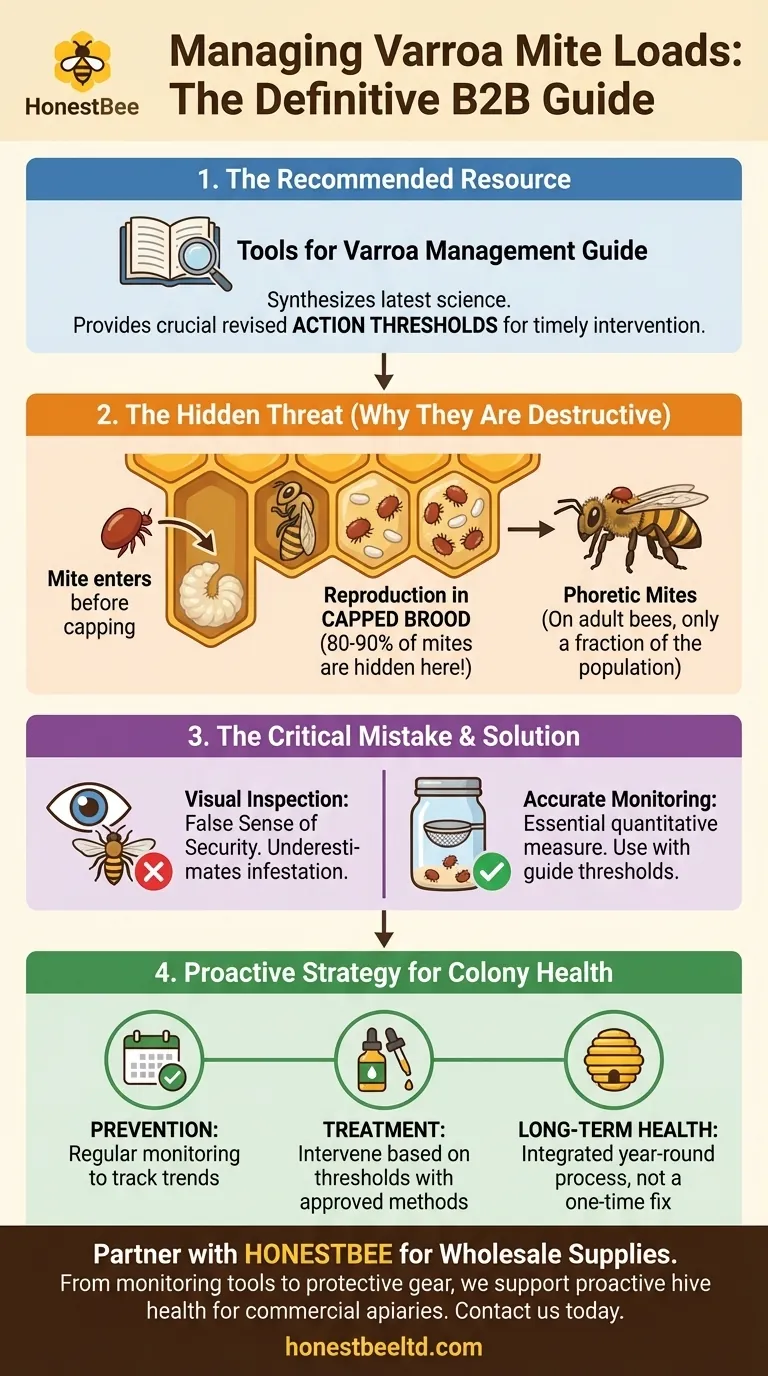
For managing Varroa mite loads in honey bee colonies, the definitive resource recommended by experts is the most recent edition of the Tools for Varroa Management guide. This guide synthesizes the latest scientific findings, providing crucial information such as revised action thresholds, which tell you precisely when intervention is necessary to protect your hives.
The core challenge of Varroa management is not just treatment, but accurate monitoring. Because the majority of mite reproduction occurs invisibly within capped brood cells, what you see on adult bees is only a small fraction of the total infestation.

Understanding the Threat: Why Varroa Mites Are So Destructive
To effectively use any management guide, you must first understand the adversary. The Varroa destructor mite is a parasitic threat that undermines colony health from the inside out.
