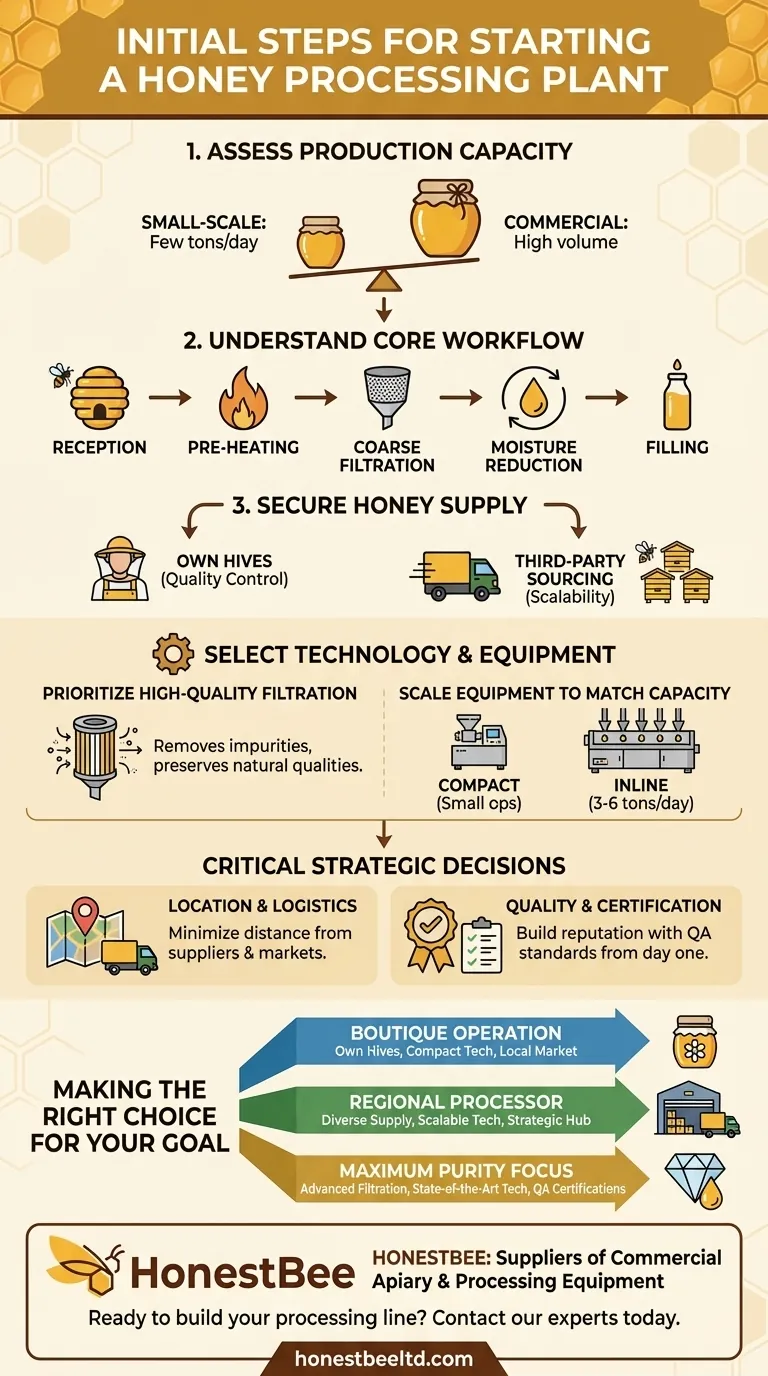
The initial steps to starting a honey processing plant involve defining your production capacity, mapping out the core processing workflow, and making strategic decisions about equipment, location, and quality control from the outset. Your first consideration must be the scale of your operation, as this will dictate nearly every subsequent investment and logistical choice.
Starting a honey processing plant is fundamentally an exercise in system design. Success isn't determined by a single piece of equipment, but by how well you align your production volume, technology choices, and logistical planning to meet your specific business goals.
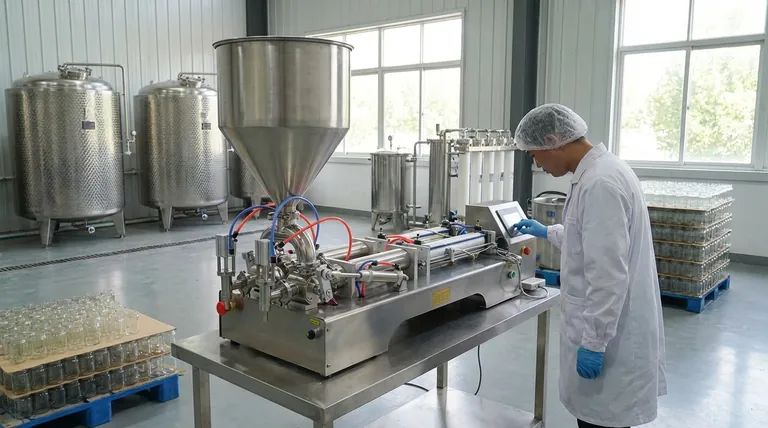

The Strategic Foundation of Your Plant
Before you purchase a single piece of equipment, you must define the operational scope of your facility. These initial decisions will form the blueprint for your entire business.
