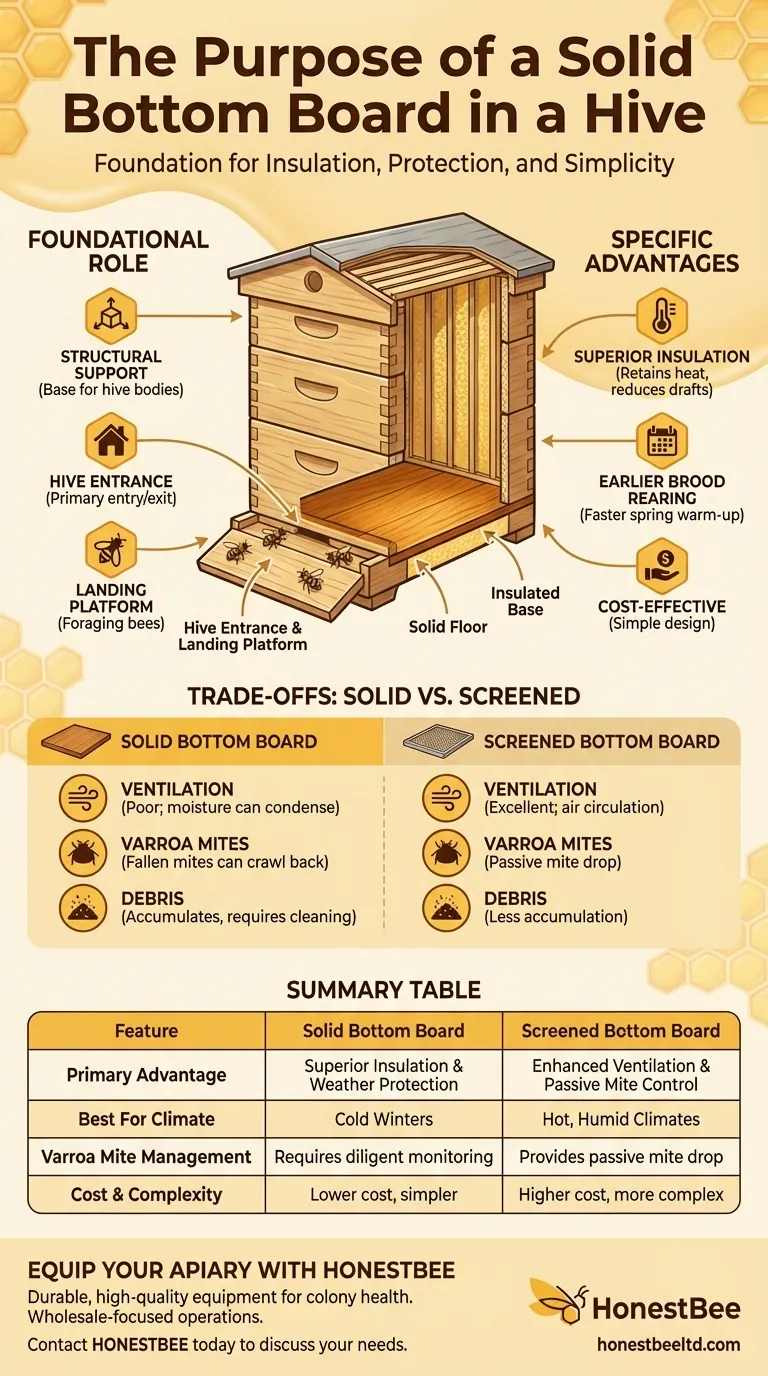
In short, the primary purpose of a solid bottom board is to provide a solid, insulated floor for the beehive. It serves as the foundation of the hive structure, protecting the colony from cold drafts, wind chill, and pests that might enter from below.
The decision to use a solid bottom board is fundamentally a choice for superior insulation and weather protection. This comes at the cost of reduced ventilation and a different approach to pest management compared to its screened counterpart.

The Foundational Role of the Bottom Board
Before focusing on what makes a solid board unique, it's important to understand the universal functions of any bottom board, whether solid or screened.
Provides Structural Support
The bottom board is the floor and foundation of the entire hive. It provides a stable base upon which the hive bodies, supers, and covers rest.
Creates the Hive Entrance
When a hive body is placed on the bottom board, a gap is created at the front. This opening serves as the primary entrance and exit for the entire colony.
