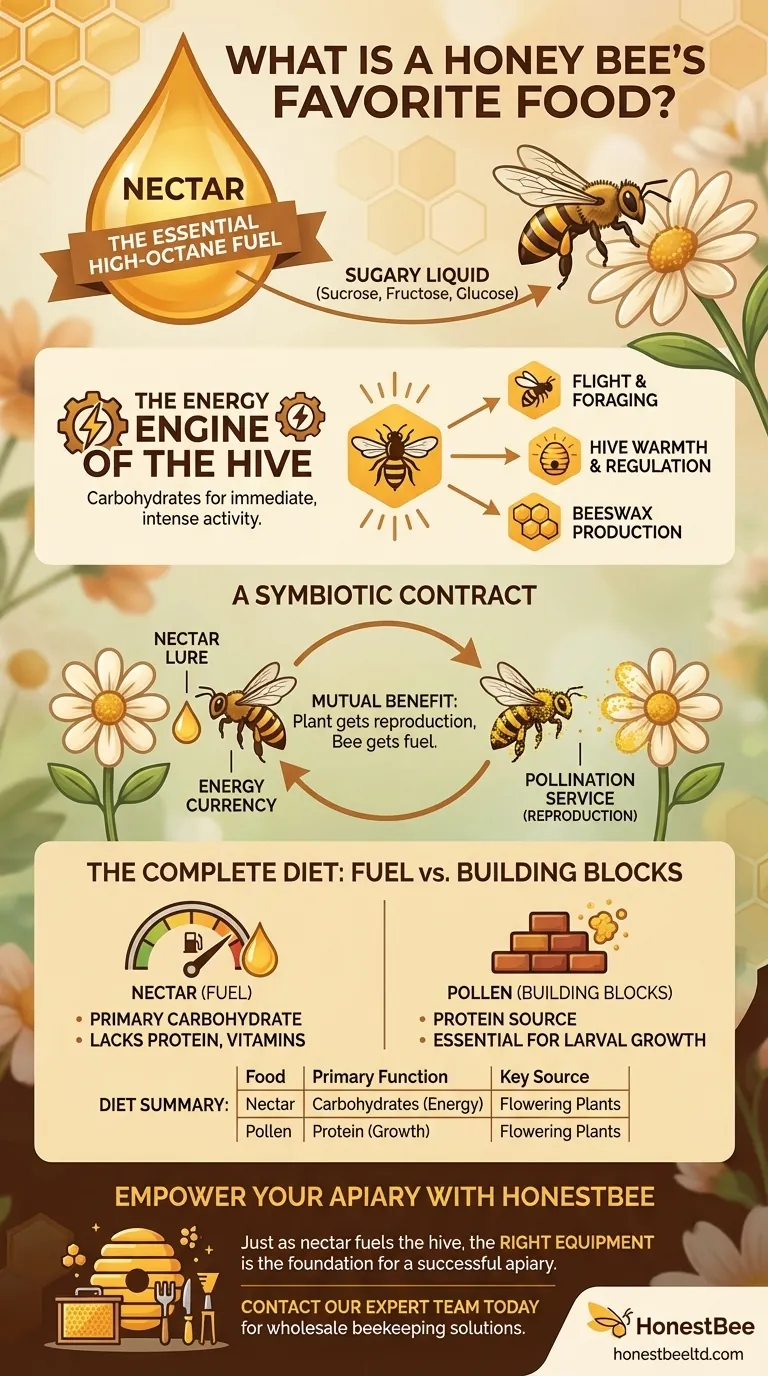
A honey bee's favorite and most essential food is nectar. This sugary liquid, produced by flowering plants, is the primary source of carbohydrates that fuels nearly all of a bee's high-energy activities, from flight and foraging to maintaining the warmth of the hive.
The relationship between a honey bee and nectar is fundamentally a symbiotic contract. Nectar is the energy currency that powers the bee, and in exchange for this fuel, the bee provides the critical pollination service that allows the plant to reproduce.

The Role of Nectar as High-Octane Fuel
A honey bee's life is one of constant, demanding work. Nectar provides the raw energy required to sustain this level of activity, functioning much like high-octane fuel for a finely tuned engine.
