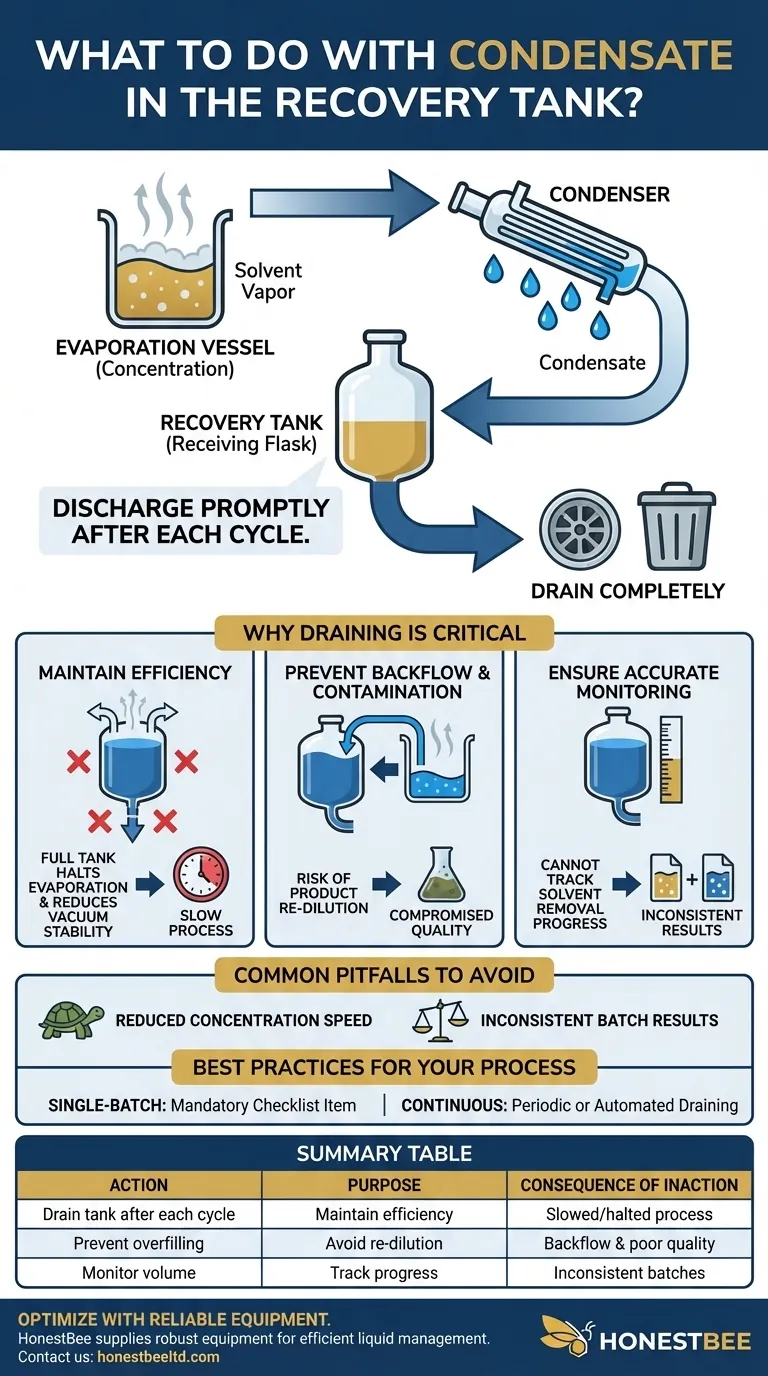
In short, the condensate in the recovery tank must be discharged promptly. This simple but critical step ensures the efficiency and integrity of the entire concentration process. It is standard practice to drain the recovery tank completely after each concentration cycle is finished.
The primary goal of concentration is to separate a solvent from a solute. Allowing the collected solvent (condensate) to accumulate in the recovery tank directly jeopardizes this goal by reducing system efficiency and creating a risk of product re-dilution.

The Role of Condensate in Concentration
To understand why draining is so critical, we must first understand the function of the recovery system.
From Vapor to Liquid
Concentration systems, such as rotary or falling film evaporators, work by turning a solvent (like water or ethanol) into a vapor, leaving the desired, less volatile substance behind. This vapor is then channeled away from the primary vessel and into a condenser.
