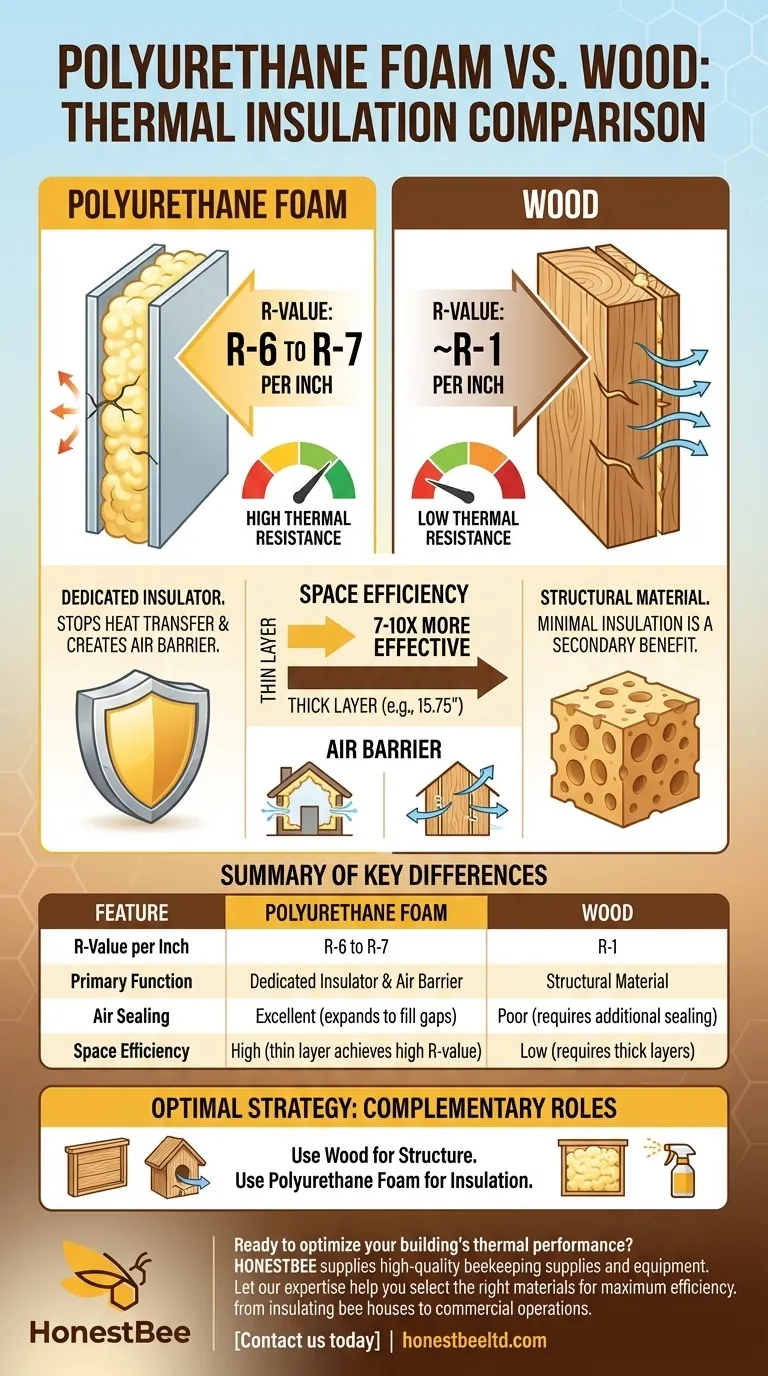
From a purely thermal perspective, polyurethane foam is vastly superior to wood as an insulator. On average, polyurethane provides about seven to ten times more thermal resistance than wood for the same thickness, meaning a much thinner layer of foam is required to achieve the same insulating effect.
The core difference is not just a matter of degree; it's a fundamental distinction in material purpose. Polyurethane foam is a specialized insulator designed to stop heat transfer, while wood is a structural material that offers minimal insulation as a secondary benefit.

Understanding Thermal Resistance (R-Value)
To compare materials accurately, we must use a standardized metric. The industry standard for measuring an insulator's effectiveness is its R-value.
What R-Value Represents
R-value indicates a material's resistance to conductive heat flow. A higher R-value signifies better insulating performance.
This value is not arbitrary; it's a quantitative measure. An R-value of 20 is twice as effective at resisting heat transfer as an R-value of 10.
The R-Value of Polyurethane Foam
Closed-cell polyurethane foam, a common type used in construction, has a very high R-value, typically ranging from R-6 to R-7 per inch of thickness.
