatments have an impact on the bees, brood, and queen. A thorough inspection is required to gauge the colony's health.
Inspecting Brood Health
Look for a healthy brood pattern. The queen should be laying eggs in a solid, contiguous pattern with few empty cells.
A scattered, "shotgun" brood pattern can be a sign of a failing queen, which can be an unfortunate side effect of some harsh chemical treatments.
Evaluating Queen Performance
Confirm the presence and performance of your queen. Look for eggs, young larvae, and a generally calm demeanor within the hive.
Some treatments can cause the queen to stop laying temporarily. While she often resumes, you must verify this. If the queen is missing or failing, the colony will not survive without intervention.
Monitoring Colony Morale
Observe the hive's entrance. A healthy, recovering colony will have strong flight activity with foragers actively bringing in pollen and nectar. A lethargic, quiet hive is a major red flag that indicates deeper problems.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Potential Failures
No varroa treatment is perfect, and every application carries some degree of risk. Understanding these trade-offs is part of responsible mite management.
Why Treatments Fail
Beyond resistance, treatments can fail due to re-infestation. Your clean hive can be quickly overwhelmed by mites from collapsing, untreated colonies nearby—an event known as a "mite bomb."
The Stress of Intervention
The chemicals or acids used in treatments are, by design, toxic to some degree. This adds stress to the colony, which can temporarily weaken its collective immune response and make it more susceptible to viruses that the mites transmit.
Contamination and Residue
Always follow treatment instructions precisely, especially regarding the presence of honey supers. Some chemicals can be absorbed by beeswax and honey, creating contamination issues if not used correctly. This is why respecting withdrawal periods is non-negotiable.
Next Steps Based on Your Findings
Your post-treatment plan should be tailored to what your inspections reveal.
- If your primary focus is a low mite count and a strong colony: Your work is done for now. Shift your focus to seasonal management, such as feeding for winter preparation or adding space for the honey flow.
- If your primary focus is a stubbornly high mite count: You must act again. Consider rotating to a treatment with a different mode of action to overcome potential resistance and treat the colony immediately.
- If your primary focus is a weak colony despite a low mite count: The treatment may have taken a toll. Prioritize colony recovery by providing supplemental feeding (1:1 sugar syrup) and considering whether to requeen or combine the hive with a stronger one.
Effective varroa management is a continuous cycle of monitoring, intervention, and assessment that secures the long-term health of your bees.
Summary Table:
| Post-Treatment Step | Key Action | Ideal Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Verify Efficacy | Perform a mite count 2 weeks post-treatment. | Mite infestation rate below 2%. |
| Assess Colony Health | Inspect brood pattern and queen performance. | Solid brood pattern; active, laying queen. |
| Monitor Recovery | Observe hive activity and provide support if needed. | Strong flight activity with foragers bringing in pollen. |
| Plan Next Steps | Act based on inspection results (e.g., feed, re-treat, combine). | Colony is healthy and prepared for the season. |
Ensure your apiary's health with the right equipment. Effective varroa management is essential for commercial success. HONESTBEE supplies durable, high-quality beekeeping supplies and equipment to commercial apiaries and distributors through our wholesale-focused operations. From protective gear to mite treatment tools, we provide what you need to maintain thriving colonies.
Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss your wholesale needs and secure reliable equipment for your operation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Adjustable Formic and Acetic Acid Dispenser for Bee Mite Treatment
- Professional Bamboo Queen Isolation Cage
- Varroa Easy Check Mite Tester Kit Counter Alcohol Wash Jar
- Gourd Shaped Hanging Wasp Trap Professional Wasp Catcher
- Professional Pneumatic Wire Embedder for Beehive Frames
People Also Ask
- How does a precision evaporative formic acid dispenser treat Varroa mites? Master Controlled Pest Management
- Why does organic beekeeping emphasize non-synthetic chemical treatments? Protect Your Hive Purity & Prevent Resistance
- How should Varroa mite treatments be integrated into the spring beekeeping schedule? Expert April-May Timing Guide
- What is the application method for cardboard-based Varroa mite treatments? Maximize Hive Health with Correct Placement
- What are the common technical treatments used for Varroa mite control in the spring? Optimize Colony Health Today



















