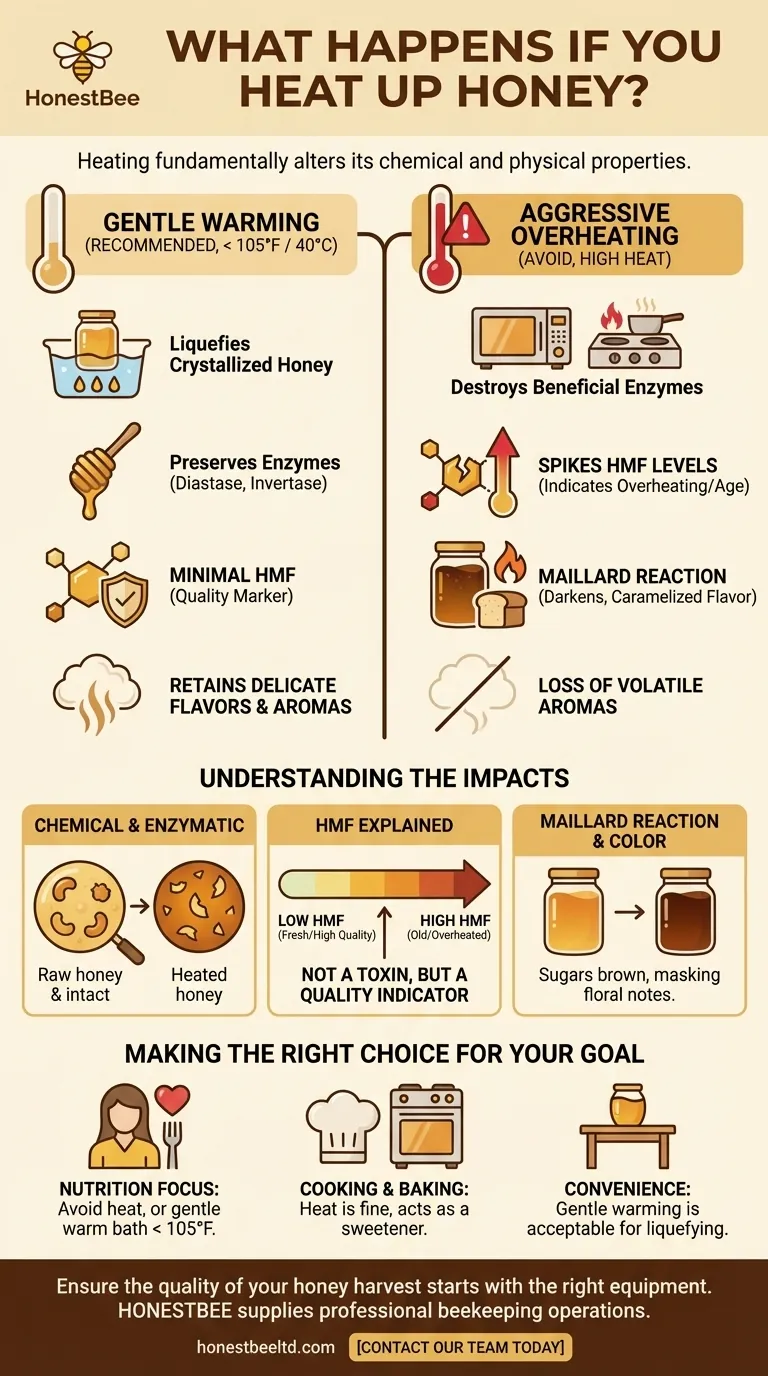
Heating honey fundamentally alters its chemical and physical properties, reducing its unique qualities. When exposed to high temperatures, its beneficial enzymes are destroyed, its delicate flavors and aromas are lost, its color darkens, and a chemical byproduct known as HMF is created. This process effectively changes raw, complex honey into a simpler sweetener.
The core issue is not whether heat is "bad," but that there is a significant difference between gentle warming and aggressive overheating. While gentle, controlled warming is a common and safe practice to liquefy crystallized honey, high heat permanently degrades its nutritional profile and complex taste.

The Chemical and Enzymatic Impact of Heat
Heating honey triggers a cascade of changes that affect its composition, flavor, and appearance. These changes are irreversible and directly related to the temperature and duration of the heat exposure.
Degradation of Natural Enzymes
Raw honey contains natural enzymes, such as diastase and invertase, which are introduced by bees. These enzymes are a key marker of honey's quality and are sensitive to heat.
Even moderate heat begins to break down these enzymes, diminishing the unique beneficial properties associated with raw honey.
The Maillard Reaction and Darkening
When heated, the sugars in honey (primarily fructose and glucose) undergo a process called the Maillard reaction. This is the same chemical reaction responsible for the browning of bread or searing of meat.
