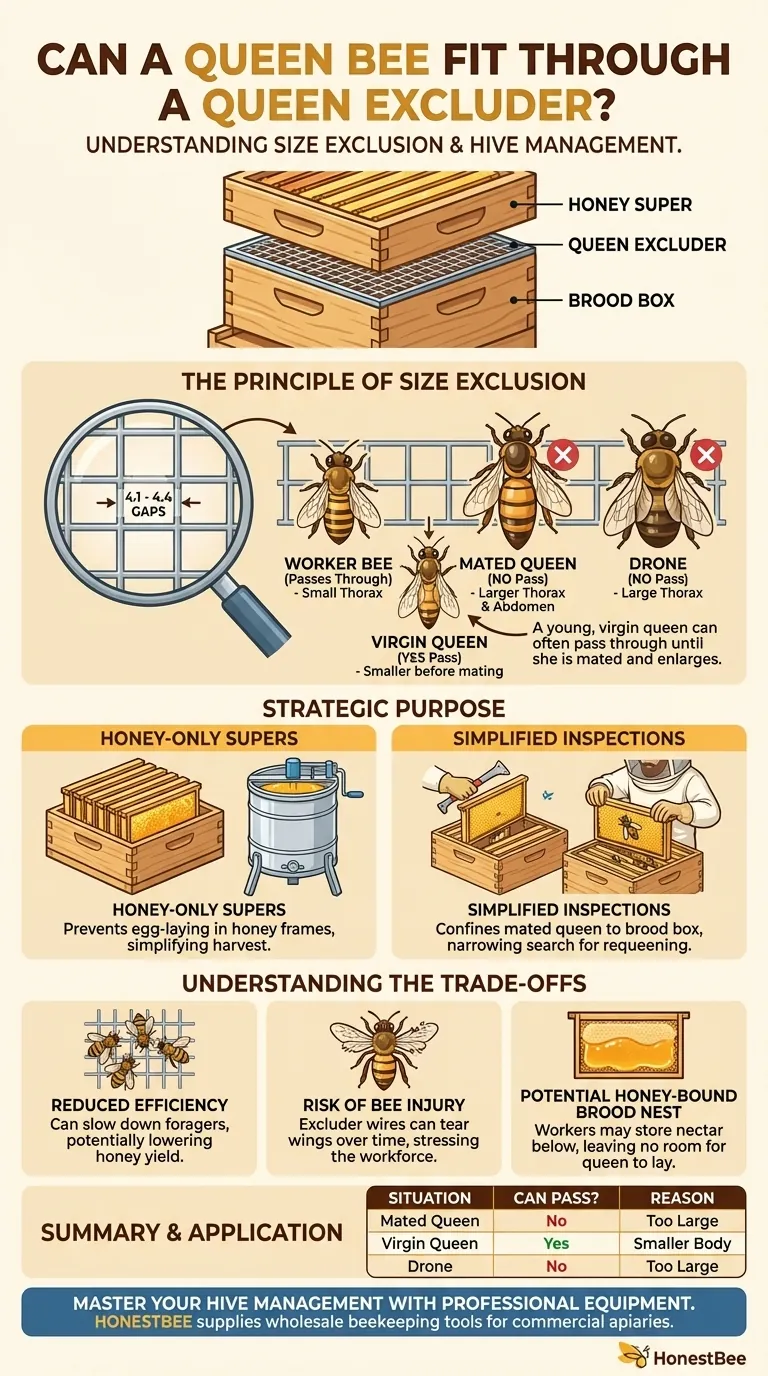
Under normal circumstances, a mature, mated queen bee cannot fit through a standard queen excluder. The device is engineered with gaps, typically between 4.1 and 4.4 millimeters, that are large enough for worker bees to pass through but too narrow for the larger thorax of a laying queen or a male drone.
A queen excluder is a reliable tool for controlling where a mated queen lays her eggs, but it is not infallible. Its effectiveness depends on the queen's developmental stage, and its use comes with distinct trade-offs for hive productivity.

How a Queen Excluder Functions
A queen excluder is a simple but effective tool based on a fundamental biological difference between the bees in a colony. Understanding its mechanics reveals its strengths and its limitations.
The Principle of Size Exclusion
The entire concept hinges on size. The thorax of a worker bee is small enough to squeeze through the 4.1 mm to 4.4 mm gaps in the excluder's grid.
In contrast, a healthy, mated queen bee has a significantly larger thorax and abdomen, making it physically impossible for her to pass through.
The Target: Queens and Drones
The excluder's primary goal is to confine the queen to the lower brood boxes, where she lays eggs and raises new bees.
