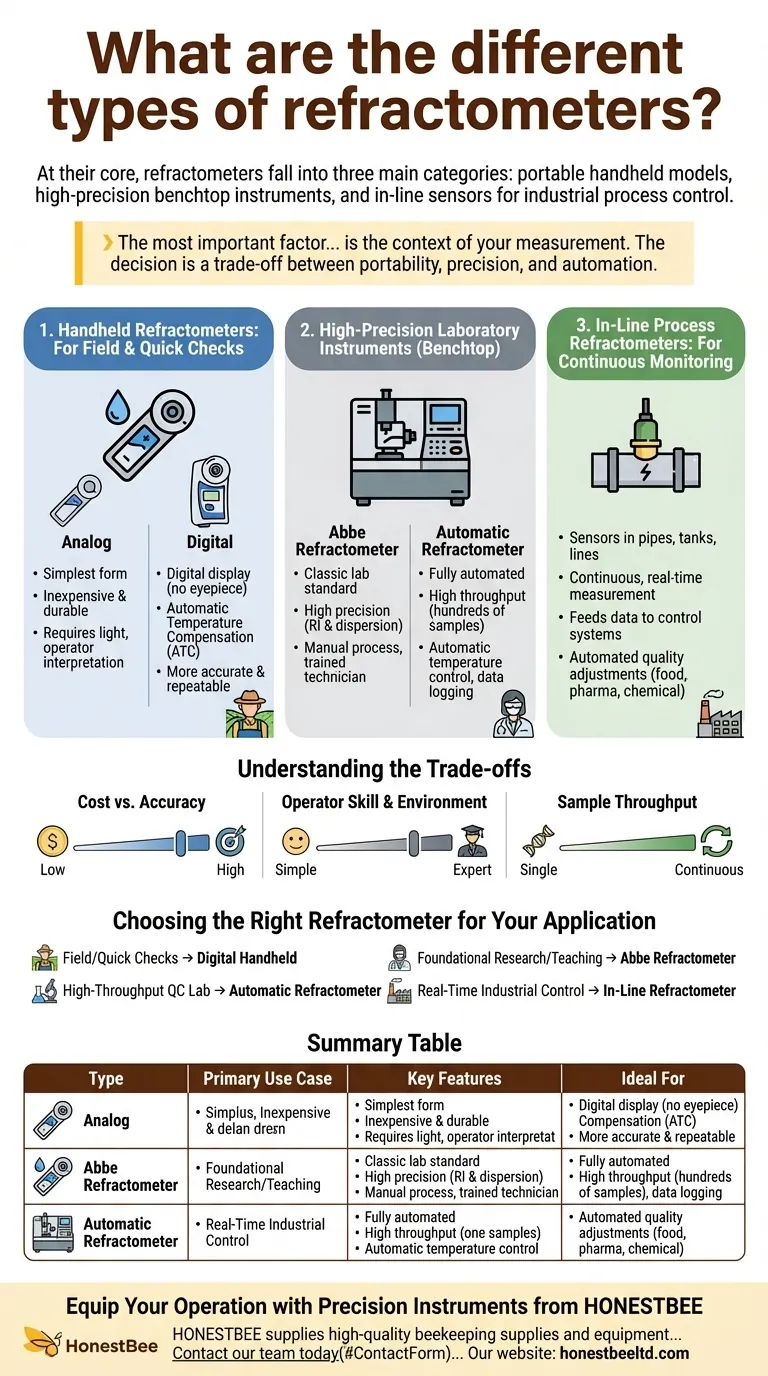
At their core, refractometers fall into three main categories based on their application: portable handheld models for field use, high-precision benchtop instruments for laboratory analysis, and in-line sensors for industrial process control. Each type is designed to measure the refractive index of a liquid, but they differ significantly in precision, cost, and operational complexity.
The most important factor in choosing a refractometer is not the technology itself, but the context of your measurement. The decision is a trade-off between portability for quick checks, precision for research-grade accuracy, and automation for industrial process control.

The Core Categories: Portability vs. Precision
The most common distinction is between instruments you can carry with you and those that remain in a fixed location. This choice fundamentally dictates the accuracy and features available.
Handheld Refractometers: For Field and Quick Checks
These are the most common and accessible types, designed for speed and convenience.
Analog handheld refractometers are the simplest form. You place a drop of liquid on the prism, close the cover, and look through an eyepiece to read a value on a built-in scale. They are inexpensive and durable but require good lighting and are subject to operator interpretation.
Digital handheld refractometers represent a significant step up. They replace the eyepiece and scale with a digital display, which eliminates ambiguity in readings. Most digital models also include Automatic Temperature Compensation (ATC), a critical feature that corrects for temperature variations, leading to far more accurate and repeatable results.
