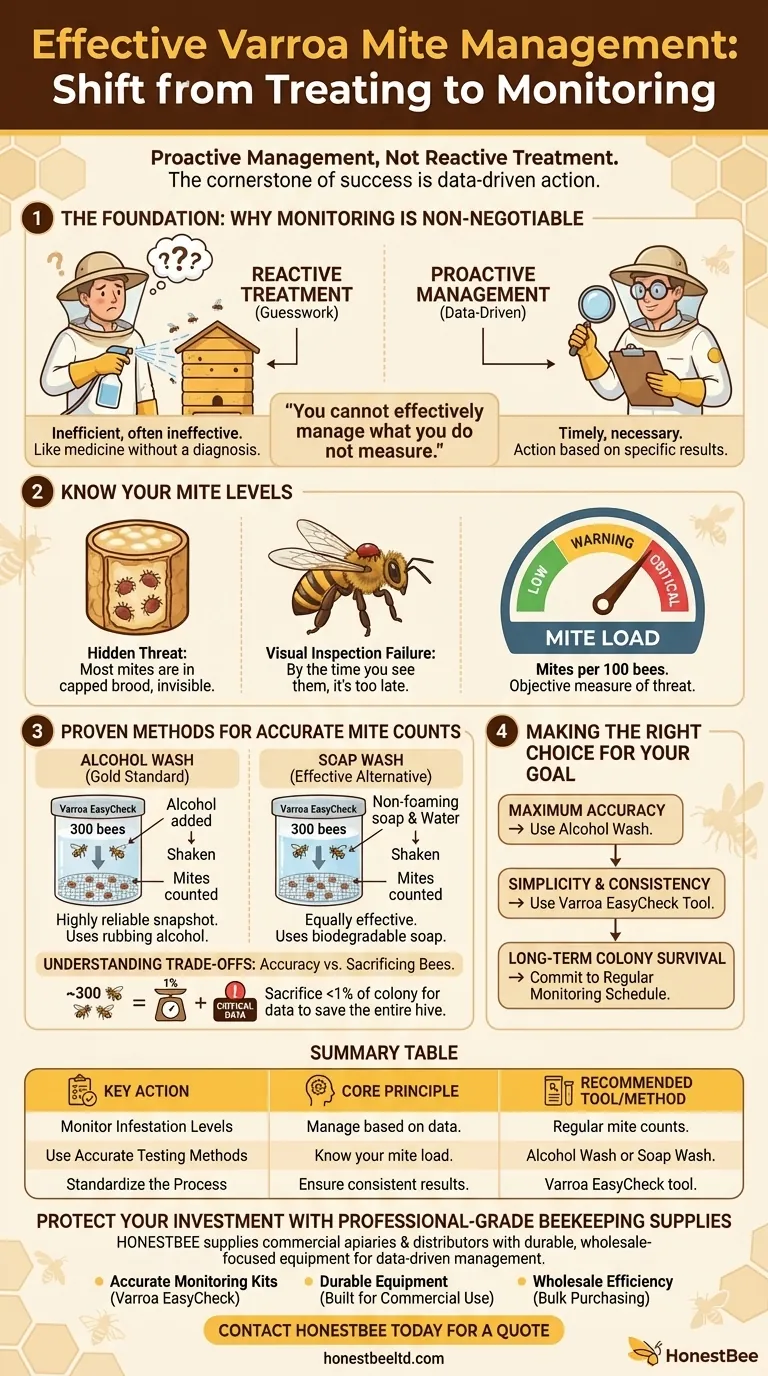
To effectively manage Varroa mites, a beekeeper must shift from simply treating a hive to actively monitoring infestation levels. The cornerstone of modern, successful Varroa management is a disciplined cycle of testing your colonies to gather data, and then taking action based on those specific results. Without this crucial step, any treatment is merely a guess.
The single most critical shift for a beekeeper is moving from a reactive "treatment" mindset to a proactive "management" strategy. You cannot effectively manage what you do not measure, and failing to monitor mite levels is the most common reason for colony loss.

The Foundation: Why Monitoring is Non-Negotiable
Treating for mites without first knowing your infestation level is like taking medicine without a diagnosis. It's inefficient and often ineffective. A monitoring-first approach ensures your efforts are timely and necessary.
The Failure of Visual Inspection
Relying on seeing mites on the backs of adult bees is a significant mistake. By the time you can easily spot them, the infestation is already at a critical, often irreversible, stage.
The vast majority of Varroa mites in a colony reside within the capped brood cells, hidden from view. What you see on adult bees is only the tip of the iceberg, representing a tiny fraction of the total mite population.