How Mites Weaken the Colony
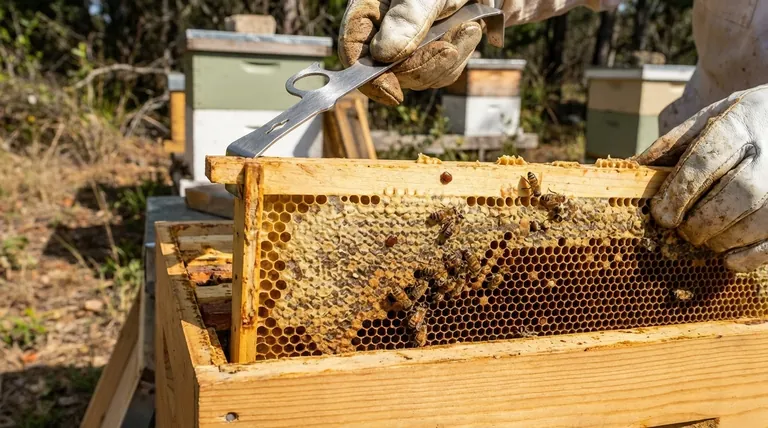
Varroa mites are external parasites that feed on the fat bodies of both adult honey bees and their developing young (brood). This feeding action weakens the individual bees, compromises their immune systems, and reduces their lifespan, leading to a gradual decline in the colony's overall health and population.
The Hidden Danger in Brood Cells
The most significant damage is done out of sight. A mated female mite enters a brood cell just before it is capped, laying multiple eggs that hatch and mature alongside the developing bee pupa. The majority of a colony's mite population is always hidden within these capped cells, reproducing rapidly.
The Problem of Phoretic Mites
The mites you can see on the backs of adult bees are in their "phoretic" phase—essentially, they are just in transit. While their presence is an indicator of an infestation, they represent only a small portion of the total mite population at any given time.
How Infestations Spread
Mite populations grow within a hive but also spread between colonies. This happens primarily through robbing, where bees from a strong colony steal honey from a weaker, mite-infested one, and through drifting, where foraging bees accidentally enter the wrong hive.
The Critical Mistake: Underestimating the Mite Population
The most common failure in Varroa management is underestimating the true scale of the infestation based on visual inspection alone. This leads to inaction until the colony is already in a state of irreversible decline.
The Fallacy of Visual Inspection
Relying on seeing mites on adult bees will give you a false sense of security. Because 80-90% of the mites are reproducing inside capped brood, a seemingly clean colony can be harboring a dangerously high mite load.
The Necessity of Monitoring
Effective management is impossible without accurate monitoring. Methods like alcohol washes or powdered sugar rolls provide a quantitative measure of the phoretic mites. These numbers can then be used with the action thresholds in the management guide to determine if and when treatment is required.
Applying This Knowledge to Your Apiary
Using this understanding in conjunction with the Tools for Varroa Management guide allows you to move from a reactive to a proactive strategy for bee health.
- If your primary focus is prevention: Regularly monitor your mite levels throughout the season to understand the infestation trend before it becomes critical.
- If your primary focus is treatment: Use the action thresholds in the recommended guide to decide exactly when to intervene and to select an appropriate, approved treatment method.
- If your primary focus is long-term hive health: View Varroa management as an integrated, year-round process of monitoring and timely action, not a one-time fix.
Proactive and informed mite management is the single most important factor in ensuring your honey bee colonies survive and thrive.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Recommended Resource | Tools for Varroa Management guide |
| Core Challenge | Accurate monitoring of mites hidden in capped brood cells |
| Primary Threat | Varroa destructor mite weakens bees by feeding on fat bodies |
| Critical Action | Use monitoring methods (e.g., alcohol wash) to measure phoretic mites against action thresholds |
Protect your apiary's health and productivity with the right equipment. HONESTBEE supplies commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the wholesale supplies needed for effective Varroa management. From monitoring tools to protective gear, we provide the reliable equipment that supports proactive hive health. Contact our team today to discuss your wholesale needs and ensure your colonies thrive.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HONESTBEE Advanced Ergonomic Stainless Steel Hive Tool for Beekeeping
- Stainless Steel Queen Grafting Tool for Beekeeping and Bee Queen Grafting
- Varroa Easy Check Mite Tester Kit Counter Alcohol Wash Jar
- Plastic Chinese Queen Grafting Tool for Bee Queen Rearing
- Heavy-Duty T-Style Frame Perch
People Also Ask
- Which technical challenges in hive maintenance are addressed by using a professional stainless steel hive tool?
- What is the hole in a hive tool for? A Multi-Tool for Apiary Repairs and Maintenance
- What are the basic tools for beekeeping? Essential Starter Kit for Safe & Successful Hive Management
- How does the hive splitting process contribute to colony management? Master Your Apiary Recovery Strategies
- What is the significance of professional hive-making tools? Scale Your Stingless Bee Farm with Precision Equipment



















