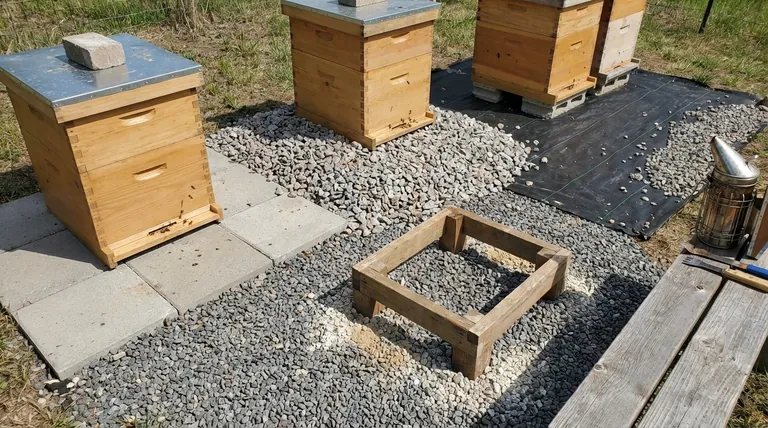
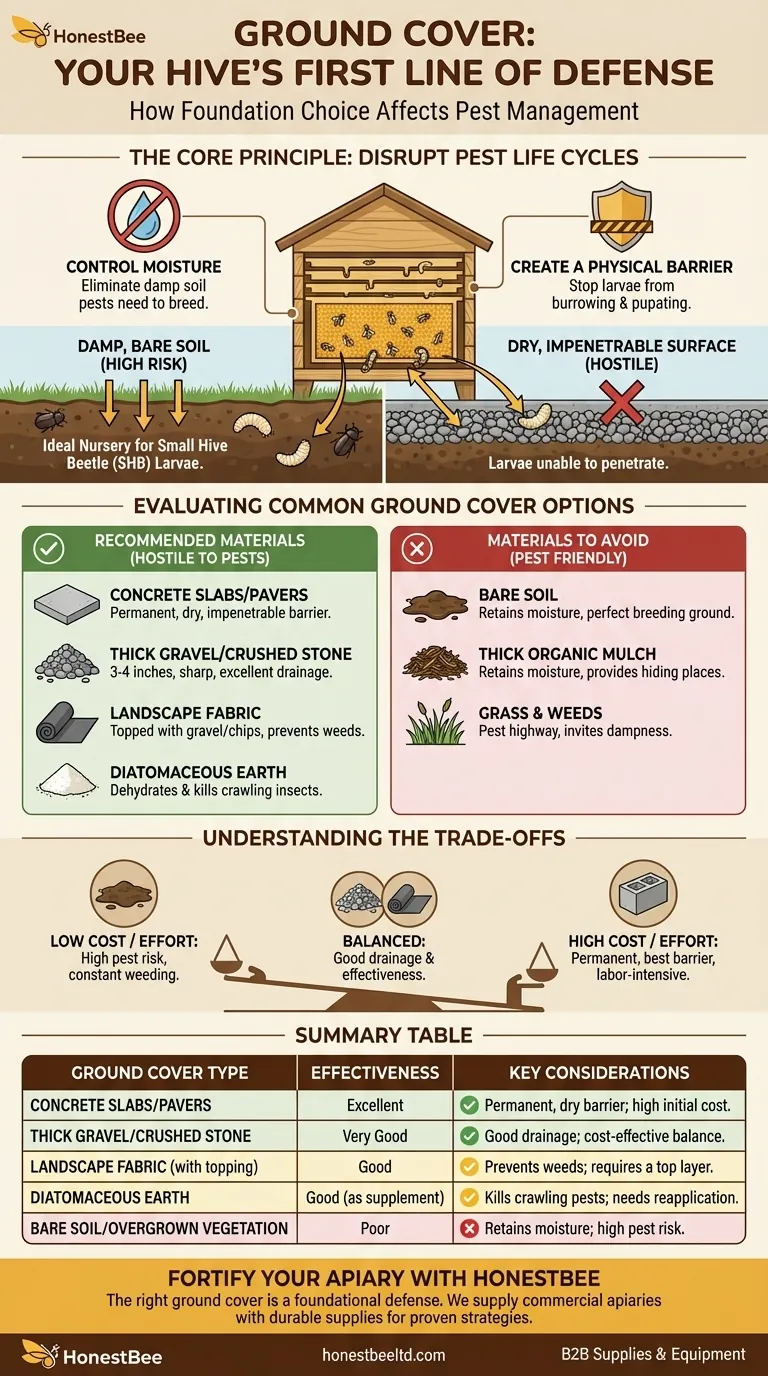
The short answer is this: The ground cover under your beehives directly impacts pest populations by controlling moisture levels and creating physical barriers that disrupt their life cycles. A dry, well-drained, and often impenetrable surface is a powerful tool for Integrated Pest Management, deterring pests like the Small Hive Beetle.
The central goal of managing the ground under your hives is to create an environment that is hostile to pests. This means eliminating the damp soil pests need to breed and creating a physical barrier they cannot penetrate to complete their life cycle.

The Core Principle: Disrupting Pest Life Cycles
Choosing the right ground cover is not about aesthetics; it is a strategic decision that directly influences the health and resilience of your colony. The entire strategy revolves around manipulating the micro-environment at the base of the hive.
Controlling Moisture
Many common hive pests, particularly the Small Hive Beetle (SHB), thrive in damp conditions. Bare, compacted soil that holds water creates an ideal nursery for these destructive insects.
By ensuring the ground is dry and well-drained, you remove a critical element these pests need to survive and reproduce.