The condenser uses a cooling medium to lower the vapor's temperature, causing it to change state back into a liquid. This recovered liquid is known as condensate.
The Function of the Recovery Tank
The recovery tank, or receiving flask, is simply the vessel that collects this condensate. Its job is to safely contain the removed solvent, keeping it physically separate from the now-concentrated product.
Why Draining Condensate is Critical
Failing to empty the recovery tank can lead to a cascade of problems that undermine the entire process.
Maintaining System Efficiency
Most concentration processes operate under a vacuum to lower the solvent's boiling point, making evaporation faster and more gentle. A full or nearly full recovery tank can reduce the available volume in the system, which can negatively impact the stability of the vacuum.
If the tank is full, there is nowhere for new condensate to go. This effectively halts the evaporation process, as the solvent vapor has no path to exit the system.
Preventing Contamination and Backflow
The most significant risk of a full recovery tank is backflow. If the tank overfills, the pressure differential can push the liquid condensate back through the system and into the primary concentration vessel.
This re-introduces the solvent you just worked to remove, re-diluting your product and defeating the purpose of the operation. It wastes time, energy, and can compromise the final product's quality.
Ensuring Accurate Process Monitoring
The volume of condensate collected is a direct measure of how much solvent has been removed. This is often a key process parameter. A full tank prevents you from accurately monitoring the progress of the concentration.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Neglecting this simple maintenance step is one of the most common operational errors.
Reduced Concentration Speed
The first sign of an overfilled recovery tank is a dramatic slowdown or complete stop in the rate of evaporation. Operators may mistakenly troubleshoot other parts of the system when the root cause is simply a full flask.
Inconsistent Batch Results
If condensate management is inconsistent, batch-to-batch results will be unreliable. Some batches may be perfectly concentrated, while others are accidentally re-diluted due to overfilling, leading to poor quality control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Integrating condensate management into your standard operating procedure is essential for repeatable, efficient results.
- If your primary focus is single-batch production: Make draining the recovery tank a mandatory checklist item at the end of every single run.
- If your primary focus is continuous or long-duration processing: Implement a protocol for periodically draining the tank during the run or invest in a system with an automated discharge mechanism.
Properly managing your condensate is a foundational step that ensures the reliability and success of your concentration work.
Summary Table:
| Action | Purpose | Consequence of Inaction |
|---|---|---|
| Drain tank after each cycle | Maintain system efficiency & vacuum stability | Slowed or halted evaporation process |
| Prevent tank overfilling | Avoid product re-dilution and contamination | Risk of backflow, compromising final product quality |
| Monitor condensate volume | Accurately track solvent removal progress | Inconsistent batch results and poor quality control |
Optimize Your Concentration Process with the Right Equipment
Proper condensate management is fundamental to efficient and reliable concentration. The right recovery tanks and system components are key to preventing downtime and product loss.
HONESTBEE supplies robust beekeeping supplies and equipment, including systems designed for reliable liquid management, to commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors through our wholesale-focused operations. We understand the importance of durable, efficient equipment for maintaining process integrity.
Let us help you build a more reliable operation. Contact our experts today to discuss your equipment needs and ensure your processes run smoothly and efficiently.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Stainless Steel Honey Storage and Settling Tank with Double Strainer
- Professional Honey Storage Tank with Agitation System
- Stainless Steel Heated Honey Tank Warming Heating Tank
- Stainless Steel Uncapping Tank with Stand and Strainer
- 0.5T Capacity Honey Dehumidifier Dryer with Vacuum Heating and Thickening Filtering Machine
People Also Ask
- What role do high-specification food-grade honey storage tanks play in the maturation process? | Pure Honey Solutions
- What is the function of stainless steel settling tanks in honey processing? Achieve Natural Purity and Clarity
- Can I store honey in stainless steel? A Guide to Safe, Long-Term Honey Storage
- What is the purpose of a settling tank or de-aerator in honey clarification? Achieve Professional Liquid Clarity
- What is the role of specialized settling containers with side nozzles? Optimize Your Honey Primary Filtration



