Assess Your Production Capacity
The most critical first step is determining the volume of honey you intend to process. This decision influences your equipment needs, facility size, and overall budget.
A small-scale operation might process a few tons per day, while a larger commercial plant could handle significantly more. Be realistic about your honey supply and market demand.
Understand the Core Processing Workflow
A typical honey processing line moves raw honey through several key stages to ensure it is clean, stable, and ready for packaging.
The essential steps include reception (receiving raw honey), pre-heating (to make it less viscous), coarse filtration or straining (to remove large particles like wax), moisture reduction, and finally, filling into containers.
Secure Your Honey Supply
You must have a clear plan for sourcing your raw material. This is a fundamental choice between self-sufficiency and third-party sourcing.
Starting with your own beehives gives you direct control over quality but requires significant expertise in beekeeping. Sourcing from other beekeepers allows you to scale faster but requires building a reliable supply chain.
Selecting the Right Technology and Equipment
Your equipment choices are a direct reflection of your capacity goals and quality standards. Investing in the right technology is critical for efficiency and product purity.
Prioritize High-Quality Filtration
The quality of your filtration system directly impacts the purity and final appearance of your honey. This is a non-negotiable area for investment.
State-of-the-art extractors and filters ensure that impurities are removed effectively while preserving the honey's natural qualities.
Key Equipment for a Standard Plant
A standard processing line includes a set of core machines working in sequence. This includes reception tanks, strainers, pre-heating vessels, filtration units, moisture reduction systems (concentrators), and filling machines.
Scale Equipment to Match Capacity
The machinery you choose must match your production targets. A small operation can thrive with a compact, all-in-one filling machine.
For larger plants, an inline honey filling machine with multiple nozzles is more appropriate, with capacities often ranging from 3 to 6 tons per day.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Decisions
Building a plant involves more than just processing honey; it requires making strategic trade-offs that will impact your long-term efficiency and profitability.
Location Is More Than an Address
The physical location of your plant is a critical logistical decision. It impacts both your inbound and outbound costs.
An ideal location minimizes the distance from your honey suppliers (beekeepers) to your plant and from your plant to your primary distributors or markets.
The True Cost of Operation
Look beyond the initial purchase price of equipment. Your total cost of ownership includes installation, energy consumption, regular maintenance, and compliance with safety standards.
Factoring in these operational expenses from the beginning will give you a much more accurate financial forecast.
Build a Reputation Through Quality
While an established plant is judged on its reputation, a new plant must build one. The fastest way to do this is through an unwavering commitment to quality.
Pursuing quality assurance certifications from day one signals to the market that your processes and product meet rigorous safety and purity standards.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your initial steps should be guided by your ultimate business objective. Use your primary goal to prioritize your decisions and investments.
- If your primary focus is a small-scale, boutique operation: Begin with your own hives, invest in high-quality compact equipment, and focus on building a strong local distribution network.
- If your primary focus is becoming a regional commercial processor: Prioritize securing a diverse and reliable honey supply chain, invest in scalable inline equipment, and choose a location that serves as a strategic logistical hub.
- If your primary focus is maximizing purity and quality standards: Allocate a significant portion of your budget to state-of-the-art filtration and moisture-reduction technology, and begin the process for quality certifications immediately.
By carefully aligning your capacity, technology, and location from the outset, you build a resilient foundation for a successful honey processing operation.
Summary Table:
| Key Initial Step | Core Focus | Critical Decision |
|---|---|---|
| Assess Production Capacity | Define the scale of your operation (tons/day). | Drives all equipment and budget choices. |
| Map the Processing Workflow | Understand steps from reception to filling. | Ensures a logical and efficient system design. |
| Secure Honey Supply | Choose between own hives or third-party sourcing. | Fundamental to having a reliable raw material stream. |
| Select Equipment | Prioritize filtration and match machinery to capacity. | Directly impacts final product quality and efficiency. |
| Choose Plant Location | Minimize logistical costs for inbound/outbound shipping. | A long-term strategic decision affecting profitability. |
Ready to Build Your Honey Processing Plant?
As you plan your facility, the right equipment is the cornerstone of your success. HONESTBEE supplies commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the high-quality, reliable machinery needed for every stage of the honey processing workflow.
From robust filtration systems to scalable inline filling machines, we provide the durable equipment that commercial-scale operations depend on.
Let's discuss your production goals and build a processing line tailored for your success. Contact our experts today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Pneumatic Double Nozzle Honey Filling Bottling Packaging Machine
- Precision Durable Efficient HONESTBEE Rotary Honey Filling Machine
- Pneumatic Paste Filling Machine Bottling Packaging Machine Single Nozzle
- 10L Stainless Steel Electric Honey Press Machine
- Professional Thermostatic Conical Honey Melter
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of automated honey filling and packaging? Scale Your Apiary with Industrial Precision
- What role do automated honey filling machines play? Elevate Efficiency & Standardization in Honey Processing
- What are the primary benefits of automated honey-filling machines? Scale Your Commercial Apiary Efficiency
- What is the primary function of industrial filling equipment? Maximize Honey Profitability and Market Access
- What role do automated honey-filling machines play in trade standards? Ensure Global Export Compliance & Consistency



















