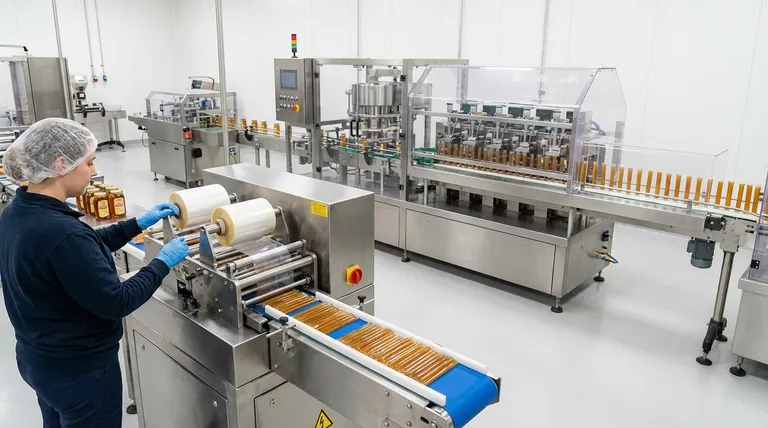
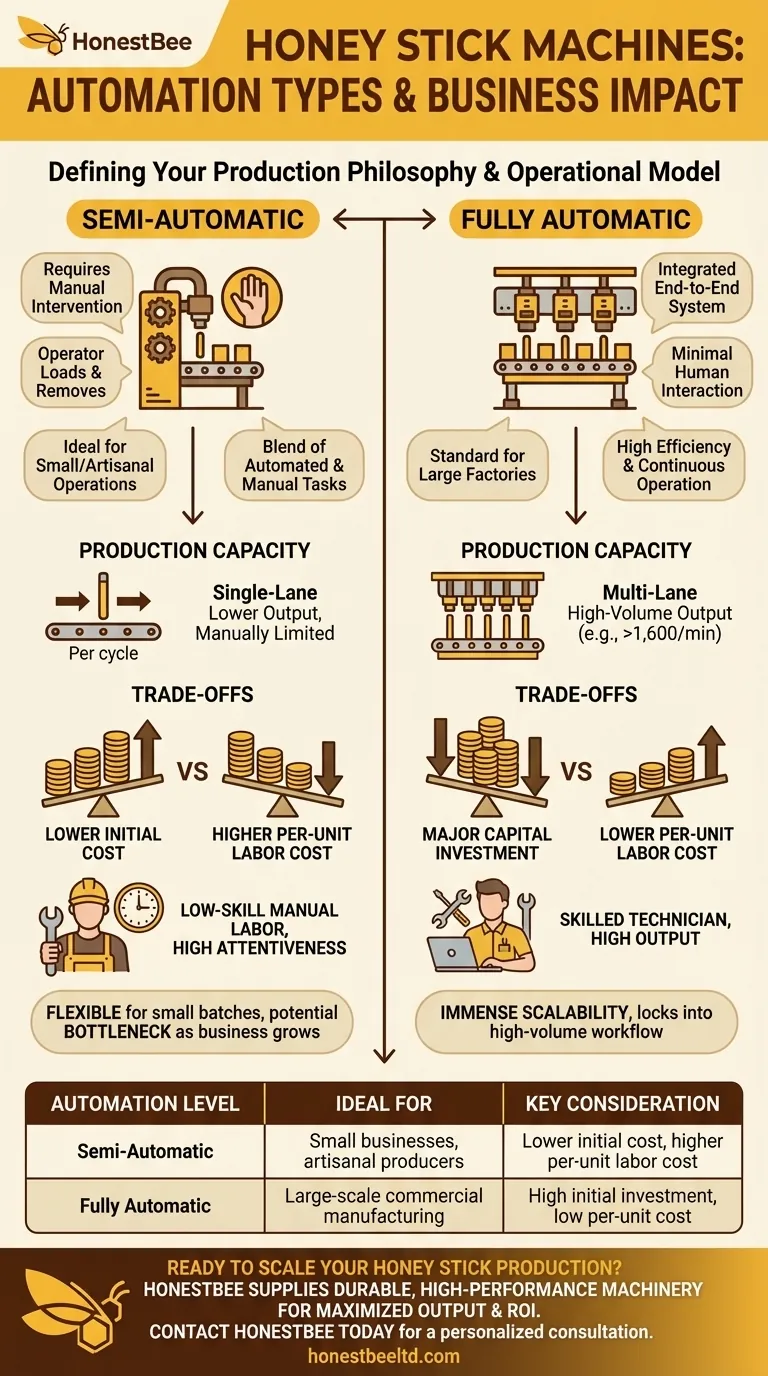
At its core, the classification of honey stick machines by automation comes down to two distinct categories: semi-automatic and fully automatic. A semi-automatic machine requires manual operator intervention for key steps like loading materials and removing finished products, while a fully automatic system handles the entire process from start to finish without assistance.
Your decision is not merely about choosing a machine, but about defining your production philosophy. The right choice aligns the equipment's operational model—and its inherent trade-offs in cost, speed, and labor—with the scale and goals of your business.

The Core Distinction: Operator Role
The fundamental difference between these two machine types is the role of the human operator during a production run. This distinction directly impacts workflow, output, and labor costs.
