At its core, the sachet filling process is a highly automated sequence where a machine forms a pouch from a flat roll of film, fills it with a precise amount of product, and then seals and cuts it into a finished sachet. Key operator steps include loading the product and packaging material, performing initial quality checks, and then monitoring the continuous production cycle.
The entire operation hinges on a single, critical principle: the filling mechanism must be perfectly matched to the product's characteristics. The machine's core function is always to form, fill, and seal, but how it fills—by weight, pump, or piston—is what determines its accuracy, speed, and suitability for a specific task.
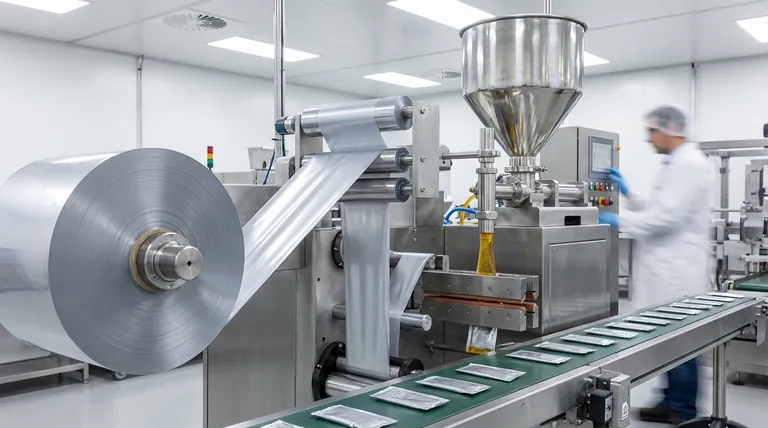

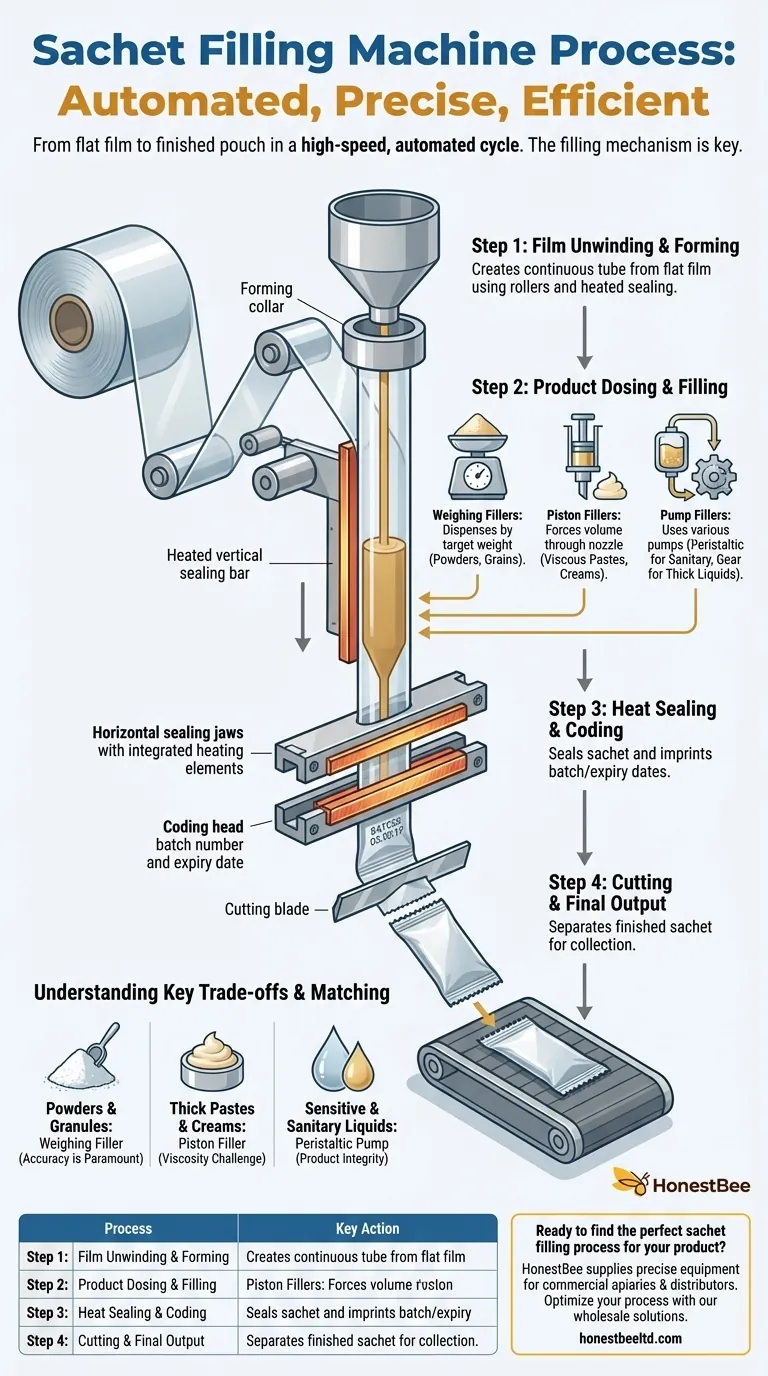
The Automated Sachet Production Cycle
A sachet filling machine executes a precise, high-speed sequence of events to transform raw materials into a finished product. Each step is carefully synchronized to ensure consistency and efficiency.