Serves as a Landing Platform
The area of the bottom board that extends forward acts as a takeoff and landing strip for foraging bees. It's a critical piece of infrastructure for the colony's daily operations.
The Specific Advantages of a Solid Bottom Board
Choosing a solid bottom board over a screened one provides a distinct set of benefits, particularly related to insulation and simplicity.
Superior Insulation and Weather Protection
This is the solid board's chief advantage. By providing a solid floor, it significantly reduces drafts and helps the colony retain heat, which is crucial for surviving cold winters.
Bees must expend energy to maintain the hive's internal temperature. A well-insulated hive allows them to conserve this energy and their honey stores.
Encourages Earlier Spring Brood Rearing
Because a solid board helps the hive warm up faster in the spring, it can encourage the queen to begin laying eggs earlier. This leads to a more rapid population build-up at the start of the season.
Cost-Effectiveness and Simplicity
Solid bottom boards are often simpler in design and cheaper to build or purchase than screened bottom boards, making them an accessible option for new beekeepers.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Solid vs. Screened
No piece of beekeeping equipment is perfect for every situation. The advantages of a solid board come with trade-offs, primarily concerning ventilation and mite control.
Ventilation and Moisture Control
A solid board offers poor ventilation. In humid climates or during winter, moisture can condense on the inner surfaces of the hive, which can stress the colony. Screened bottom boards excel here, allowing for constant air circulation.
Varroa Mite Management
Varroa mites are a major pest for honey bees. A key advantage of a screened bottom board is that mites that fall off a bee have a high chance of falling completely out of the hive.
With a solid board, fallen mites can simply crawl back onto another bee. This means beekeepers using solid boards must be diligent about other mite monitoring and treatment methods.
Debris Accumulation
Wax cappings, pollen, and other hive debris accumulate on a solid bottom board. This requires periodic cleaning by the beekeeper to prevent the buildup of pests and pathogens.
Making the Right Choice for Your Apiary
Your local climate and management style are the most important factors when choosing hive equipment. There is no single "best" answer, only the best choice for your specific goals.
- If your primary focus is overwintering bees in a cold climate: A solid bottom board offers superior insulation that can be critical for winter survival.
- If your primary focus is ventilation in a hot, humid climate: A screened bottom board is a better choice to help manage in-hive moisture and temperature.
- If your primary focus is integrated Varroa mite management: A screened bottom board provides a passive, non-chemical advantage in reducing mite populations.
- If your primary focus is a traditional, low-cost setup: The solid bottom board is a time-tested, simple, and economical foundation for any hive.
Ultimately, understanding these trade-offs empowers you to build a hive that best supports the health and productivity of your bees.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Solid Bottom Board | Screened Bottom Board |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Advantage | Superior Insulation & Weather Protection | Enhanced Ventilation & Passive Mite Control |
| Best For Climate | Cold Winters | Hot, Humid Climates |
| Varroa Mite Management | Requires diligent monitoring/treatment | Provides passive mite drop |
| Cost & Complexity | Generally lower cost, simpler design | Often higher cost, more complex |
Equip Your Apiary with the Right Foundation from HONESTBEE
Choosing the correct bottom board is critical for colony health and productivity. Whether you manage a large commercial apiary or are a distributor supplying beekeepers, HONESTBEE provides the durable, high-quality equipment you need.
We supply solid bottom boards and a full range of beekeeping supplies built for performance and longevity. Let our wholesale-focused operations support your business with reliable equipment that protects your investment.
Ready to build a stronger hive? Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss your needs and place your order.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Langstroth Solid Bottom Board for Beekeeping
- Langstroth Screen Bottom Board for Beekeeping Wholesale
- HONESTBEE Professional Long Handled Hive Tool with Precision Cutting Blade
- Professional Insulated Winter Hive Wrap for Beekeeping
- Australian Pine Wood Langstroth Screen Bottom Board for Wholesale
People Also Ask
- What are the dimensions of a Langstroth bottom board? Essential Sizing Guide for 8-Frame and 10-Frame Hives
- What is a standard bottom board in a beehive? Essential Features for Hive Foundation and Health
- What is the primary function of a solid bottom board in a beehive? Essential Foundation for Colony Stability
- What are the characteristics of a solid bottom board? A Guide to Hive Foundation & Climate Control
- What frame setups are available for the solid bottom boards? Choose the Right Foundation for Your Hive



