Understanding the Semi-Automatic Model
A semi-automatic honey stick machine blends automated processes with manual tasks. The machine will automatically handle the core functions of filling the packaging film with honey and sealing it.
However, an operator is required to initiate and complete the cycle. This makes it an ideal entry point for smaller operations.
The Operator's Responsibility
With a semi-automatic machine, the operator is an active part of the production line. Their primary duties include manually loading the roll of packaging film and removing the finished, sealed honey sticks from the machine.
This model is suitable for small to medium-sized businesses where production demand does not yet justify a fully hands-off system.
Understanding the Fully Automatic Model
A fully automatic machine is an integrated, end-to-end system designed for high-volume output with minimal human interaction. It manages every step of the process seamlessly.
Once programmed and supplied with materials, it will load the film, fill the sticks, seal them, and eject the finished products without any operator involvement during the run.
The Impact on Production
These systems are the standard in large factories and commercial operations. Their high efficiency and continuous operation make them far more cost-effective for large-scale production where maximizing sticks-per-minute is the primary goal.
How Production Capacity Shapes the Choice
Automation level is directly tied to a machine's potential output. This is often determined by its lane configuration, which dictates how many sticks are produced in a single cycle.
Single-Lane vs. Multi-Lane Design
Single-lane machines, as the name implies, produce one honey stick per cycle. They are mechanically simpler and offer a lower, more manageable output.
Multi-lane machines are engineered with multiple filling and sealing heads, allowing them to produce two, four, eight, or even more sticks simultaneously. Some high-end models can produce over 1,600 sticks per minute.
Linking Lanes to Automation
There is a strong correlation between lane count and automation. Semi-automatic machines are almost always single-lane designs, as their output is naturally limited by the need for manual intervention.
Conversely, fully automatic systems are typically multi-lane. The significant investment in full automation is only justified when paired with the high-volume output that multiple lanes provide.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a machine requires an objective look at the compromises involved with each option. Your decision will have long-term effects on cost, labor, and scalability.
Initial Cost vs. Per-Unit Cost
A semi-automatic machine has a significantly lower initial purchase price, making it more accessible for startups. However, its reliance on manual labor results in a higher per-unit production cost over time.
A fully automatic machine represents a major capital investment. This high upfront cost is offset by extremely high output and a much lower per-unit labor cost, delivering superior long-term profitability at scale.
Labor and Skill Requirements
Semi-automatic systems require consistent, low-skill manual labor to function. The primary bottleneck is the speed and attentiveness of the operator.
Fully automatic systems reduce the need for manual laborers but demand a more skilled technician for proper setup, calibration, and maintenance.
Flexibility and Scalability
The semi-automatic model offers flexibility for small batches and varied products. However, it can quickly become a production bottleneck as your business grows.
A fully automatic machine provides immense scalability. It locks you into a high-volume workflow but ensures you can meet market demand without being limited by production capacity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
Your ideal machine is the one that best serves your specific business goals. Use these guidelines to inform your decision.
- If your primary focus is a small business or artisanal production: A semi-automatic machine offers the lowest barrier to entry and provides sufficient capacity for this scale.
- If your primary focus is large-scale commercial manufacturing: A multi-lane, fully automatic machine is the only practical choice to achieve the necessary volume and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is balancing a startup budget with growth potential: Consider a high-quality single-lane fully automatic machine as a compromise, or plan to invest in a robust semi-automatic model with the clear goal of upgrading as sales increase.
Ultimately, this choice is an investment in your operational future, so select the tool that truly matches the job you need it to do.
Summary Table:
| Automation Level | Ideal For | Typical Output | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Semi-Automatic | Small businesses, artisanal producers | Lower, manual operation | Lower initial cost, higher per-unit labor cost |
| Fully Automatic | Large-scale commercial manufacturing | High-volume, continuous | High initial investment, low per-unit cost |
Ready to Scale Your Honey Stick Production?
Choosing the right automation level is critical for your apiary's efficiency and profitability. HONESTBEE supplies durable, high-performance honey stick machines to commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors.
We help you select the perfect equipment—from entry-level semi-automatic models to high-capacity fully automatic systems—to maximize your output and ROI.
Contact HONESTBEE today for a personalized consultation and wholesale pricing on the machinery that will power your growth.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Premium Heat-Resistant Glass Honey Dipper
- Modern Honeycomb Pattern Wooden Honey Dipper for Stirring and Drizzling
- Honey Concentrating and Filtering Dehumidifier Machine 2T Capacity for Honey
- 10L Stainless Steel Electric Honey Press Machine
- Electric 8 Frame Honey Spinner Extractor Equipment for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- What is the importance of professional sampling and measurement tools? Master Honey Yield Forecasting for Your Apiary
- Why is the accuracy of standardized measurement tools significant when using the PUCHTA method? Precision Brood Analysis
- Why should soap not be used to clean a honey dipper? Preserve Your Honey's Pure Taste
- How long to let honey settle before bottling? Achieve Crystal-Clear Honey for a Premium Product
- How does high moisture content affect honey's curative properties? It Spoils Them Completely



