Step 1: Film Unwinding and Forming
The process begins with a large roll of packaging material, typically a heat-sealable foil or plastic film.
The machine automatically unwinds the film and guides it through a series of rollers. It then folds the flat film and uses a heated vertical sealing bar to create the back seal, forming a continuous tube.
Step 2: Product Dosing and Filling
This is the most critical stage, where the choice of technology directly depends on the product being packaged. The machine must dispense an exact amount of product into the formed tube.
There are three primary methods for this:
- Weighing Fillers: Ideal for powders, grains, or irregular solids. The machine dispenses product until a target weight is reached, ensuring uniformity even if the product's density varies.
- Piston Fillers: The best choice for viscous liquids, creams, gels, or products with large particles. A piston draws a set volume of product from a hopper into a cylinder and then forces it through a nozzle, providing a powerful and accurate fill.
- Pump Fillers: Used for liquids of varying viscosities. Different pumps are used for different needs; peristaltic pumps are excellent for sanitary or corrosive liquids as the product only touches a disposable tube, while gear pumps handle thicker liquids.
Step 3: Heat Sealing and Coding
Once the product is inside the sachet, a pair of heated horizontal sealing jaws clamp down on the tube.
This action simultaneously forms the top seal of the filled sachet and the bottom seal of the next one. Many machines will also emboss or print a batch number and expiration date into the seal at this stage.
Step 4: Cutting and Final Output
A cutting blade then separates the finished, sealed sachet from the continuous tube of film.
The completed sachet is then discharged from the machine, typically onto a conveyor belt for collection and final packing into boxes.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Choosing the right machine configuration is not about finding the "best" technology, but the one that is correct for your specific product. Mismatching the product and filling mechanism leads to inaccurate fills, product damage, and operational failure.
For Powders and Granules
Accuracy is paramount. A weighing filler is superior to a volume-based filler for these products because density can be inconsistent. Relying on volume can lead to under-filled or over-filled sachets.
For Thick Pastes and Creams
Viscosity is the main challenge. A piston filler provides the necessary force to move thick products accurately. A standard pump would struggle, leading to slow, inconsistent filling.
For Sensitive or Sanitary Liquids
Product integrity is the goal. A peristaltic pump is ideal because the mechanical parts of the pump never touch the liquid. This prevents contamination and makes cleaning as simple as replacing a flexible tube.
Making the Right Choice for Your Product
To select the appropriate process, you must start with a clear understanding of what you are packaging.
- If your primary focus is packaging powders, coffee, or spices: Your process must be built around a weighing filling system to ensure consistent product quantity in every sachet.
- If your primary focus is packaging thick sauces, creams, or gels: A piston filler is non-negotiable for handling the high viscosity and delivering an accurate volumetric dose.
- If your primary focus is packaging sterile pharmaceuticals or corrosive liquids: A system using a peristaltic pump is the only way to guarantee product purity and simplify sanitation between batches.
Ultimately, understanding this production cycle empowers you to choose a machine that works in harmony with your product, ensuring efficiency and quality.
Summary Table:
| Step | Process | Key Action |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Film Unwinding & Forming | Creates a continuous tube from flat film. |
| 2 | Product Dosing & Filling | Precisely fills the tube (by weight, piston, or pump). |
| 3 | Heat Sealing & Coding | Seals the sachet and imprints batch/expiry dates. |
| 4 | Cutting & Final Output | Separates the finished sachet for collection. |
Ready to find the perfect sachet filling process for your product?
At HONESTBEE, we supply the precise beekeeping equipment and supplies that commercial apiaries and distributors rely on. Just as the right filling mechanism is critical for packaging success, the right tools are vital for your operation's efficiency and yield.
Let us help you optimize your process. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and discover how our wholesale-focused solutions can bring accuracy and reliability to your business.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Pneumatic Paste Filling Machine Bottling Packaging Machine Single Nozzle
- Honey Stick Filler Vertical Paste Sachet Packing Machine for Honey Sachets
- Automatic Single-Dose Snap & Squeeze Honey Sachets Packing Machine
- Semi Automatic Small Honey Bottle Filling Machine Honey Filler
- Manual Honey Filling Machine Bottling Machine for Honey
People Also Ask
- Why are industrial-grade automatic filling machines necessary for the commercial marketing of honey? Scale Your Success
- How do industrial-grade automatic honey filling machines enhance commercial value? Scale Your Apiary Efficiency
- What technical advantages do automated honey-filling machines offer? Boost Your Honey Production Efficiency Today
- How does an industrial-grade honey sachet packaging machine assist beekeepers in accessing public institution markets?
- How does a honey filling machine ensure consistent product presentation? Achieve a Professional, Drip-Free Finish
- What is the advantage of adjustable volume settings in a honey filling machine? Unlock Flexibility & Profit
- What are the causes of overheating in honey stick machines? Prevent Downtime with Proper Maintenance
- What primary technical challenges are addressed by automated honey-filling machinery? Boost Your Commercial API Precision



















