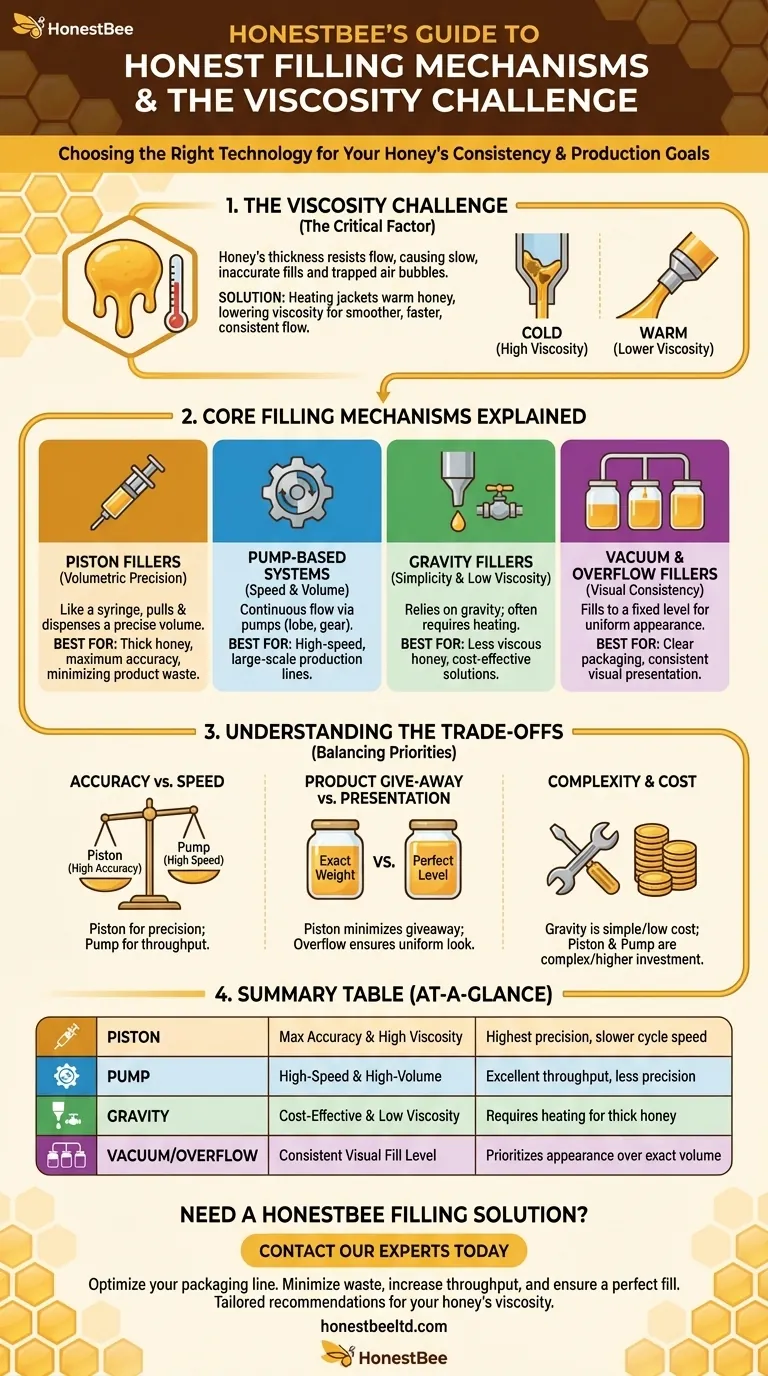
The primary honey filling mechanisms are piston fillers, pump-based systems, gravity fillers, and vacuum/overflow fillers. Each technology is designed to solve a specific challenge related to honey's unique properties, primarily its high viscosity. The choice between them hinges on balancing the need for accuracy, production speed, and the specific consistency of the honey being packaged.
The core decision in selecting a honey filling machine is not just about the mechanism, but how that mechanism handles the fundamental challenge of honey's viscosity. The best choice directly corresponds to your priorities for precision, speed, and product consistency.
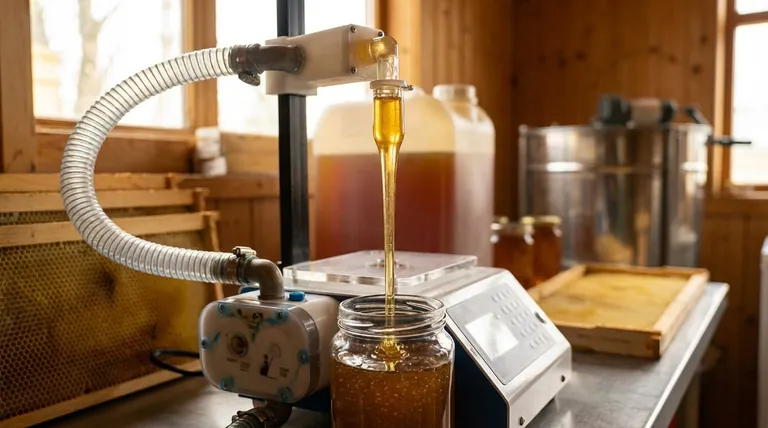

The Core Filling Mechanisms Explained
Understanding how each filler type operates reveals its inherent strengths and weaknesses, especially when dealing with a thick and valuable product like honey.
Piston Fillers: The Standard for Viscosity and Precision
A piston filler operates much like a medical syringe. It uses a cylinder and a piston to pull in a precise volume of honey from a hopper and then dispense that exact amount into the container.
