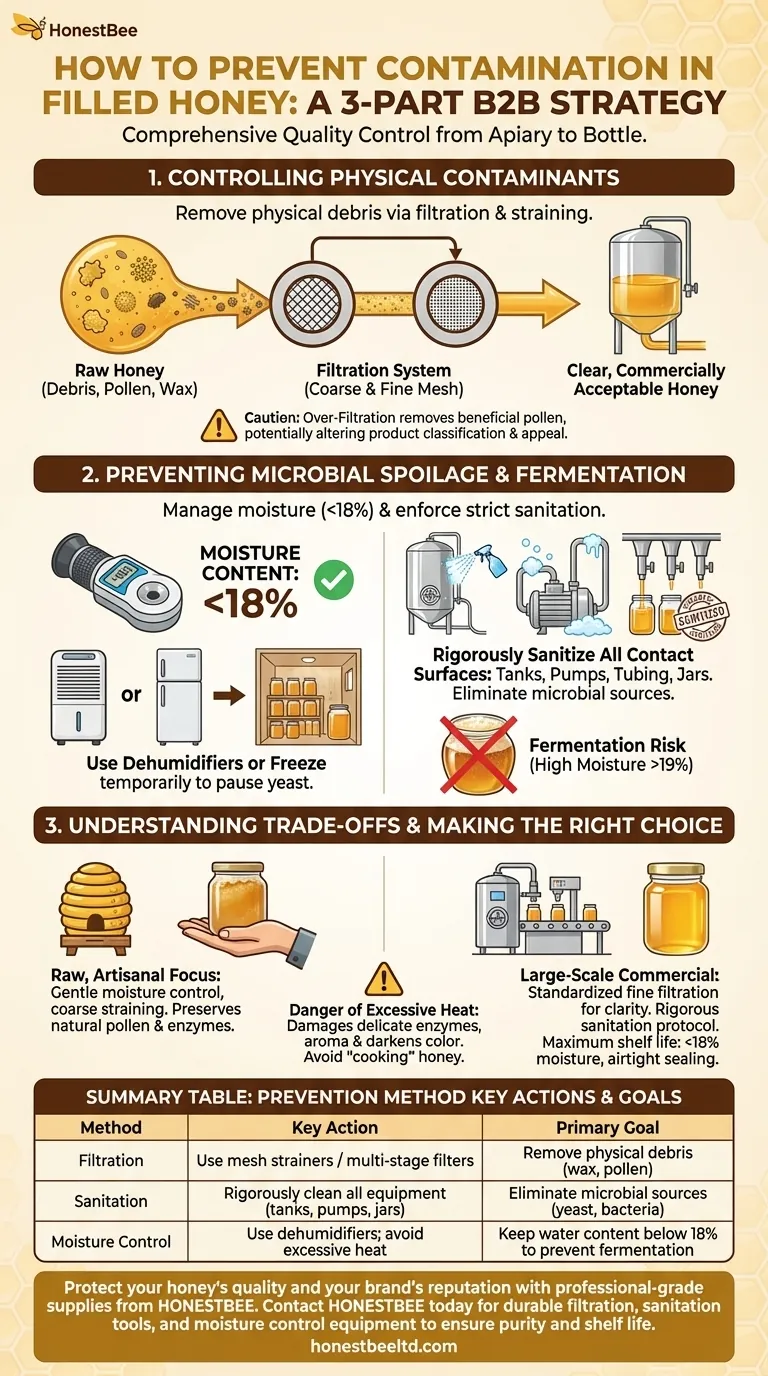
To prevent contamination in filled honey, you must implement a three-part strategy: use filtration to remove physical debris, enforce strict sanitation of all equipment, and control the honey's moisture content to prevent fermentation. These steps work together to protect the honey from physical, microbial, and chemical degradation from the moment it leaves the hive to when it's sealed in a jar.
Preventing honey contamination is not a single action but a comprehensive quality control process. It requires protecting honey's natural purity by systematically eliminating external physical impurities and managing its internal chemistry, primarily its water content, to inhibit microbial growth.

Controlling Physical Contaminants
The most visible form of contamination comes from physical particles left over from the hive and the extraction process. Proper filtration is your first line of defense.
The Role of Straining and Filtration
Raw honey naturally contains particles like bits of beeswax, pollen grains, and other hive debris. A filtration or straining system is essential to remove these impurities, ensuring a clear and commercially acceptable final product.
This process is a non-negotiable step for producing pure, high-quality honey that meets consumer expectations.
Implementing an Effective Filtration System
Filtration can range from simple mesh strainers to more complex, multi-stage systems. The goal is to remove unwanted particulates without stripping the honey of its natural characteristics. Coarse filters remove larger debris, while finer filters can remove smaller particles.
