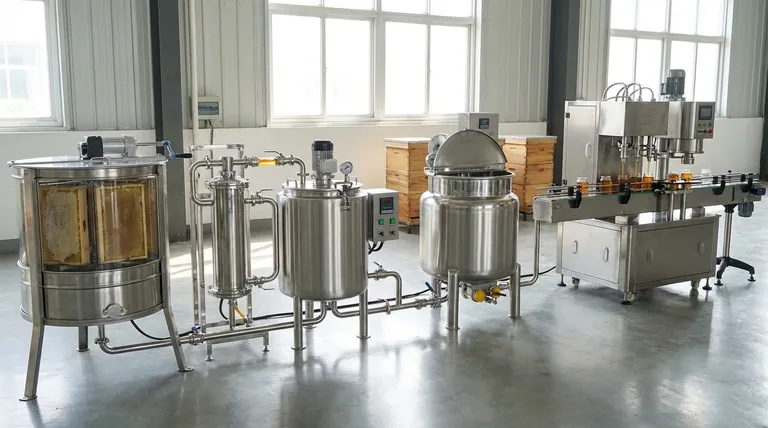
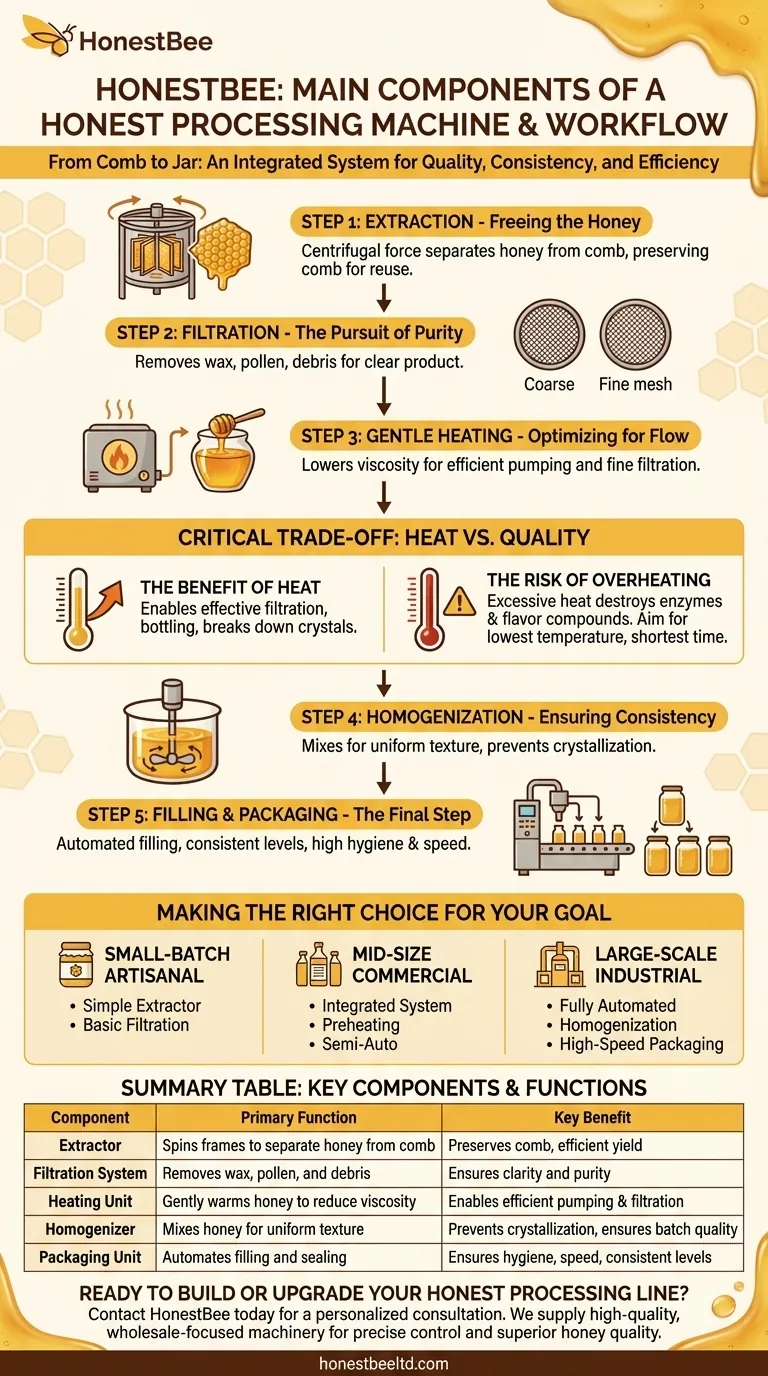
At its core, a honey processing machine is an integrated system designed to transform raw honey from the comb into a pure, consistent, and shelf-stable product. The primary components work in sequence, including an extractor to separate honey from the comb, a filtration system to remove impurities, a heating unit to improve flow, a homogenizer for uniform texture, and a packaging unit to bottle the final product. Each stage is a critical step in ensuring quality and efficiency.
