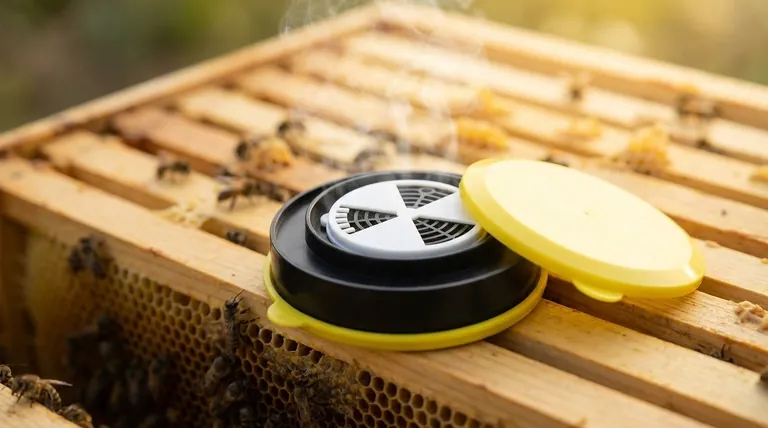
At its core, bee disinfestation equipment is a tool for controlling pests within a beehive, most notably the Varroa destructor mite. This equipment typically uses a non-chemical method—precisely controlled heat—to kill parasites that have a lower heat tolerance than the honey bees and their brood. It is an intervention used to restore the health of a colony suffering from a severe parasitic load.
The central challenge in modern beekeeping is managing the devastating Varroa destructor mite. Bee disinfestation equipment, specifically hyperthermic treatment devices, offers a chemical-free solution, but its effectiveness hinges on precise application to avoid harming the bees it's meant to save.

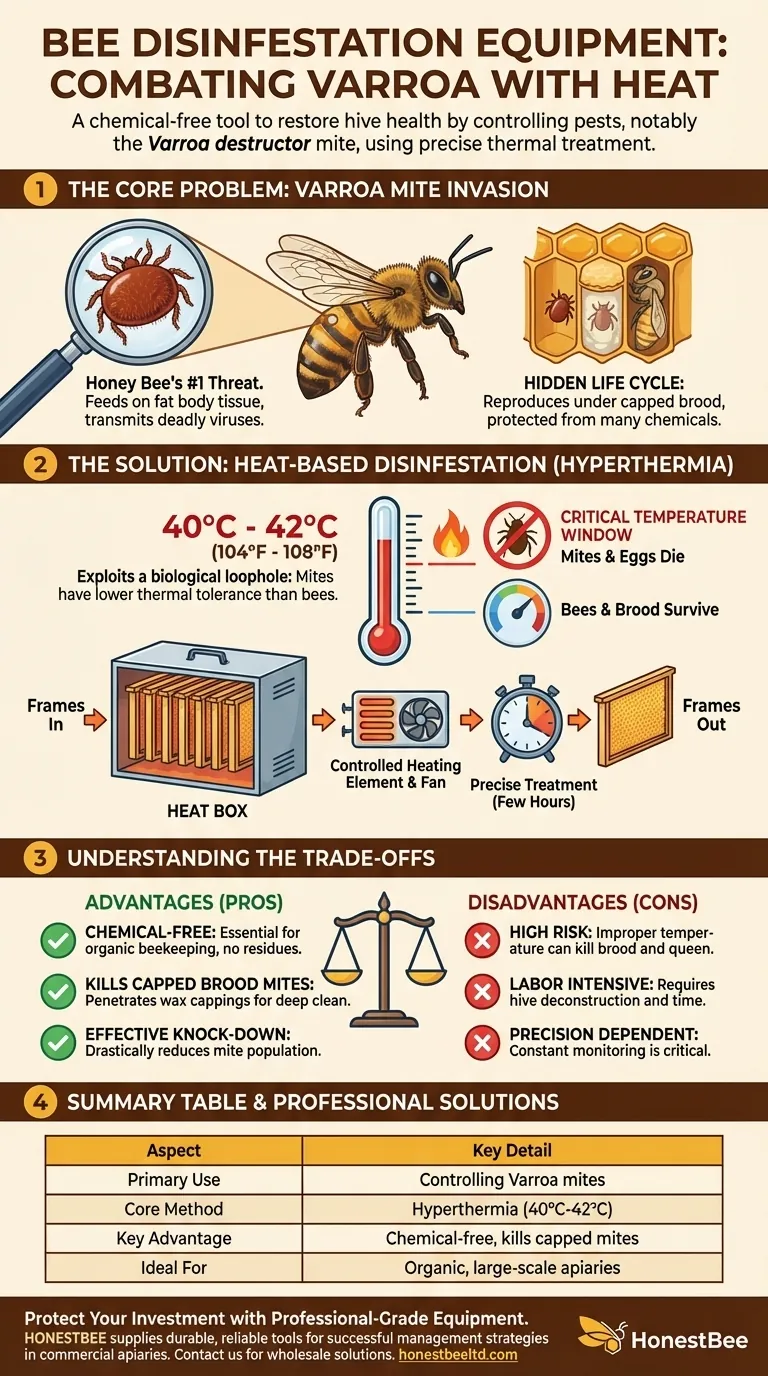
The Core Problem: The Varroa Mite Invasion
To understand the equipment, you must first understand the problem it solves. The Varroa destructor is the single greatest threat to honey bee health worldwide.
