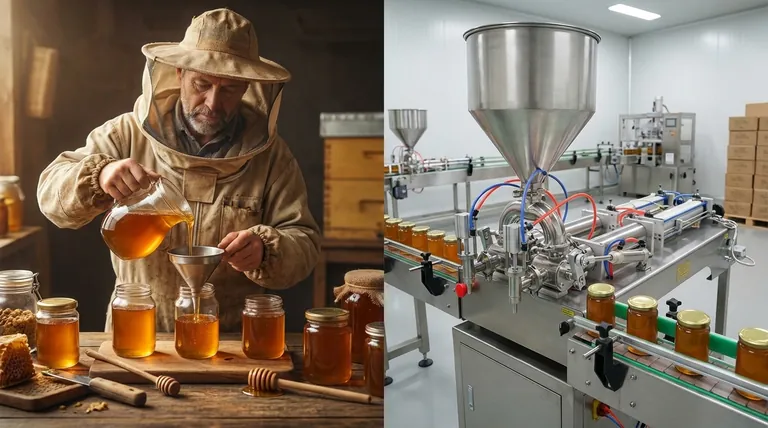
In short, automatic filling machines are built for scalability, while manual machines are not. An automatic system scales by maximizing machine output to handle higher production volumes with minimal additional labor. In contrast, scaling a manual process means directly adding more human labor, which introduces significant costs, inconsistencies, and logistical challenges as demand grows.
The core difference isn't just about speed; it's about the fundamental scaling model. Manual filling ties your production growth directly to rising labor costs, while automatic filling decouples them, allowing your output to increase far more efficiently once the initial investment is made.

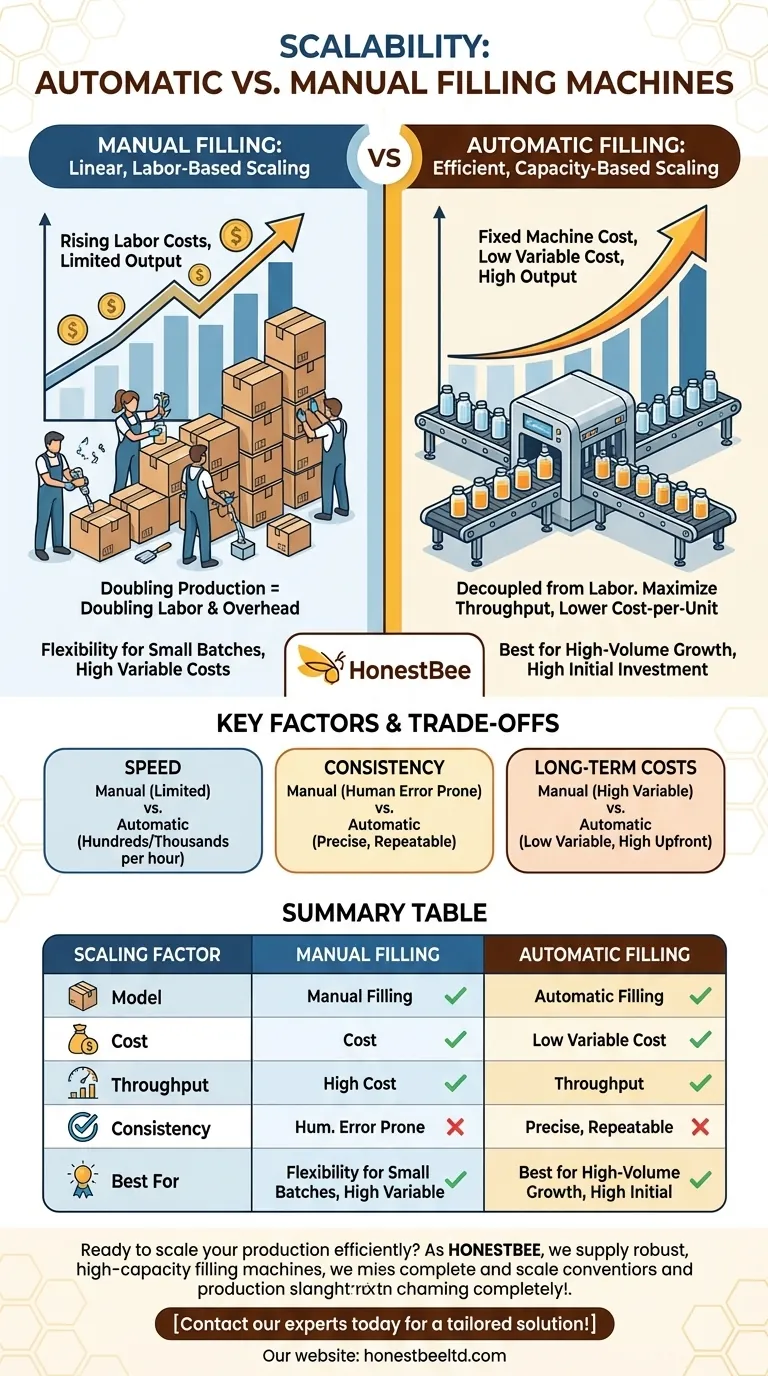
The Two Models of Production Scaling
To understand the difference in scalability, you must first see that manual and automatic systems operate on entirely different economic and operational principles. Your choice depends on whether you are optimizing for today's flexibility or tomorrow's volume.