It also effectively blocks the larger male drones from moving into the upper boxes, known as honey supers.
The Critical Exception: Virgin Queens
A young, virgin queen is a notable exception to this rule. Before she has been on her mating flights, her body is smaller and more slender.
In this state, she can often slip through the excluder. The device only becomes a reliable barrier after she is well-mated and her abdomen has enlarged for egg-laying.
The Strategic Purpose of an Excluder
Beekeepers use excluders not by default, but as a specific tool to achieve management goals. Its main purpose is to create a clear separation within the hive.
Ensuring "Honey-Only" Supers
The most common reason to use an excluder is to prevent the queen from laying eggs in the honey supers.
This ensures the frames in the upper boxes contain only honey, which vastly simplifies the harvesting and extraction process. Without an excluder, a beekeeper may find a mix of honey, pollen, and brood in the frames they intend to harvest.
Simplifying Hive Inspections
An excluder drastically narrows the search area when you need to find the queen. If you see fresh eggs and young larvae, you know she is in the box below the excluder.
This is particularly valuable when requeening a hive, as it allows you to confine and locate the old queen efficiently before introducing a new one.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While useful, a queen excluder is not a perfect solution and introduces potential downsides that every beekeeper must weigh.
Reduced Hive Efficiency
The grid, while passable for workers, can slow them down. Foraging bees returning with nectar may be more reluctant to cross the barrier, potentially creating a "traffic jam."
This can lead to a slight reduction in the speed at which honey is stored in the supers. Some beekeepers feel this friction can lead to a lower overall honey yield.
Risk of Bee Injury
The metal or plastic wires of the excluder can be abrasive. As worker bees repeatedly squeeze through, they can suffer from torn or frayed wings.
While this doesn't impact every bee, it is a cumulative stress on the colony's workforce over a season.
Potential for a "Honey-Bound" Brood Nest
If workers are hesitant to move nectar upstairs, they may begin storing it in the brood chamber instead.
This can create a "honey-bound" condition where the queen runs out of empty cells to lay eggs, slowing colony growth and potentially triggering a swarm.
How to Apply This to Your Hive
Your decision to use a queen excluder should be based on your specific beekeeping goals and management style.
- If your primary focus is honey purity: Use an excluder to keep brood out of your honey supers and simplify your extraction process.
- If your primary focus is simplified hive management: An excluder is an invaluable tool for quickly locating the queen or isolating her for requeening.
- If you are managing new or splitting colonies: Do not rely on an excluder to contain a virgin queen, as she can likely pass through it until she is mated.
- If your goal is minimizing hive interference: You may choose to forgo an excluder, accepting some brood in honey frames in exchange for completely unrestricted bee movement.
Ultimately, the queen excluder is a strategic tool, and understanding its limitations is the key to using it effectively.
Summary Table:
| Situation | Can the Queen Pass? | Key Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Mated Queen | No | Larger thorax & abdomen are too big for 4.1-4.4 mm gaps. |
| Virgin Queen | Yes | Smaller, slender body before mating flights. |
| Drone (Male Bee) | No | Thorax is also too large for the excluder gaps. |
Master Your Hive Management with the Right Equipment
Understanding the precise role of a queen excluder is key to maximizing your apiary's health and productivity. Whether you're a commercial beekeeper focused on pure honey harvests or a distributor supplying top-tier equipment, having reliable, correctly sized tools is non-negotiable.
HONESTBEE supplies professional-grade beekeeping supplies and equipment to commercial apiaries and distributors through our wholesale-focused operations. We provide the durable, effective tools you need to manage your hives with confidence.
Ready to optimize your operation? Let's discuss your specific needs.
Contact HONESTBEE today to explore our wholesale catalog and get the right equipment for your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Professional Plastic Queen Excluder for Modern Beekeeping
- High Performance Plastic Queen Excluder for Beekeeping and Apiary Management
- HONESTBEE 6 Frame Three Use Electric Honey Extractor for Beekeeping
- Wooden Queen Bee Excluder for Beekeeping
- electric honey extractor honey centrifuge 3 frame honey extractor stainless steel honey frame extractor
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of using queen excluders in research? Enhance Data Integrity and Hive Control
- How do queen excluders assist in the management of honey production? Optimize Your Harvest Purity and Efficiency
- What is the primary function of a Queen Excluder in honey purity? The Key to Commercial Grade Harvests
- Why is a queen excluder used in honey collection? Ensure Purity & Efficiency in Commercial Beekeeping
- How does a queen excluder facilitate the production of high-quality commercial honey? Ensure Purity & Efficiency



