Preventing Microbial Spoilage
The most significant threat to honey's shelf life is not bacteria, but a specific type of spoilage caused by yeast: fermentation. This is almost entirely a function of moisture.
The Threat of High Moisture Content
Honey is naturally antimicrobial due to its low water activity and acidity. However, if the moisture content rises above approximately 18-19%, naturally occurring osmophilic (sugar-tolerant) yeasts can activate and begin to ferment the sugars.
This fermentation spoils the honey, giving it a sour, alcoholic taste and a frothy appearance. The root cause is almost always honey that was harvested too early or stored in a humid environment.
Techniques for Moisture Management
You can actively manage moisture content to prevent fermentation. Using a dehumidifier in your processing and storage rooms is highly effective at drawing excess water out of the air and the honey itself.
For temporary measures, freezing high-moisture honey immediately after harvest can pause all yeast activity until you can properly reduce its moisture content.
The Critical Importance of Sanitation
Even if moisture levels are perfect, contamination can be introduced from external sources. All surfaces that come into contact with the honey must be rigorously cleaned and sanitized.
This includes tanks, pumps, tubing, filling nozzles, and the final jars. Unclean surfaces can introduce yeast, bacteria, and off-flavors that will ruin the product. A documented sanitation protocol is the mark of a professional operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Achieving purity involves making decisions that can affect the final product's character. Understanding these trade-offs is key to producing the exact type of honey you intend.
The Risk of Over-Filtration
While filtration cleans the honey, ultra-fine filtration can remove beneficial pollen grains. In many regions, a honey's floral source and classification are verified by its pollen content. Removing it can technically render it "not honey" by some standards and diminishes its artisanal appeal.
The Danger of Excessive Heat
Some producers use heat to lower moisture content or decrease viscosity for easier bottling. While gentle warming (using a bucket heater, for example) is acceptable, excessive heat is damaging.
High temperatures can destroy the delicate enzymes and aromatic compounds that make honey unique, and can also darken its color. Never "cook" your honey to dry it out.
Making the Right Choice for Your Product
Your approach to contamination prevention should align with your final product goals.
- If your primary focus is raw, artisanal honey: Prioritize gentle moisture control with dehumidifiers and use only coarse straining to preserve natural pollen and enzymes.
- If your primary focus is large-scale commercial production: Implement standardized fine filtration for clarity and consistency, and enforce a rigorous, documented sanitation schedule for all equipment.
- If your primary focus is maximum shelf life: Verify that the final moisture content is below 18% using a honey refractometer and ensure all containers are sanitized and sealed airtight.
Ultimately, protecting your honey's integrity is a continuous process of vigilance from the apiary to the bottle.
Summary Table:
| Prevention Method | Key Action | Primary Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Filtration | Use mesh strainers or multi-stage filters | Remove physical debris (wax, pollen) |
| Sanitation | Rigorously clean all equipment (tanks, pumps, jars) | Eliminate microbial sources (yeast, bacteria) |
| Moisture Control | Use dehumidifiers; avoid excessive heat | Keep water content below 18% to prevent fermentation |
Protect your honey's quality and your brand's reputation with professional-grade supplies from HONESTBEE.
Whether you're a commercial apiary focused on large-scale production or a distributor requiring reliable equipment, our wholesale-focused operations provide the durable filtration systems, sanitation tools, and moisture control equipment you need to implement a foolproof contamination prevention strategy.
Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss your specific needs and ensure every jar of honey you produce meets the highest standards of purity and shelf life.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Honey Concentrating Vacuum Heating Thickening Machine Dehumidifier for Honey
- Professional Thermostatic Conical Honey Melter
- Electric 8 Frame Honey Spinner Extractor Equipment for Beekeeping
- High Quality Honey Dehumidifier Dryer Thickening Machine for Beekeeping
- Inverted Squeezable Honey Jar with No Drip Flip Top Cap for Easy Pouring
People Also Ask
- In what ways do automatic filling machines impact labor costs? Cut Expenses and Boost Efficiency
- How does the physicochemical analysis of honey inform filling processes? Optimize Your Commercial Production Line
- Why is customer support important when purchasing a honey filling machine? Ensure Maximum Uptime for Your Bottling Line
- How do automatic honey filling machines contribute to the value addition of commercial honey? Boost Brand Consistency
- What sizes of jars and containers can the filling machine accommodate? Versatile Solutions for Every Packaging Size
- What are the primary benefits and features of a honey filling machine? Boost Efficiency with Automated Precision
- How does a packaging machine work? A Guide to Form-Fill-Seal vs. Premade Pouch Systems
- How does production volume affect the selection of a honey packaging machine? Choose the Right Automation Level



