How Manual Filling Scales: A Linear, Labor-Based Model
Manual filling is defined by its direct reliance on human operators. To increase output, you must add more people, more workstations, and more physical space.
This creates a linear scaling model. Doubling your production target often requires nearly doubling your labor costs and operational footprint. This approach quickly reaches a point of diminishing returns due to management overhead and human limitations.
How Automatic Filling Scales: An Efficient, Capacity-Based Model
Automatic filling machines represent a significant upfront capital investment, but they scale in a fundamentally more efficient way.
Once installed, increasing production is a matter of running the machine faster or for longer shifts. The cost per unit filled drops dramatically as volume increases because your primary costs (the machine itself) are fixed. This makes automatic fillers ideal for businesses anticipating or experiencing rapid growth.
Key Factors Influenced by Your Scaling Model
The scaling model you choose has direct consequences for speed, consistency, and long-term operational costs. It dictates the very structure of your production line.
Production Speed and Throughput
This is the most obvious difference. An automatic filler can process hundreds or even thousands of containers per hour, a rate a human operator can never sustainably match.
This high throughput is the engine of scalability. It allows you to meet sudden spikes in demand or large purchase orders without needing to frantically hire and train new staff.
Consistency and Precision
At scale, consistency is paramount. Automatic machines deliver a precise, repeatable fill volume for every single container, minimizing product waste and ensuring quality control.
Manual filling, by contrast, is subject to human error and fatigue. Variations between operators or even from the same operator over a long shift can lead to costly inconsistencies in a high-volume environment.
Long-Term Operational Costs
Manual filling has a low barrier to entry but high variable costs. Your largest ongoing expense is labor, which scales directly with production.
Automatic filling has a high initial cost but low variable costs. Beyond maintenance and energy, the cost to fill one more unit is negligible. This model becomes far more profitable at high volumes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a system is not just about a single metric; it's about balancing costs, flexibility, and your strategic goals. An objective analysis reveals clear advantages for each approach depending on the context.
The Upfront Cost of Automation
The primary barrier to automatic filling is the significant initial budget required. This capital expenditure can be prohibitive for startups or small businesses with limited funds.
The Flexibility of Manual Operations
Manual filling offers superior flexibility for small, diverse, or custom production runs. Changing between different products, container sizes, or formulas is simple and requires no complex machine recalibration.
The Break-Even Point
The decision to switch from manual to automatic hinges on a financial break-even analysis. You must determine the production volume at which the cumulative high labor costs of manual filling surpass the amortized cost of an automated system. Planning for this crossover is a critical strategic exercise for any growing business.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be a direct reflection of your business strategy and production reality. There is a right answer, but it depends entirely on your specific objectives.
- If your primary focus is low initial cost and high flexibility for small batches: A manual filling process is the most logical and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is preparing for growth and achieving the lowest cost-per-unit at high volume: Investing in an automatic filling machine is a necessary step to enable efficient scaling.
- If your primary focus is balancing budget constraints with a desire for precision and moderate growth: Consider the production volume where manual labor becomes unsustainable and begin planning your transition to an automated system.
Choosing the right filling method is a foundational decision that will shape your operational capacity and cost structure for years to come.
Summary Table:
| Scaling Factor | Manual Filling | Automatic Filling |
|---|---|---|
| Scaling Model | Linear, labor-based | Efficient, capacity-based |
| Cost Structure | High variable labor costs | High initial cost, low variable cost |
| Throughput | Limited by human speed | Hundreds to thousands of units per hour |
| Consistency | Prone to human error | Precise and repeatable |
| Best For | Small batches, high flexibility | High-volume growth, lowest cost-per-unit |
Ready to scale your production efficiently?
As HONESTBEE, we supply robust, high-capacity filling machines and beekeeping equipment to commercial apiaries and distributors. Our automatic filling solutions are designed to help you maximize throughput, ensure product consistency, and reduce long-term operational costs as you grow.
Let us help you build a scalable production line that meets your future demands. Contact our experts today for a tailored solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Pneumatic Double Nozzle Honey Filling Bottling Packaging Machine
- Automated Rotary Bottle Unscrambler for Honey Production Line
- Semi Automatic Round Bottle Labeling Machine
- Honey Concentrating Vacuum Heating Thickening Machine Dehumidifier for Honey
- Professional Thermostatic Conical Honey Melter
People Also Ask
- What are the main processes of a sachet filling and packing machine? Streamline Your Packaging Line
- What types of honey stick machines are available based on the style of the stick pack? Choose the Perfect Packaging Format
- What role does an industrial honey filling machine play in scaling commercial beekeeping? Boost Speed and Precision
- What are the main types of volumetric filling machines? Find the Right Filler for Your Product
- How do automated honey packaging and filling systems support diversified product lines? Enhance Your Brand Identity
- What is the role of honey filling and packaging systems? Automate Your Path to Premium Retail Markets
- What are the benefits of using automated honey filling machines? Boost Efficiency and Preserve Quality
- What role does automated filling and packaging machinery play in the commercialization of stingless bee products?



