The Principle: Know Your Mite Levels
Effective management hinges on knowing the mite load, which is typically expressed as the number of mites per 100 bees. This number provides a clear, objective measure of the threat to your colony.
By consistently tracking this number, you can intervene precisely when needed—not too early, which wastes resources and can stress the bees, and not too late, which risks colony collapse.
Proven Methods for Accurate Mite Counts
To get a reliable mite count, you must dislodge mites from a sample of adult bees. The two most common and trusted methods use alcohol or soapy water to separate the mites for an easy count.
The Alcohol Wash Method
The alcohol wash is considered the gold standard for accuracy. It provides a highly reliable snapshot of the mite load within the hive.
The process involves collecting a sample of bees (typically a half-cup, or about 300 bees) in a specialized container like the Varroa EasyCheck. You then add rubbing alcohol and shake the container to dislodge the mites, which can then be easily counted.
The Soap Wash Method
A soap wash is a very similar and equally effective alternative to the alcohol wash. It uses a non-foaming, biodegradable soap mixed with water instead of alcohol.
Like the alcohol wash, this method provides a reliable result for assessing the mite population. The choice between alcohol and soap often comes down to beekeeper preference and material availability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a management strategy involves understanding the pros and cons of each method. While monitoring is essential, the methods themselves require careful consideration.
Accuracy vs. Sacrificing Bees
Both the alcohol wash and soap wash are lethal to the sample of bees collected. While sacrificing around 300 bees may feel difficult, it represents less than 1% of a healthy colony's population.
This small, controlled loss provides the critical data needed to save the entire colony of 30,000-60,000 bees from a mite-induced collapse. The accuracy gained is almost always worth the cost of the sample.
The High Cost of Inaction
The most significant pitfall is failing to monitor at all. Many beekeepers lose their colonies because they either assume their bees are fine or apply treatments blindly without knowing if they are working.
Consistent monitoring is the only way to confirm if your chosen treatments are effective and to catch rising mite populations before they overwhelm the colony's ability to survive.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach to mite testing should align with your primary objective as a beekeeper.
- If your primary focus is maximum accuracy: Use the alcohol wash method, as it is widely considered the most reliable way to get a definitive mite count.
- If your primary focus is simplicity and consistency: Use a dedicated tool like the Varroa EasyCheck with either an alcohol or soap wash to standardize your process and get reliable results every time.
- If your primary focus is long-term colony survival: Commit to a regular monitoring schedule (e.g., monthly) to ensure you always have the data needed to protect your bees.
Ultimately, successful beekeeping in the age of Varroa is defined by your commitment to vigilant, data-driven management.
Summary Table:
| Key Action | Core Principle | Recommended Tool/Method |
|---|---|---|
| Monitor Infestation Levels | Manage based on data, not guesswork. | Regular mite counts (e.g., monthly). |
| Use Accurate Testing Methods | Know your mite load (mites per 100 bees). | Alcohol Wash or Soap Wash. |
| Standardize the Process | Ensure consistent, reliable results. | Varroa EasyCheck tool. |
Protect Your Investment with Professional-Grade Beekeeping Supplies
Effective varroa mite management requires reliable tools and consistent practices. HONESTBEE supplies commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the durable, wholesale-focused equipment needed for a data-driven approach.
We provide the tools for success:
- Accurate Monitoring Kits: Like the Varroa EasyCheck, for precise mite counts.
- Durable Equipment: Built to withstand the demands of commercial operations.
- Wholesale Efficiency: Streamline your supply chain with bulk purchasing.
Ready to build a more resilient apiary? Let's discuss your specific needs.
Contact HONESTBEE today for a quote and equip your operation for long-term success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Adjustable Formic and Acetic Acid Dispenser for Bee Mite Treatment
- Professional Bamboo Queen Isolation Cage
- High Performance Plastic Queen Excluder for Beekeeping and Apiary Management
- HONESTBEE Heavy Duty All Metal Frame Wire Crimper Tool
- Professional Pneumatic Wire Embedder for Beehive Frames
People Also Ask
- What activities do bees perform in the brood box and supers? Maximize Your Apiary Efficiency
- How does a precision evaporative formic acid dispenser treat Varroa mites? Master Controlled Pest Management
- What is the application method for cardboard-based Varroa mite treatments? Maximize Hive Health with Correct Placement
- Why is a high-precision larva and pupa extraction process required when analyzing Varroa mite reproductive success?
- How should Varroa mite treatments be integrated into the spring beekeeping schedule? Expert April-May Timing Guide



