High-Precision Laboratory Instruments
When accuracy and repeatability are paramount, benchtop refractometers are the standard. These are larger, more sensitive instruments designed for use in a controlled lab environment.
The Abbe Refractometer: The Classic Lab Standard
The Abbe refractometer is the traditional workhorse for research and quality control labs. It is a highly versatile benchtop instrument capable of measuring refractive index and dispersion with high precision.
Operating an Abbe refractometer is a manual process that requires a trained technician. The user must apply the sample, adjust illumination, and align crosshairs through an eyepiece to determine the reading.
Automated and In-Process Measurement
For industrial and high-throughput applications, measurement must be continuous, rapid, and free from human error. This is where automated and in-line systems excel.
Automatic Refractometers: For High-Throughput Labs
These are modern, fully-automated benchtop systems. An operator simply places a sample, and the instrument performs the measurement, temperature control, and data logging automatically.
Their primary advantage is speed and consistency, making them ideal for quality control labs that process hundreds of samples daily.
In-Line Process Refractometers: For Continuous Monitoring
These are not standalone instruments but robust sensors installed directly into pipes, tanks, and production lines. They provide continuous, real-time measurement of the liquid concentration as it flows.
This data is fed directly into a plant's control system, allowing for automated adjustments to maintain consistent product quality in industries like food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and chemical manufacturing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a refractometer involves balancing competing priorities. Understanding these trade-offs is key to avoiding a poor investment.
Cost vs. Accuracy
There is a direct and steep correlation between cost and accuracy. An analog handheld may cost under $100, while a high-precision automatic or in-line system can cost tens of thousands. Paying for precision you don't need is a common mistake.
Operator Skill and Environment
Handheld models are designed for use by anyone, anywhere. In contrast, Abbe refractometers require a stable bench and a trained operator. In-line systems require significant engineering and installation expertise.
Sample Throughput
Handheld and Abbe refractometers are designed for single, discrete measurements. Automatic and in-line systems are built for continuous or high-volume testing where manual measurement would be a critical bottleneck.
Choosing the Right Refractometer for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by your specific operational goal.
- If your primary focus is quick fieldwork or on-the-spot checks (e.g., brewing, agriculture, coolant maintenance): A digital handheld refractometer offers the best balance of portability, ease of use, and accuracy.
- If your primary focus is foundational research or teaching in a laboratory: The Abbe refractometer remains a versatile and precise instrument for a wide range of samples.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput quality control in a lab: An automatic refractometer is essential for achieving the required speed, consistency, and data traceability.
- If your primary focus is real-time industrial process control: An in-line refractometer is the only solution for continuous monitoring and automated quality assurance.
Ultimately, selecting the correct instrument is about clearly defining your measurement requirements before evaluating the hardware.
Summary Table:
| Type | Primary Use Case | Key Features | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Handheld (Analog/Digital) | Field & Quick Checks | Portability, Ease of Use, ATC (Digital) | Brewers, Farmers, Maintenance Techs |
| Benchtop (Abbe/Automatic) | Laboratory Analysis | High Precision, Versatility (Abbe), Automation (Automatic) | Research Labs, Quality Control |
| In-Line Process | Industrial Control | Continuous Real-Time Monitoring, Process Integration | Food & Beverage, Pharmaceutical, Chemical Manufacturing |
Equip Your Operation with Precision Instruments from HONESTBEE
Choosing the right refractometer is critical for accurate results, whether you're a commercial apiary monitoring honey quality or a distributor supplying reliable equipment. HONESTBEE supplies high-quality beekeeping supplies and equipment through wholesale-focused operations, ensuring you have the tools for success.
Let us help you source the right equipment for your needs. Contact our team today to discuss your requirements and benefit from our expertise in serving commercial beekeepers and distributors.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Digital Honey Refractometer for Precision Measurement of Optimal Honey Quality
- Precision Honey Refractometer Instrument for Quality Assessment
- Semi Automatic Round Bottle Labeling Machine
- Professional Stainless Steel J-Hook Hive Tool
- HONESTBEE 72 Frame Industrial Electric Honey Extractor for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- Why are handheld refractometers critical for quality control in honey distribution? Ensure Purity & Prevent Spoilage
- What should be considered regarding the measurement range of a honey refractometer? Ensure Peak Honey Quality
- Why is a high-precision refractometer considered essential for honey quality? Master Moisture Control for Stability
- What are the main benefits of using a honey refractometer? Ensure Honey Quality & Market Compliance
- How should a honey refractometer be calibrated for accuracy? Master Precision in Honey Moisture Analysis








