Understanding the basics before using a honey refractometer is critical because this is a precision instrument, not a simple tool. Failing to understand core principles like temperature compensation and proper calibration can lead to inaccurate moisture readings. These errors can result in your entire honey harvest fermenting and spoiling, or failing to meet legal standards for sale.
A honey refractometer provides a number, but understanding the principles behind that number is what empowers you to guarantee the quality and longevity of your honey. Simply following steps without comprehension gives you data; understanding the basics gives you confidence.

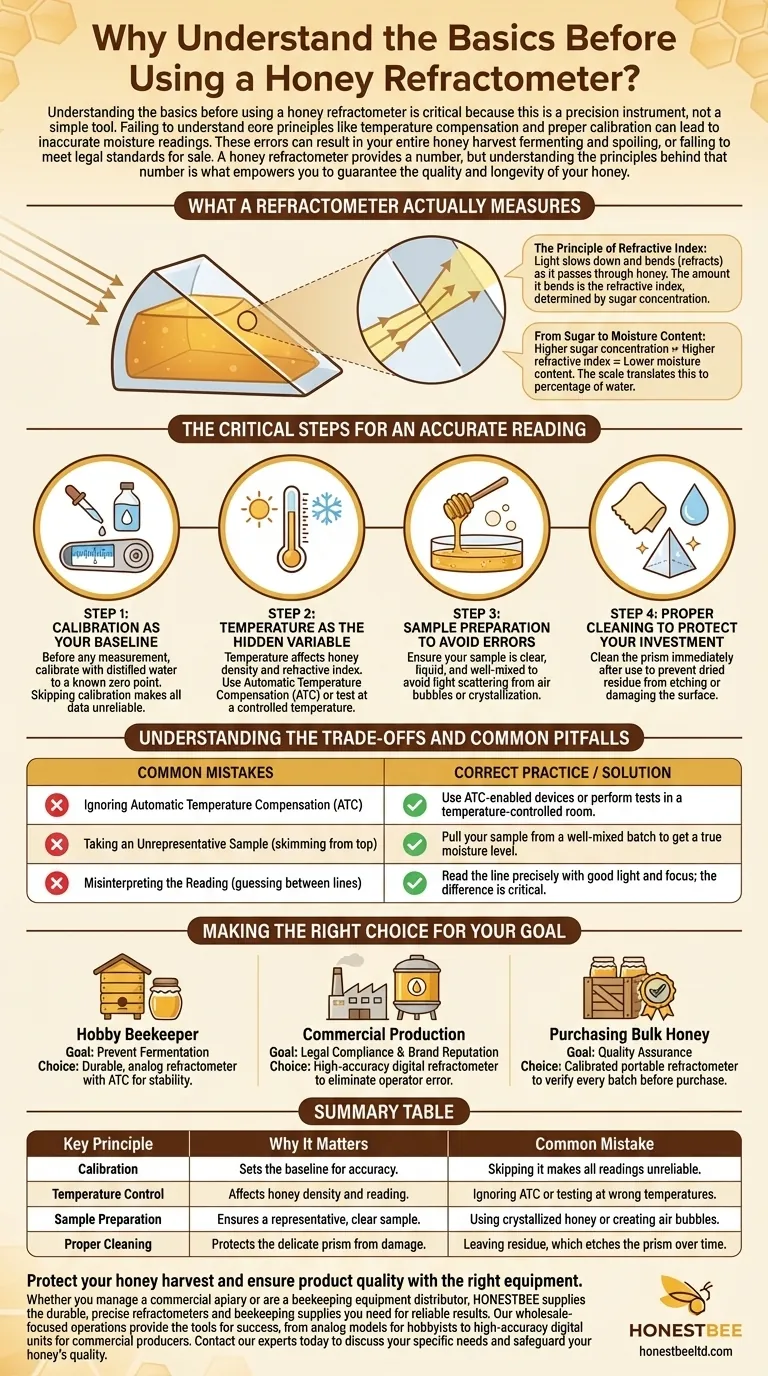
What a Refractometer Actually Measures
A refractometer doesn't directly measure water. It measures how light bends as it passes through the honey, a principle that is directly correlated to the honey's moisture content.
The Principle of Refractive Index
When light passes from the air into a liquid like honey, it slows down and changes direction, or refracts. The amount it bends is called the refractive index.
This bending is determined by the density of the liquid. Since honey is primarily a solution of sugar in water, a higher concentration of sugar makes it denser and causes light to bend more.
From Sugar to Moisture Content
The scale on a honey refractometer is designed to translate this refractive index into a practical measurement. While it's actually measuring sugar density, the scale displays the inverse: the percentage of water.
A higher refractive index means higher sugar concentration, which corresponds to a lower moisture content—the ideal state for stable, long-lasting honey.
The Critical Steps for an Accurate Reading
Following the correct procedure isn't just about getting a reading; it's about getting a reliable reading. Each step is designed to eliminate variables that could compromise your results.