Why Varroa is a Devastating Threat
Varroa mites are external parasites that attach to adult bees and developing brood. They feed on the bee's fat body tissue, an organ crucial for immune function, detoxification, and energy storage.
This feeding action weakens the bee and, more critically, transmits a host of deadly viruses. An unmanaged Varroa infestation will almost always lead to the death of a honey bee colony.
The Mite's Hidden Life Cycle
The most destructive phase of the Varroa life cycle occurs out of sight. The female mite enters a brood cell just before it is capped with wax. Inside, she lays eggs and reproduces, with her offspring feeding on the developing bee pupa.
Because they are protected under the brood capping, these mites are shielded from many chemical treatments that only affect mites on adult bees.
How Heat-Based Disinfestation Works (Hyperthermia)
Hyperthermic or "heat" treatment is the primary method employed by modern bee disinfestation equipment. It works by exploiting a biological loophole.
The Principle of Thermal Tolerance
Honey bees and Varroa mites have different tolerances to high temperatures. Varroa mites and their eggs begin to die when exposed to temperatures between 40°C and 42°C (104°F and 108°F).
Adult bees and, to a slightly lesser extent, bee brood can survive these temperatures for the limited duration of the treatment. The equipment is designed to hold the hive components within this narrow thermal window.
The "Heat Box" Method
The most common device is an insulated chamber or "heat box." The beekeeper temporarily removes frames of bees and brood from the hive and places them inside the unit.
A controlled heating element, often paired with a convection fan for even air distribution, slowly raises the internal temperature to the target zone. The treatment typically lasts for a few hours before the frames are returned to the hive.
The Critical Temperature Window
Success is entirely dependent on precision. If the temperature is too low, the mites will survive. If the temperature is too high or held for too long, it can kill the bee brood, sterilize drones, and even kill the queen.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Heat treatment is a powerful but demanding technique. It is not a simple replacement for other methods and requires a clear understanding of its pros and cons.
Advantage: Chemical-Free Treatment
This is the primary appeal. Hyperthermia allows beekeepers to control mites without introducing any chemicals (miticides) into the hive. This is essential for certified organic beekeeping and for beekeepers who want to avoid contaminating honey and wax.
Advantage: Kills Mites in Capped Brood
Unlike many "soft" chemical treatments, heat penetrates the wax cappings. This allows it to kill the mites where they reproduce, drastically reducing the hive's overall mite population in a single treatment.
Disadvantage: High Risk if Done Improperly
The risk of "cooking" your bees is real. An equipment malfunction or operator error can swiftly destroy your brood and cripple the colony. It is a high-stakes procedure that requires careful monitoring.
Disadvantage: Labor and Time Intensive
The process is not fast. It involves deconstructing the hive, treating the frames for several hours, and then reassembling everything. For beekeepers with many hives, this can be a significant logistical challenge compared to faster chemical applications.
Is Heat Treatment Right for Your Apiary?
Deciding to use hyperthermic disinfestation equipment is a strategic choice based on your beekeeping philosophy, risk tolerance, and operational scale.
- If your primary focus is organic or treatment-free beekeeping: Heat treatment is a powerful tool to consider, as it provides a highly effective mite knock-down without any chemical inputs.
- If your primary focus is efficiency and low labor: Traditional, approved miticides may be a more practical choice, especially for larger apiaries where time is a major constraint.
- If you are a new beekeeper: It is critical to first master basic hive management and simpler mite monitoring techniques before attempting high-risk procedures like hyperthermia.
Ultimately, understanding the principles behind the equipment is the first step toward making a responsible choice for the long-term health of your hives.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | Controlling Varroa destructor mites and other pests. |
| Core Method | Hyperthermia (heat treatment) within a 40°C - 42°C (104°F - 108°F) window. |
| Key Advantage | Chemical-free, effective against mites in capped brood. |
| Key Consideration | High risk if done improperly; labor and time intensive. |
| Ideal For | Organic beekeepers, those seeking to avoid chemical residues. |
Protect Your Investment with Professional-Grade Equipment
For commercial apiaries and distributors, effective Varroa mite control isn't just an option—it's essential for protecting your colonies and your bottom line. HONESTBEE supplies the durable, reliable beekeeping supplies and equipment you need to implement successful management strategies.
We understand the challenges of large-scale operations. Let us equip you with the tools for healthier, more productive hives.
Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss wholesale solutions for your apiary or distribution business.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Adjustable Formic and Acetic Acid Dispenser for Bee Mite Treatment
- Beehive Handle and Frame Rest Cutting Machine: Your Specialized Hive Machine
- Full Set Beekeeping Electronic Bee Venom Collector Machine Device for Bee Venom Collecting
- Varroa Easy Check Mite Tester Kit Counter Alcohol Wash Jar
- HONESTBEE Heavy Duty All Metal Frame Wire Crimper Tool
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-precision larva and pupa extraction process required when analyzing Varroa mite reproductive success?
- What activities do bees perform in the brood box and supers? Maximize Your Apiary Efficiency
- Why does organic beekeeping emphasize non-synthetic chemical treatments? Protect Your Hive Purity & Prevent Resistance
- What is the application method for cardboard-based Varroa mite treatments? Maximize Hive Health with Correct Placement
- What are the common technical treatments used for Varroa mite control in the spring? Optimize Colony Health Today



















