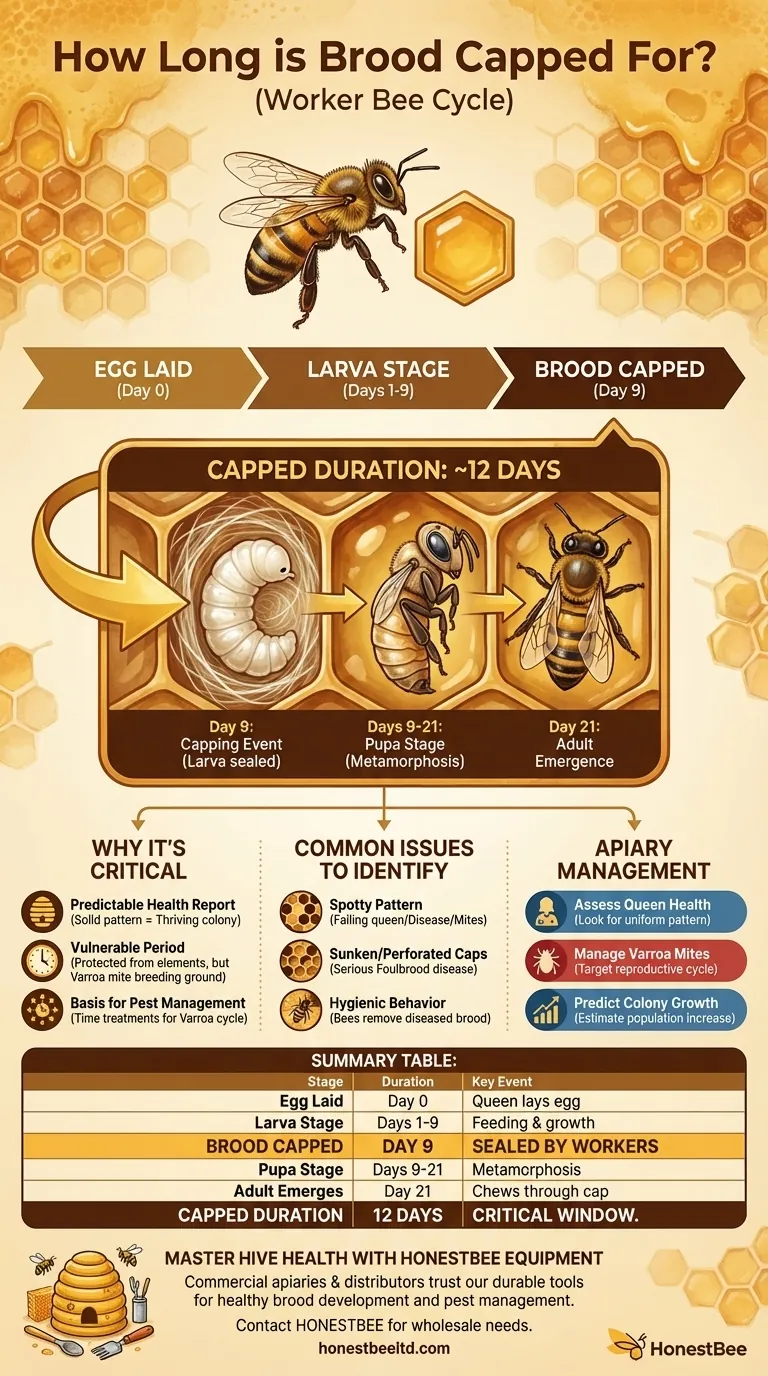
For a honeybee worker, the brood is capped for approximately 12 days. This is the final and most transformative stage of its development, where a larva metamorphoses into a fully formed adult bee, all while sealed within its wax cell.
Understanding the 12-day capped brood cycle is more than just trivia; it is a fundamental tool for beekeepers to accurately assess hive health, predict population growth, and time crucial management interventions without disturbing the colony's most sensitive phase.
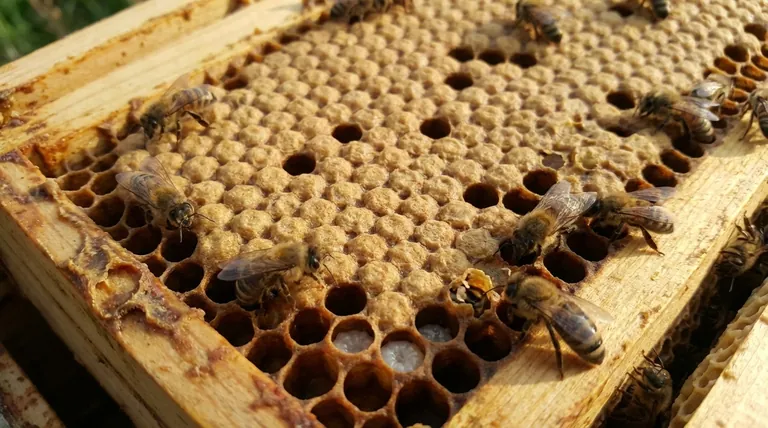

The Journey Under the Cap
The capping of a brood cell marks the beginning of a remarkable transformation. It's a predictable process that serves as a vital clock for the entire colony.