What Exactly is Nectar?
Nectar is a sweet liquid secreted by plants from special glands called nectaries. Its primary purpose is to attract pollinators like bees.
The composition is simple but effective, consisting mainly of a solution of sugars—primarily sucrose, fructose, and glucose—dissolved in water.
The Energy Engine of the Hive
These sugars are the bee's source of carbohydrates. They are metabolized to provide the immediate energy needed for the intense muscular activity of flight.
This energy also powers the collective effort of the colony, including regulating the hive's temperature and producing the beeswax needed for honeycomb construction.
A Mutually Beneficial Partnership
The bee's preference for nectar is not a one-sided affair. It sits at the center of one of nature's most crucial and elegant partnerships.
The Plant's Strategic Offering
Plants produce nectar as a deliberate strategy. It is an irresistible lure designed to attract bees and other animals.
By offering this valuable food source, the plant ensures that pollinators will visit its flowers.
The Bee's Critical Service
As a bee moves from flower to flower to collect nectar, it inadvertently becomes covered in the plant's pollen.
When it visits the next flower, some of this pollen is transferred, enabling fertilization and the plant's reproduction. This process is the foundation of countless ecosystems.
Understanding the Limitations
While nectar is the primary food for adult bees, it's essential to understand that it does not provide complete nutrition on its own. It represents one half of the hive's required diet.
Nectar is Not a Complete Food
Nectar is almost pure carbohydrate. It lacks the significant amounts of protein, lipids, vitamins, and minerals necessary for growth and development.
The Role of Pollen
To get these other vital nutrients, bees also collect pollen. Pollen is the hive's protein source, and it is absolutely essential for raising young bees (larvae).
Think of it this way: nectar is the fuel, while pollen is the building block for a healthy and growing colony.
How This Applies to You
Understanding the bee's dietary needs allows us to see their role—and ours—in the broader ecosystem more clearly.
- If your primary focus is gardening: Planting a diverse range of native, flowering plants that bloom at different times ensures a consistent nectar supply for local pollinators.
- If your primary focus is ecology: The bee's dependence on nectar is a perfect example of co-evolution and is a cornerstone of biodiversity, driving the reproductive success of a vast range of plants.
- If your primary focus is understanding bees: Remember that a healthy hive requires both nectar for energy and pollen for growth, and their collection of both is what makes them such indispensable pollinators.
Ultimately, a honey bee's favorite food is the lifeblood of a system far larger than itself, powering both the hive and the health of our shared environment.
Summary Table:
| Honey Bee's Diet | Primary Function | Key Source |
|---|---|---|
| Nectar | Carbohydrates for energy (flight, hive warmth) | Flowering plants |
| Pollen | Protein for growth and larval development | Flowering plants |
Empower Your Apiary with HONESTBEE
Just as nectar is the essential fuel for a thriving hive, having the right equipment is the foundation for a successful and productive apiary. At HONESTBEE, we supply commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the high-quality, reliable supplies needed to support healthy colonies and maximize honey production.
Let us help you build a stronger operation. Contact our expert team today to discuss your wholesale needs and explore our full range of beekeeping solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HONESTBEE Entrance Bee Feeder Professional Hive Nutrition Solution for Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE Professional Entrance Bee Feeder Hive Nutrition Solution
- HONESTBEE Professional Hive Top Bee Feeder Feeding Solution
- In-Hive Dual Compartment Frame Bee Feeder for Targeted Colony Nutrition
- Rapid Bee Feeder White Plastic 2L Round Top Feeder for 8 or 10-Frame Bee Hives
People Also Ask
- What is a bee entrance feeder and what are its drawbacks? Essential Guide to Hive Security and Feeding Efficiency
- What is an entrance feeder and what are its characteristics? Essential Guide for Effortless Hive Feeding
- How does the entrance feeder method work? A Guide to Simple But Risky Hive Feeding
- Are entrance feeders good for bees? Prioritize Hive Health Over Convenience
- What is an entrance feeder? A Guide to Its Simple Design and High Robbing Risk



















