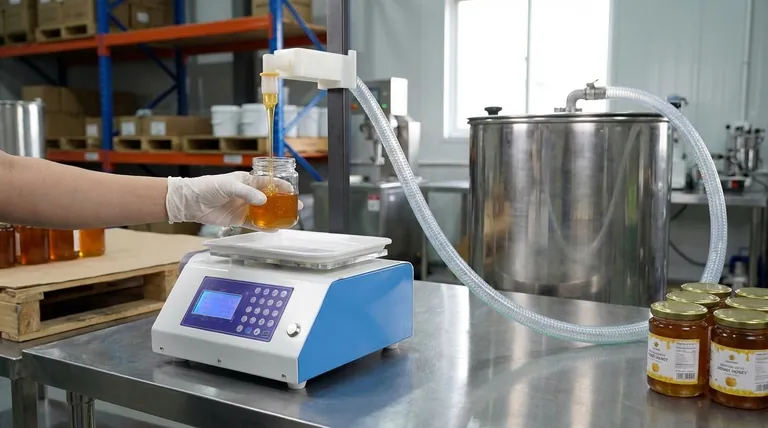
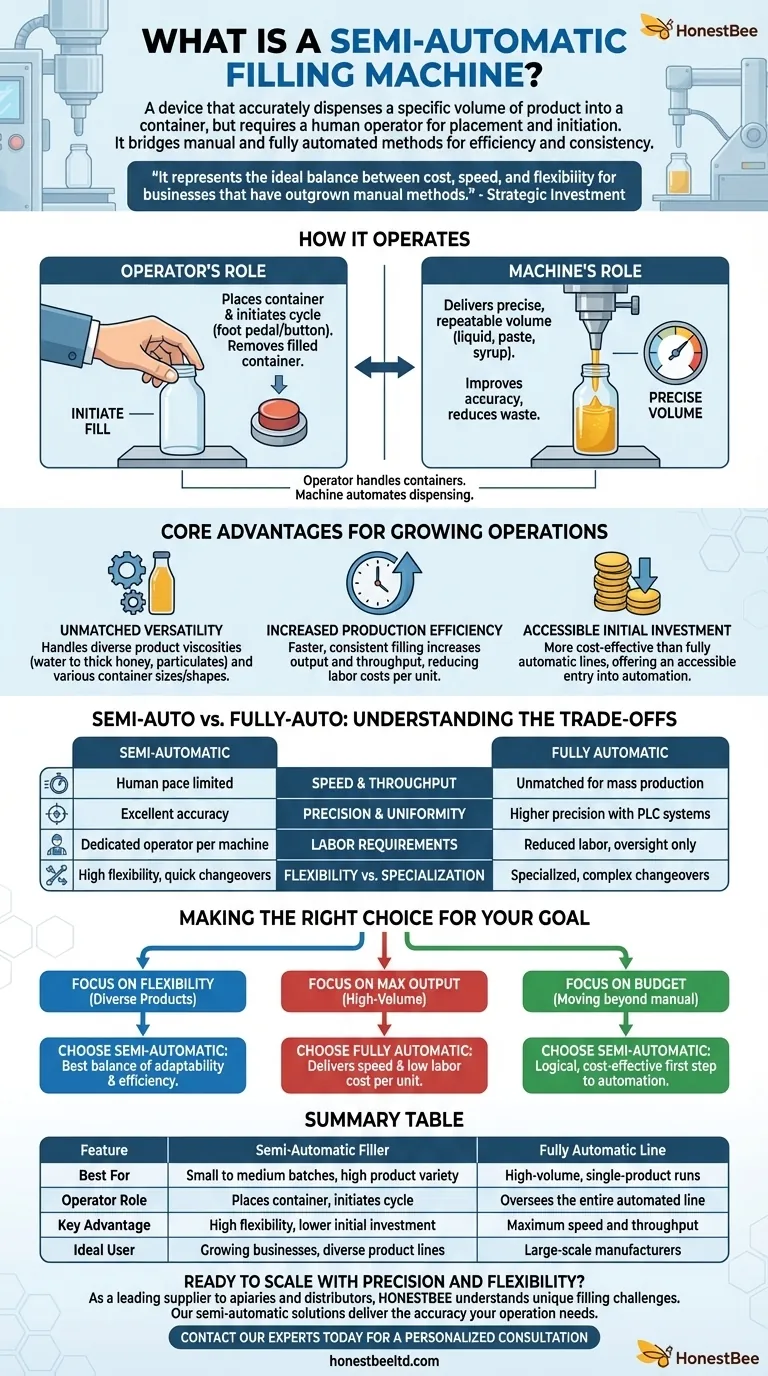
At its core, a semi-automatic filling machine is a device that accurately dispenses a specific volume of product into a container, but requires a human operator to place the container and initiate the fill cycle. It bridges the gap between purely manual filling and fully automated production lines, offering a significant boost in efficiency and consistency for small to medium-sized operations.
The central takeaway is that a semi-automatic filler is not just a piece of equipment, but a strategic investment. It represents the ideal balance between cost, speed, and flexibility for businesses that have outgrown manual methods but are not yet ready for the scale and expense of full automation.

How a Semi-Automatic Filler Operates
A semi-automatic system splits the workload between a person and a machine. This partnership is designed to optimize the most repetitive and error-prone part of the filling process.