This reaction not only darkens the honey's color but also alters its taste, often masking delicate floral notes with a more generic, caramelized flavor.
Loss of Delicate Aromas
The unique scent of different honey varietals comes from volatile aromatic compounds from the original nectar. These compounds are extremely delicate and evaporate easily when heated.
The result is a honey that has lost its distinctive aroma and, consequently, a significant portion of its complex flavor profile.
Understanding HMF (Hydroxymethylfurfural)
One of the most discussed effects of heating honey is the formation of a compound called 5-hydroxymethylfurfural, or HMF.
What is HMF?
HMF is an organic compound that forms when sugars are broken down by heat in an acidic environment. Since honey is both acidic and full of sugar, its formation is inevitable when honey is heated or stored for long periods.
Is It a Safety Concern?
While some sources label HMF as toxic, its presence in heated honey is not a practical safety concern. HMF is found in many common heat-processed foods, including baked goods, coffee, and dried fruit, often at much higher levels than in warmed honey.
HMF as a Quality Marker
Instead of a toxin, HMF is best understood as a freshness and quality indicator. International food standards use HMF levels to determine if honey has been overheated during processing or is simply old. Low HMF levels signify high-quality, carefully handled honey.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Gentle Warming vs. Overheating
The goal is not to eliminate heat entirely but to apply it intelligently. The key is control.
The Problem of Crystallization
Nearly all raw honey will naturally crystallize over time. This is a normal process and does not mean the honey has gone bad. However, to use it as a liquid, it must be re-liquefied.
Best Practice: Gentle Warming
To preserve honey's quality while making it liquid again, use a gentle warm water bath. Place the honey jar in a pot of warm—not boiling—water and let it sit until the crystals dissolve.
Keeping the temperature below 105°F (40°C) minimizes damage to enzymes and the formation of HMF, preserving the honey’s natural character.
What to Avoid: Overheating
Aggressive heating methods, such as microwaving or direct heat on a stovetop, cause rapid and significant degradation. This level of heat quickly destroys beneficial enzymes, boils off delicate aromas, and spikes HMF levels.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your approach to heating honey should depend entirely on how you intend to use it.
- If your primary focus is preserving maximum nutritional value: Avoid heating altogether. If you must liquefy crystallized honey, use a very gentle warm water bath kept below 105°F (40°C).
- If your primary focus is cooking or baking: Do not worry about the heat. The high temperatures of your recipe will alter the honey, and its role is primarily that of a sweetener.
- If your primary focus is simply liquefying a jar for table use: Gentle warming is a perfectly acceptable trade-off for convenience, as the minor degradation will not significantly impact everyday enjoyment.
Understanding the effects of heat empowers you to use honey in a way that aligns with your specific goals, whether for health, flavor, or convenience.
Summary Table:
| Heating Effect | Consequence | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|---|
| Enzyme Degradation | Loss of beneficial enzymes like diastase and invertase. | Reduces nutritional quality of raw honey. |
| Maillard Reaction | Honey darkens in color; flavor becomes more caramelized. | Masks delicate floral notes. |
| HMF Formation | Creation of Hydroxymethylfurfural, a quality marker. | High HMF indicates overheating or age. |
| Aroma Loss | Volatile aromatic compounds evaporate. | Honey loses its unique, complex scent. |
Ensure the quality of your honey harvest starts with the right equipment. Proper handling, from extraction to storage, is crucial for preserving the natural enzymes and flavors that make your honey exceptional. HONESTBEE supplies commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with high-quality, durable supplies designed for professional beekeeping operations. Let's discuss how our wholesale-focused solutions can support your quality standards—contact our team today to learn more.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Beeswax Melter for Candle Making Honey Bee Wax Melter
- Steam Beeswax Melter Wax Warmer for Wax Processing
- HONESTBEE 72 Frame Industrial Electric Honey Extractor for Beekeeping
- 10L Stainless Steel Electric Honey Press Machine
- 8-Frame Electric Self-Reversing Honey Extractor Spinner for Commercial Honey Extraction Equipment
People Also Ask
- What temperature can raw honey be heated to? Preserve Enzymes and Avoid Degradation
- How do you remove crystallized honey from frames? Re-liquefy honey with gentle heat techniques.
- How to get crystallized honey out of frames? Safely reliquefy honey without damaging comb.
- What is the purpose of heating honey to 35-40°C during pretreatment? Optimize Viscosity for Precise Analysis
- Is it safe to heat raw honey? Preserve the health benefits of your raw honey
- Why is honey sometimes heated before the filtering process? Master Viscosity Control for Efficient Honey Production
- Why are aluminum fin heat sinks essential in beehive heating units? Ensure Colony Safety with Thermal Management
- What is the recommended method for heating honey to preserve its quality? Expert Guide for Commercial Apiaries



