Understanding the components of a honey processing machine is less about the individual parts and more about understanding the process control each part provides. Each stage—from extraction to packaging—is a critical control point for ensuring honey quality, safety, and consistency.

From Comb to Jar: The Honey Processing Workflow
A honey processing line functions as a continuous workflow. While machines vary by size and complexity, they almost universally follow a logical sequence to refine the raw honey.
Step 1: Extraction - Freeing the Honey
The process begins with the extractor. After the wax cappings are removed from the honeycomb frames, the frames are placed inside this device.
The extractor uses centrifugal force, spinning the frames at high speed to pull the honey out of the comb's cells without destroying the comb itself.
Step 2: Filtration - The Pursuit of Purity
Once extracted, the raw honey contains various impurities, such as bits of wax, pollen, and other debris from the hive.
The honey is passed through a filtration system. This often involves a coarse filter to catch larger particles, followed by a fine filter to ensure a clear, pure final product.
Step 3: Gentle Heating - Optimizing for Flow
Raw honey is highly viscous, making it difficult to filter and pump efficiently. To solve this, a heating or preheating unit is used.
The machine gently warms the honey, lowering its viscosity. This allows it to flow easily through the filters and pipes, preparing it for the next stages of processing.
Step 4: Homogenization - Ensuring Consistency
To guarantee that every jar of honey from a batch has the same texture and quality, the honey is passed through a homogenizer or agitator.
This component thoroughly mixes the honey to create a uniform consistency. It also helps break down any small sugar crystals that may have started to form, which can delay future crystallization and ensure a smooth texture.
Step 5: Filling and Packaging - The Final Step
The final stage is the automated packaging unit. This component handles the precise filling of jars or other containers.
Automation at this stage ensures consistent fill levels, improves hygiene by minimizing manual handling, and dramatically increases the speed of production for distribution.
Understanding the Critical Trade-off: Heat vs. Quality
The most sensitive part of honey processing is the application of heat. While necessary for efficiency, it presents a significant trade-off that separates standard honey from premium-quality honey.
The Benefit of Heat
Controlled heating is essential in any commercial operation. It enables effective fine filtration, breaks down crystallization nuclei, and makes the honey easy to bottle. Without it, processing would be incredibly slow and inefficient.
The Risk of Overheating
Excessive or uncontrolled heat will degrade the honey's quality. High temperatures can destroy the beneficial enzymes, such as diastase, and eliminate the delicate, volatile flavor and aroma compounds that define a honey's unique character.
This is the key difference between minimally processed, high-value honey and many mass-market products. The goal is always to use the lowest possible temperature for the shortest possible time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific components you need depend entirely on your production scale and desired product quality.
- If your primary focus is small-batch artisanal production: You can prioritize a simple extractor and a basic filtration system, often forgoing automated heating and homogenization to preserve the honey's raw characteristics.
- If your primary focus is mid-size commercial growth: An integrated system with a controlled preheating unit and semi-automated packaging becomes critical for achieving consistent quality and meeting market demand.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial output: A fully automated line with precise homogenization, low-temperature concentration, and high-speed packaging is necessary to ensure standardization and efficiency.
Ultimately, mastering your honey's quality comes from mastering the process that shapes it.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Extractor | Spins frames to separate honey from comb | Preserves comb for reuse, efficient yield |
| Filtration System | Removes wax, pollen, and other debris | Ensures clarity and purity of final product |
| Heating Unit | Gently warms honey to reduce viscosity | Enables efficient pumping and fine filtration |
| Homogenizer | Mixes honey for uniform texture and consistency | Prevents crystallization, guarantees batch quality |
| Packaging Unit | Automates filling and sealing of containers | Ensures hygiene, speed, and consistent fill levels |
Ready to build or upgrade your honey processing line?
At HONESTBEE, we supply commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the high-quality, wholesale-focused machinery and components needed for success. Whether you're scaling up artisanal production or optimizing a large-scale industrial operation, our expertise ensures you get the right equipment for precise process control and superior honey quality.
Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation and discover how our solutions can enhance your efficiency and protect your product's integrity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Double Wall Honey Heating Stirring Homogenizer Mixing Machine with Various Capacity
- Stainless Steel Manual 8 Frame Radial Honey Extractor Machine for Beehives
- HONESTBEE 6 Frame Self Reversing Electric Honey Extractor for Beekeeping
- Professional 4 Frame Self Reversing Electric Honey Extractor for Beekeeping
- Electric 8 Frame Honey Spinner Extractor Equipment for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- Why is the use of standardized honey harvesting tools critical? Enhance Purity and Colony Health in Your Apiary
- Why is vacuum homogenization and stirring equipment critical for manufacturing fortified honey? Enhance Honey Potency
- What are the technical advantages of using standardized honey supers for honey collection? Maximize Your Apiary Yield
- What are the key components of a honey processing machine? Build Your Efficient Honey Production Line
- What is the role of a honey super in the honey harvesting workflow? Master the Art of Pure & Efficient Honey Production



