Creating a Physical Barrier
The Small Hive Beetle has a crucial vulnerability in its life cycle. Once the beetle larvae have fed on pollen and brood, they exit the hive and burrow into the nearby soil to pupate.
A hard or impenetrable ground cover, like concrete or a thick layer of sharp gravel, physically stops the larvae from completing this process, breaking the cycle and reducing future beetle populations.
Reducing Cover and Access
Overgrown grass and weeds provide a perfect highway for pests like ants to gain access to the hive. This vegetation can also create cover for rodents and maintain a damp microclimate.
Keeping the area immediately around the hive clear of vegetation is a simple but highly effective pest management technique.
Evaluating Common Ground Cover Options
Your choice of material will have a significant impact on your success. The options range from simple and natural to more permanent, constructed solutions.
Recommended Materials
- Concrete Slabs or Paving Stones: This is the gold standard for pest prevention. It provides a dry, permanent barrier that SHB larvae cannot penetrate and is easy to keep clean.
- Thick Gravel or Crushed Stone: A layer of at least 3-4 inches of sharp, inorganic material is highly effective. It ensures excellent drainage and is difficult for larvae to burrow through successfully.
- Heavy-Duty Landscape Fabric: While not a solution on its own, a high-quality fabric topped with gravel or wood chips can prevent weed growth and form an additional barrier.
- Diatomaceous Earth (Food Grade): This can be spread on the ground under and around hives. The microscopic, sharp particles can dehydrate and kill SHB larvae and other crawling insects attempting to burrow.
Materials to Use with Caution or Avoid
- Bare Soil: This is the highest-risk option. It retains moisture and provides a perfect, unobstructed breeding ground for Small Hive Beetles.
- Thick Organic Mulch: While it can suppress weeds, deep organic mulch like straw or bark can retain too much moisture and provide hiding places for pests. If used, it should be a thin layer that is regularly raked and replaced.
- Grass and Weeds: Allowing vegetation to grow up to the hive entrance invites moisture and provides easy access for ants and other pests.
Understanding the Trade-offs
There is no single perfect solution for every beekeeper. Your decision should be based on your budget, location, and the level of pest pressure you face.
Effectiveness vs. Cost and Labor
A poured concrete slab is the most effective pest barrier but is also the most expensive and labor-intensive option. It represents a permanent decision for your apiary location.
Conversely, keeping the ground bare is free but requires constant maintenance (weeding) and offers the least amount of pest protection. A thick layer of gravel often represents the best balance of cost, effort, and effectiveness.
Climate Considerations
In very wet or humid climates, preventing moisture buildup is paramount. Here, non-organic options like concrete or gravel are strongly preferred.
In arid climates, bare ground may be less of a risk, but it can create dust issues. A simple layer of wood chips on landscape fabric might be sufficient to control weeds and pests.
Making the Right Choice for Your Apiary
Ultimately, your ground cover strategy is a key part of your hive defense system.
- If your primary focus is maximum pest control and low maintenance: Install permanent concrete slabs or heavy-duty paving stones under your hives.
- If your primary focus is a balance of effectiveness and cost: Use a high-quality landscape fabric topped with a deep layer (3-4 inches) of gravel or crushed stone.
- If your primary focus is a low-budget or natural approach: Meticulously clear all vegetation for at least three feet around the hive, ensure the soil is well-drained, and consider top-dressing with diatomaceous earth during periods of high pest pressure.
Choosing the right foundation for your hive is a proactive step that pays dividends in colony health and your own peace of mind.
Summary Table:
| Ground Cover Type | Pest Management Effectiveness | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Concrete Slabs / Pavers | Excellent | Permanent, dry barrier; high initial cost. |
| Thick Gravel / Crushed Stone | Very Good | Good drainage; cost-effective balance. |
| Landscape Fabric (with topping) | Good | Prevents weeds; requires a top layer. |
| Diatomaceous Earth | Good (as supplement) | Kills crawling pests; needs reapplication. |
| Bare Soil / Overgrown Vegetation | Poor | Retains moisture; high pest risk. |
Ready to fortify your apiary against pests?
The right ground cover is a foundational defense for your hives. At HONESTBEE, we supply commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the durable supplies needed to implement these proven strategies. From heavy-duty landscape fabric to essential tools for maintaining a pest-resistant apiary, our wholesale-focused operations provide the reliable equipment for healthier, more productive colonies.
Let's build a stronger foundation for your beekeeping business. Contact our team today to discuss your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Professional Insulated Winter Hive Wrap for Beekeeping
- Inner Beehive Cover for Beekeeping Bee Hive Inner Cover
- Beehive Entrance Discs Plastic Bee Entrance Disc for Bee Hives
- Professional Drop-Style Hive Handles for Beekeeping
- Professional Grade Foldable Beehive Handles
People Also Ask
- Why are glacial acetic acid fumigation and caustic soda rinsing essential in preventing Nosema ceranae transmission?
- How can beekeepers protect honey bee hives from mice during the winter? Expert Exclusion and Prevention Tips
- How do wax moths damage stored beekeeping frames and comb? Protect Your Equipment from Larvae Destruction
- Why is it necessary to stock beekeeping detergents and epidemic prevention tools? Ensure Bio-Security & Market Access
- How does a portable fluorescence detection device assist in field screening of Nosematosis? Protect Your Bee Colonies
- How does the use of precision laboratory monitoring equipment improve disease control? Optimize Commercial Bee Health
- How is oil-impregnated cotton yarn utilized as a defense mechanism for stingless bee hives? Protect Against Predators
- How does the use of cold storage equipment protect beekeeping hardware from Wax Moth damage? Secure Your Hive Assets



