Step 1: Calibration as Your Baseline for Accuracy
Before any measurement, you must calibrate the refractometer. This is typically done with a special calibration liquid or distilled water, which sets the instrument to a known zero point.
Skipping calibration is like using a scale that isn't zeroed out. Every subsequent measurement will be off, making your data fundamentally unreliable.
Step 2: Temperature as The Hidden Variable
The temperature of honey significantly affects its density and, therefore, its refractive index. A reading taken on cold honey will be different from one taken on warm honey, even if the moisture content is identical.
For an accurate result, both the honey sample and the refractometer itself must be at the same ambient temperature. Many modern units feature Automatic Temperature Compensation (ATC), which corrects for variations, but it's still best practice to let your sample acclimate.
Step 3: Sample Preparation to Avoid Errors
Air bubbles and crystallization in a honey sample can scatter light, leading to a blurry or incorrect reading on the scale.
Ensure your sample is clear and liquid. If the honey has been stored, gently stir it to ensure the moisture is evenly distributed, as water can sometimes separate and rise to the top.
Step 4: Proper Cleaning to Protect Your Investment
After each use, the prism and cover plate must be cleaned immediately with a soft, damp cloth.
Dried honey residue will not only make your next reading inaccurate but can also permanently etch or damage the delicate surface of the prism, ruining the instrument.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
Knowing what can go wrong is as important as knowing the correct procedure. Awareness of these common mistakes is what separates a novice from an expert user.
Ignoring Automatic Temperature Compensation (ATC)
Assuming any refractometer will be accurate at any temperature is a costly mistake. If your device lacks ATC, you must perform your tests in a temperature-controlled environment and use conversion charts.
For most users, purchasing a model with built-in ATC is the single most important feature for ensuring consistent, reliable results without complex calculations.
Taking an Unrepresentative Sample
Measuring honey skimmed from the very top of a large tank may not be representative of the entire batch. Moisture can migrate, creating layers with different water content.
Always pull your sample from a well-mixed batch to get a true picture of its overall moisture level.
Misinterpreting the Reading
The line on the refractometer scale must be read precisely. The difference between 18% moisture (stable honey) and 20% moisture (at risk of fermentation) is small but critically important.
Do not guess or round. Ensure you have good light and use the focusing eyepiece to get a sharp, unambiguous reading.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your objective determines the tool and the process. Use these guidelines to apply this knowledge effectively.
- If your primary focus is hobby beekeeping: Your main goal is preventing fermentation. A durable, analog refractometer with ATC is a cost-effective and reliable choice for ensuring your honey is stable for storage and sharing.
- If your primary focus is commercial production: Your goals are legal compliance and brand reputation. Invest in a high-accuracy digital refractometer, which offers easier readings and removes operator error, ensuring every batch meets quality standards.
- If your primary focus is purchasing bulk honey: Your goal is quality assurance. A calibrated, portable refractometer is an essential tool to verify the moisture content of every batch before you buy, protecting your investment.
Ultimately, mastering the honey refractometer is about taking direct control over the quality and integrity of your product.
Summary Table:
| Key Principle | Why It Matters | Common Mistake |
|---|---|---|
| Calibration | Sets the baseline for accuracy. | Skipping it makes all readings unreliable. |
| Temperature Control | Affects honey density and the reading. | Ignoring ATC or testing at wrong temperatures. |
| Sample Preparation | Ensures a representative, clear sample. | Using crystallized honey or creating air bubbles. |
| Proper Cleaning | Protects the delicate prism from damage. | Leaving residue, which etches the prism over time. |
Protect your honey harvest and ensure product quality with the right equipment.
Whether you manage a commercial apiary or are a beekeeping equipment distributor, HONESTBEE supplies the durable, precise refractometers and beekeeping supplies you need for reliable results. Our wholesale-focused operations provide the tools for success, from analog models for hobbyists to high-accuracy digital units for commercial producers.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and safeguard your honey's quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Precision Honey Refractometer Instrument for Quality Assessment
- Premium Heat-Resistant Glass Honey Dipper
- HONESTBEE 3-Frame Manual Acrylic Honey Extractor
- electric honey extractor honey centrifuge 3 frame honey extractor stainless steel honey frame extractor
- 10L Stainless Steel Electric Honey Press Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the principle and importance of using a refractometer for honey moisture? Ensure Quality & Prevent Fermentation
- What is the function of a honey refractometer in beekeeping? Ensure Harvest Quality and Prevent Fermentation
- What is the primary function of a desktop refractometer? Ensure Honey Quality and Prevent Fermentation
- Why is a laboratory benchtop refractometer essential for honey? Secure Stability & Quality
- What role does a high-precision refractometer play in honey moisture analysis? Ensure Honey Quality & Stability



