This high density of thermal resistance is why it's so effective. Even a thin application can significantly slow down heat transfer.
The R-Value of Wood
The R-value of wood is much lower, generally around R-1 per inch of thickness. The exact value can vary slightly depending on the wood species and its moisture content.
This means to get an R-value of 15, you would need approximately 15 inches of solid wood, which is impractical for most building applications. The reference's example of 1.57 inches of foam matching 15.75 inches of wood illustrates a 10:1 performance ratio.
The Practical Implications of This Difference
This stark contrast in R-value has significant consequences for building design, energy efficiency, and overall performance.
Space Efficiency and Design
Because foam provides high R-values in a thin profile, it allows architects and builders to achieve modern energy code requirements without building exceptionally thick walls.
Using polyurethane foam inside a standard 2x6 wall cavity can yield an R-value over R-20, while filling it with only wood (as in a log home) would yield an R-value of less than R-6.
Creating an Air Barrier
Beyond its R-value, closed-cell polyurethane spray foam expands to fill every crack and crevice, creating a nearly perfect air barrier.
This is a critical advantage over wood. Air leakage (drafts) can account for a massive portion of a building's energy loss. Wood construction, with its many joints and seams, does not stop this air movement on its own.
Structural vs. Insulative Roles
It's essential to recognize that these materials serve different primary functions. Wood is a structural material first and foremost; its insulating properties are a minor, secondary characteristic.
Polyurethane foam is a dedicated insulator. It offers negligible structural support and is used specifically to manage heat flow and air sealing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a material is never just about one metric. A balanced decision requires acknowledging the downsides and other factors.
Structural Integrity
Wood provides the essential framework for most buildings. Foam cannot replace wood's structural role. You cannot build a house frame out of polyurethane foam.
The two materials are not interchangeable; they are complementary components in a modern building assembly.
Cost and Application
High-performance polyurethane foam typically has a higher upfront material and installation cost compared to traditional insulation materials like fiberglass or the incidental insulation provided by wood sheathing.
Spray foam also requires professional installation with specialized equipment to ensure it cures correctly and performs as expected.
Environmental Considerations
Wood is a renewable resource, sequestering carbon as it grows. Its primary environmental impact comes from harvesting and transportation.
Polyurethane foam is a petroleum-based plastic product. While it saves immense energy over a building's lifespan, its production has a higher initial carbon footprint, and disposal at end-of-life is a consideration.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The best material choice depends entirely on the specific goal you are trying to achieve within a project.
- If your primary focus is maximum thermal performance and air sealing: Polyurethane foam is the undisputed superior choice for insulation.
- If your primary focus is structural support: Wood is the necessary material for framing, and its minimal R-value is simply an incidental benefit.
- If your primary focus is a high-performance building: The optimal strategy is to use both materials for their intended purposes—a wood frame for structure and polyurethane foam for insulation within that frame.
Ultimately, understanding the distinct roles of each material empowers you to design and build more effective, efficient systems.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Polyurethane Foam | Wood |
|---|---|---|
| R-Value per Inch | R-6 to R-7 | R-1 |
| Primary Function | Dedicated Insulator & Air Barrier | Structural Material |
| Air Sealing | Excellent (expands to fill gaps) | Poor (requires additional sealing) |
| Space Efficiency | High (thin layer achieves high R-value) | Low (requires thick layers for insulation) |
Ready to optimize your building's thermal performance?
HONESTBEE supplies high-quality beekeeping supplies and equipment to commercial apiaries and distributors through wholesale-focused operations. Whether you're insulating bee houses or optimizing your commercial operation's energy efficiency, our expertise can help you select the right materials for maximum performance.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can bring superior insulation and efficiency to your beekeeping business!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inner Beehive Cover for Beekeeping Bee Hive Inner Cover
- High Performance Plastic Queen Excluder for Beekeeping and Apiary Management
- Professional Plastic Queen Excluder for Modern Beekeeping
- Professional Galvanized Hive Strap with Secure Locking Buckle for Beekeeping
- Durable Galvanized Steel Spring Queen Bee Cage
People Also Ask
- What is an inner cover in a beehive and what are its features? A Key Tool for Hive Health & Management
- How is the inner cover used to promote ventilation? Master Hive Climate Control for Healthy Bees
- What is the role of the inner cover in a beehive? Essential Climate Control for Hive Health
- What is the function of the center hole in the inner cover? Master Hive Ventilation and Feeding
- What is the function of an inner cover in a beehive? Essential for Hive Health & Management