The Capping Event
Around the ninth day after the egg was laid, the larva is fully grown. At this point, house bees work to seal the cell with a porous cap made of beeswax.
The Pupa Stage
Safely sealed, the larva spins a cocoon and enters the pupa stage. The pupa, initially white and motionless, gradually develops the features and coloration of an adult bee. This is where eyes, legs, wings, and antennae take their final form.
The Emergence
On approximately the 21st day from when the egg was laid, the development is complete. The new adult worker bee chews a hole through the wax capping and emerges to join the colony's workforce. The duration from capping (day 9) to emergence (day 21) is therefore 12 days.
Why This 12-Day Window Is Critical
This fixed timeline is not just a biological curiosity; it's a key indicator of a hive's condition and trajectory. A beekeeper who understands this cycle can read the story of their hive.
A Predictable Health Report
A solid, contiguous pattern of capped brood is a primary sign of a healthy, well-mated, and productive queen. It shows she is laying consistently and the colony is thriving.
A Protected but Vulnerable Period
The wax cap protects the developing pupa from physical disturbances and fluctuations in the hive environment. However, this sealed environment is also the ideal breeding ground for the hive's most significant pest: the Varroa destructor mite.
The Basis for Pest Management
Varroa mites reproduce exclusively within sealed brood cells. Understanding the 12-day cycle is essential for timing treatments designed to interrupt the mite's life cycle.
Common Issues to Identify in Capped Brood
The appearance of the capped brood provides a clear window into the hidden health of the colony. Deviations from a healthy pattern are a call to action.
A "Spotty" Brood Pattern
A scattered, inconsistent pattern with many empty cells can signal a failing queen, disease, or a high mite infestation causing pupal death.
Sunken or Perforated Caps
Healthy caps are slightly raised and light brown. Caps that appear sunken, greasy, dark, or have small holes can be a symptom of serious brood diseases like American or European Foulbrood.
Evidence of Hygienic Behavior
Observing bees uncapping cells and removing the pupae inside is not always a bad sign. This can be hygienic behavior, where bees proactively remove mite-infested or diseased brood to protect the colony.
How to Use This Knowledge in Your Apiary
By interpreting the state of the capped brood, you can make more informed and timely decisions for your hives.
- If your primary focus is assessing queen health: Look for a solid, uniform pattern of capped brood, which indicates she is laying consistently and effectively.
- If your primary focus is managing varroa mites: Time your treatments to target the mite's reproductive cycle, which is inextricably linked to the capped brood phase.
- If your primary focus is predicting colony growth: Use the amount of capped brood to estimate how many new workers will emerge in the next two weeks to prepare for a nectar flow or prevent swarming.
By mastering the timeline of the capped brood, you move from simply keeping bees to truly understanding the rhythm of your colony.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Duration (Worker Bee) | Key Event |
|---|---|---|
| Egg Laid | Day 0 | Queen lays an egg in a cell. |
| Larva Stage | Days 1-9 | Larva is fed and grows. |
| Brood Capped | Day 9 | Worker bees seal the cell with wax. |
| Pupa Stage | Days 9-21 | Metamorphosis into an adult bee occurs. |
| Adult Emerges | Day 21 | New bee chews through the cap to join the colony. |
| Capped Duration | 12 Days | The critical window from capping to emergence. |
Master Your Hive's Health with the Right Equipment
Understanding the brood cycle is the first step; effectively managing it requires reliable, high-quality beekeeping supplies. HONESTBEE is your trusted partner, supplying commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the durable tools needed for success.
We help you protect your investment by providing equipment that supports healthy brood development and effective pest management.
Ready to equip your operation for peak productivity? Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss your wholesale needs and discover how our supplies can contribute to the vitality of your colonies.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Flatting and Embossing Machine with Tray for Beekeeping
- Retractable Chinese Queen Rearing Grafting Tools Equipment
- Stainless Steel Honey Press Wax Press with Tank
- Beehive Entrance Discs Plastic Bee Entrance Disc for Bee Hives
- Jenter Queen Rearing Kit Complete Set for Bee Breeding
People Also Ask
- Which types of honey are more likely to crystallize quickly? High-Glucose Floral Sources Explained
- Why are professional training programs essential for modern beekeeping? Master Advanced Tech for Higher Yields
- What role does a standardized apiary play in establishing a honey and pollen forage calendar? Optimize Hive Productivity
- What are the two main ways to obtain a queen bee when starting a new hive? Choose the Right Start for Your Apiary
- What is the value of high-capacity industrial scales for periodic hive weighing? Optimize Wintering & Bee Selection
- Why are industrial-grade electric stoves required for honey titration? Ensure Precise Reducing Sugar Analysis
- How do beehive temperature and humidity sensors evaluate nectar quality? Optimize Forage Assessment with Smart Data
- What are the uses of honey in various industries? Unlock Its Functional Power in Food, Pharma & Cosmetics



















