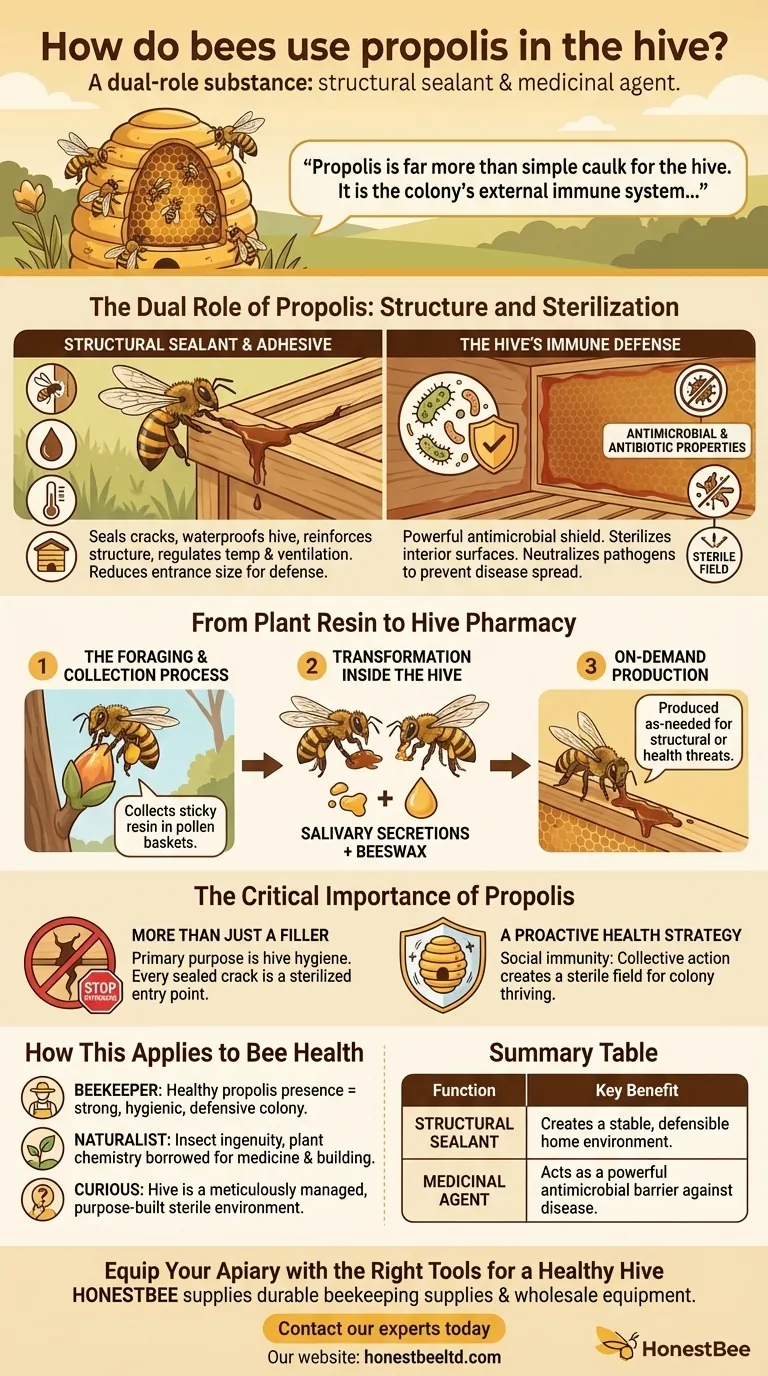
In short, bees use propolis as both a structural sealant and a medicinal agent. This remarkable substance functions as a versatile "bee glue" to seal cracks and waterproof the hive, while also acting as a powerful antimicrobial shield to protect the colony from disease.
Propolis is far more than simple caulk for the hive. It is the colony's external immune system, a sophisticated biodefense material engineered by bees to ensure their collective health and structural integrity.
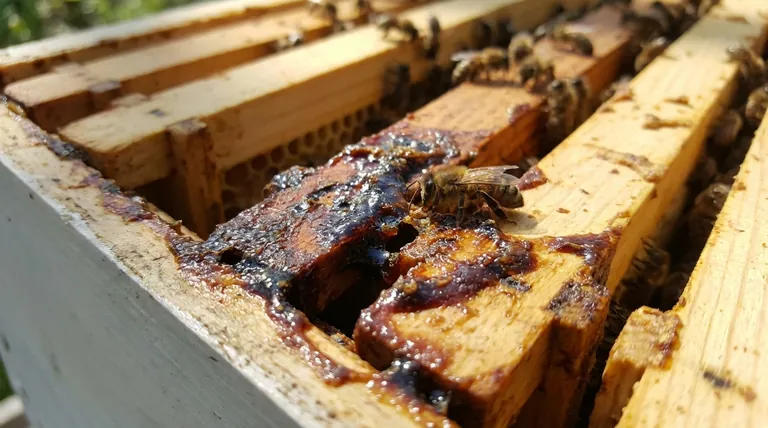

The Dual Role of Propolis: Structure and Sterilization
Bees deploy propolis with two critical objectives in mind: fortifying their home and keeping it sterile. These functions are inextricably linked to the survival of the colony.