This method, known as volumetric filling, is extremely accurate and consistent. Because it actively forces the product out, it is exceptionally well-suited for thick, viscous liquids like honey that do not flow easily on their own.
Pump-Based Fillers: The Choice for Speed and Volume
Pump-based systems use various types of pumps (such as lobe, gear, or progressive cavity pumps) to move honey from a bulk source to the container. The fill volume is controlled by the pump's speed and the time it runs.
These systems are often chosen for high-speed and high-volume operations. They can provide a continuous flow of product, making them more efficient for large-scale production lines compared to the discrete cycles of a piston filler.
Gravity Fillers: Simplicity for Lower Viscosity
As the name implies, a gravity filler relies on the force of gravity to work. The honey is held in a hopper located above the filling nozzles, and a valve opens to allow the product to flow down into the container.
This is the simplest and often most cost-effective mechanism. However, it is best suited for low-viscosity liquids. While it can be adapted for honey, this typically requires a heating system to thin the product and ensure a consistent flow rate.
Vacuum & Overflow Fillers: For Consistent Visual Fill Levels
Less common for honey but still relevant, these fillers prioritize appearance over precise volume. A vacuum filler creates a seal on the container and uses a vacuum to draw the honey in, while an overflow filler fills the container until the liquid reaches an "overflow" port.
The primary advantage is ensuring that every container is filled to the exact same visual level, which is critical for products sold in clear packaging. This creates a uniform look on the retail shelf, even if the internal volume of the containers varies slightly.
The Critical Factor: The Challenge of Viscosity
You cannot choose a filling mechanism without first addressing honey's thickness. Viscosity is the measure of a fluid's resistance to flow, and it is the central problem that these machines are engineered to solve.
Why Honey's Thickness Matters
High viscosity makes honey flow slowly and unevenly. This can lead to inaccurate fills in simple systems like gravity fillers and can trap air bubbles, which are undesirable for both appearance and product preservation.
The Role of Heating Systems
To combat high viscosity, many honey filling machines incorporate heating jackets or elements in their hoppers and product pathways.
Gently warming the honey lowers its viscosity, allowing it to flow more like a thinner liquid. This ensures a smoother, faster, and more consistent fill, regardless of the primary filling mechanism being used.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a filling technology involves balancing competing priorities. What you gain in one area, you often compromise in another.
Accuracy vs. Speed
Piston fillers offer the highest volumetric accuracy but their start-stop cycle can limit top-end production speed. High-speed pump systems can fill more containers per minute but may sacrifice a small degree of single-fill precision.
Product Give-Away vs. Presentation
A piston filler guarantees you are dispensing the exact weight or volume you promise on your label, minimizing costly "product give-away." An overflow filler guarantees a perfect cosmetic fill level but may slightly overfill some containers to achieve it.
Complexity and Cost
Simple gravity fillers are mechanically straightforward and less expensive. Piston and pump-based systems are more complex, involving more moving parts, which increases their initial cost and maintenance requirements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
Select the technology that aligns directly with your production goals and product characteristics.
- If your primary focus is maximum accuracy and minimizing product waste: A piston filler is the definitive choice, especially for high-value or very thick honey.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, large-scale production: A pump-based filling system will provide the throughput required for industrial operations.
- If your primary focus is a cost-effective solution for less viscous honey: A gravity filler, likely paired with a heating system, offers a simple and efficient option.
- If your primary focus is a perfect visual presentation in clear jars: An overflow filler will ensure every container on the shelf looks identical.
Ultimately, the right machine is the one that handles your honey's specific properties while meeting your business's demands for accuracy, speed, and quality.
Summary Table:
| Mechanism | Best For | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Piston Filler | Maximum Accuracy & High Viscosity | Highest precision, slower cycle speed |
| Pump-Based Filler | High-Speed & High-Volume | Excellent throughput, less precision |
| Gravity Filler | Cost-Effectiveness & Low Viscosity | Requires heating for thick honey |
| Vacuum/Overflow Filler | Consistent Visual Fill Level | Prioritizes appearance over exact volume |
Need a honey filling machine that balances precision, speed, and cost for your operation?
At HONESTBEE, we supply commercial apiaries and equipment distributors with the right filling technology to optimize their packaging line. We help you minimize product waste, increase throughput, and ensure a perfect fill every time.
Contact our experts today for a personalized recommendation on piston, pump, and other filling solutions tailored to your honey's viscosity and production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Economy Small Honey Filling Machine Honey Bottle Filler Packaging Machine
- Small Honey Filling Machine Sachet Packing Equipment Single Nozzle
- Commercial Rotary Honey Filling Machine for Production
- Precision Automated Packaging Turntable Honey Spoon Filling Sealing Packing Machine
- Double Wall Honey Heating Stirring Homogenizer Mixing Machine with Various Capacity
People Also Ask
- Why is professional honey filtering and filling equipment necessary for high-quality chestnut honey production?
- How do industrial-grade honey-filling machines contribute to the market value of honey? Unlock Premium Brand Potential
- What technical advantages do automatic honey filling machines offer? Optimize Your Commercial Honey Bottling Today
- What is the significance of high-precision honey-filling machines? Preserve Quality and Maximize Efficiency
- What is the primary function of medical-grade syringes in stingless bee honey collection? Ensure Purity & Integrity
- What types of products can semi-automatic filling machines handle? Boost Your Production Versatility
- How does a piston filling machine work for honey packaging? Achieve Precise, Drip-Free Filling
- What operational advantages does automated honey filling machinery provide? Scale Your Honey Production Efficiently



