The Role of the Operator
The operator is responsible for the handling of containers. Their primary tasks are placing an empty bottle, jar, or pouch into position and then activating the machine, often with a foot pedal or push button.
Once the fill is complete, the operator removes the filled container and repeats the process with the next one.
The Role of the Machine
The machine's sole responsibility is to deliver a precise, repeatable volume of product. Whether the product is a thin liquid, a thick paste, or a syrup, the machine ensures each container receives the exact same amount.
This automation of the dispensing action is what dramatically improves accuracy and reduces product waste compared to filling by hand.
The Key Difference from Full Automation
A fully automatic filling machine eliminates the need for an operator to handle each container. It uses conveyors to move containers into place, sensors to detect their presence, and then initiates the fill automatically before moving them down the line for capping and labeling.
Semi-automatic systems do one task perfectly, while fully automatic systems integrate multiple tasks into a continuous, hands-off process.
Core Advantages for Growing Operations
For many businesses, a semi-automatic filler is the most logical next step in scaling production. It addresses key bottlenecks without requiring a complete overhaul of the production floor.
Unmatched Versatility
These machines are highly adaptable. A single filler can often be configured to handle a wide range of product viscosities, from free-flowing water to thick honey and even products with particulates like salsa.
They can also be quickly adjusted to accommodate different container sizes and shapes, making them ideal for companies with a diverse product portfolio.
Increased Production Efficiency
By automating the measurement and dispensing, semi-automatic fillers significantly increase output. An operator with a machine can fill containers much faster and more consistently than someone working with scoops or pitchers.
This leads to higher throughput and reduced labor costs per unit.
Accessible Initial Investment
Compared to the high capital expenditure required for a fully automatic line, a semi-automatic machine is a much more cost-effective investment.
This makes it an accessible entry point into automation, allowing businesses to improve their process and capacity with a more manageable budget.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Semi-Auto vs. Fully-Auto
Choosing the right machine requires an objective look at the trade-offs. The best choice depends entirely on your specific production goals and volume.
Speed and Throughput
For sheer mass production, a fully automatic system is unmatched. Its continuous, integrated process is designed for high-volume, low-variety runs. A semi-automatic machine's speed is ultimately limited by the pace of its human operator.
Precision and Uniformity
While semi-automatic fillers provide excellent accuracy, high-end automatic machines with advanced PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) systems can offer an even higher degree of precision and uniformity across tens of thousands of fills.
Labor Requirements
A semi-automatic machine requires a dedicated operator for it to run. A fully automatic line is designed to reduce direct labor, often requiring only one person to oversee an entire packaging line.
Flexibility vs. Specialization
Semi-automatic machines excel at flexibility. Switching between different products or containers can be done quickly. Fully automatic lines are more specialized and changing them over for a new product can be a more complex and time-consuming process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct filling technology is about aligning the equipment's capabilities with your business's immediate and near-future needs.
- If your primary focus is flexibility for a diverse product line: A semi-automatic machine offers the best balance of adaptability and efficiency for your investment.
- If your primary focus is maximizing output for a high-volume product: A fully automatic machine will deliver the speed and low labor cost per unit needed for mass production.
- If your primary focus is moving beyond manual filling on a tight budget: A semi-automatic filler is the most logical and cost-effective first step into automation.
Ultimately, choosing the right machine empowers your business to scale production intelligently and sustainably.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Semi-Automatic Filler | Fully Automatic Line |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | Small to medium batches, high product variety | High-volume, single-product runs |
| Operator Role | Places container, initiates cycle | Oversees the entire automated line |
| Key Advantage | High flexibility, lower initial investment | Maximum speed and throughput |
| Ideal User | Growing businesses, diverse product lines | Large-scale manufacturers |
Ready to scale your production with precision and flexibility?
As a leading wholesale supplier to commercial apiaries and distributors, HONESTBEE understands the unique filling challenges of viscous products like honey, syrups, and creams. Our semi-automatic filling solutions are designed to deliver the accuracy and versatility your growing operation needs.
Let us help you find the perfect machine to boost your efficiency and reduce waste. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation and discover the HONESTBEE difference.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Semi Automatic Small Honey Bottle Filling Machine Honey Filler
- Double Nozzle Small Honey Filling Machine Honey Sachet Packing Packaging Equipment
- Precision Durable Efficient HONESTBEE Rotary Honey Filling Machine
- Pneumatic Double Nozzle Honey Filling Bottling Packaging Machine
- Pneumatic Paste Filling Machine Bottling Packaging Machine Single Nozzle
People Also Ask
- How do automated honey-filling machines and processing equipment help apiaries mitigate risks? Beat Climate-Induced Yields
- How do industrial honey-filling and packaging machines provide commercial value? Scale Your Apiary to Retail Standards
- How do industrial honey-filling machines enhance the production value of raw honey? Maximize Your Retail Potential
- What is the importance of high-precision weighing and packaging machinery in honey export? Maximize Value and Integrity
- In what ways do high-precision honey-filling machines improve product quality? Boost Your Commercial Honey Standards
- How do industrial honey filling machines impact economic efficiency? Scale Your Output and Maximize Profit Margins
- What technical requirements must honey filtering and filling equipment meet? Expert Guide for Heat-Sensitive Honey
- What technical advantages do industrial-grade honey filling machines provide? Boost Efficiency for Commercial Apiaries



