A Structural Sealant and Adhesive
Bees are master architects, and propolis is one of their essential building materials. They use it to fill any unwanted gaps or cracks in the hive walls.
This sealing action serves to waterproof the interior, protecting the colony from rain and moisture. It also reinforces the hive's structure and helps regulate internal temperature and ventilation.
Critically, bees also use propolis to reduce the size of the hive entrance, especially before winter. This creates a more defensible bottleneck against intruders like wasps or robbing bees.
The Hive's Immune Defense
The most vital function of propolis is medicinal. The hive is a warm, dense, and humid environment—a perfect breeding ground for bacteria, fungi, and viruses.
Propolis has potent antimicrobial and antibiotic properties. Bees meticulously coat the interior surfaces of the hive with a thin layer of it, effectively sterilizing their living space.
This propolis envelope acts as a chemical barrier, neutralizing pathogens as they enter the hive and preventing the spread of disease among the tens of thousands of tightly packed inhabitants.
From Plant Resin to Hive Pharmacy
Propolis is not a substance bees create from scratch. It is a carefully crafted compound transformed from raw materials collected outside the hive.
The Foraging and Collection Process
It begins with forager bees visiting trees and other plants to collect sticky resins. These bees use their mouthparts to scrape up the resin and then pack it onto the pollen baskets on their hind legs, just as they would with pollen.
Transformation Inside the Hive
Once the forager returns, she requires help from other hive-mates to unload the sticky cargo. Worker bees then take the raw resin and begin a transformation process.
They chew the resin, mixing it with their own salivary secretions and a small amount of beeswax. This intricate process turns the raw plant material into the finished, powerful substance known as propolis.
On-Demand Production
Unlike honey or pollen, propolis is not stored in large quantities. It is produced on an as-needed basis when the colony identifies a structural vulnerability or a potential health threat, making it a responsive defense mechanism.
The Critical Importance of Propolis
Understanding propolis requires moving past the simple "bee glue" analogy. Its presence and use are direct indicators of a colony's health, proactivity, and defensive capabilities.
More Than Just a Filler
To see propolis only as a sealant is to miss its primary purpose. Its structural use is secondary to its role in hive hygiene. Every crack sealed is not just a draft plugged, but a potential entry point for pathogens that is now sterilized.
A Proactive Health Strategy
By lining the entire hive, bees create a sterile field. This proactive strategy is a form of social immunity, where the collective actions of the group protect every individual. It is one of the most important reasons honey bee colonies can thrive in such dense populations.
How This Applies to Bee Health
Understanding the function of propolis provides insight into the sophisticated world of the honey bee and what makes a colony successful.
- If you are a beekeeper: Recognize that a healthy presence of propolis is a sign of a strong, hygienic colony actively defending itself.
- If you are a naturalist: View propolis as a prime example of how insects interact with their environment, borrowing chemistry from plants to create their own medicine and building materials.
- If you are simply curious about bees: Understand that the beehive is not just a structure, but a meticulously managed sterile environment defended by a purpose-built substance.
Propolis stands as a testament to the ingenuity of the honey bee, a single substance that serves as the colony's fortress wall, raincoat, and pharmacy.
Summary Table:
| Function | How Bees Use Propolis | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Structural Sealant | Seals cracks, waterproofs hive, reduces entrance size | Creates a stable, defensible home environment |
| Medicinal Agent | Coats interior surfaces to sterilize the hive | Acts as a powerful antimicrobial barrier against disease |
Equip Your Apiary with the Right Tools for a Healthy Hive
Just as bees expertly use propolis to maintain their colony's health, commercial beekeepers and distributors rely on high-quality equipment for success. HONESTBEE supplies the durable beekeeping supplies and wholesale equipment that commercial apiaries and distributors need to support strong, productive colonies.
Contact our experts today to discuss your wholesale needs and discover how our products can contribute to the health and efficiency of your beekeeping operations.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2 Frame Stainless Steel Manual Honey Spinner Extractor for Beekeeping
- Plastic Hand Crank 2 Frame Honey Extractor Low Price
- HONESTBEE 6 Frame Three Use Electric Honey Extractor for Beekeeping
- 0.5T Capacity Honey Dehumidifier Dryer with Vacuum Heating and Thickening Filtering Machine
- Stainless Steel 3 Frame Manual Honey Extractor Spinner for Bee Honey Extraction
People Also Ask
- What is the primary purpose of using professional plastic propolis collection traps? Achieve High-Purity Raw Material
- Why are professional scraping tools necessary for collecting raw propolis? Ensure Purity & Efficiency in Your Harvest
- What role does propolis play in the hive? The Dual-Purpose Secret to Beehive Health
- How do honey bees recycle propolis? A Masterclass in Hive Efficiency and Resourcefulness
- Can any hive have a propolis trap? Only if your colony is strong enough.
- How do the processing equipment requirements for Geopropolis differ from standard propolis? Expert Guide
- What is the function of propolis traps in improving the yield of bee by-products? Boost Purity & Hive ROI
- What hive condition is necessary before harvesting propolis? Ensure a Strong Colony for Sustainable Yields



















