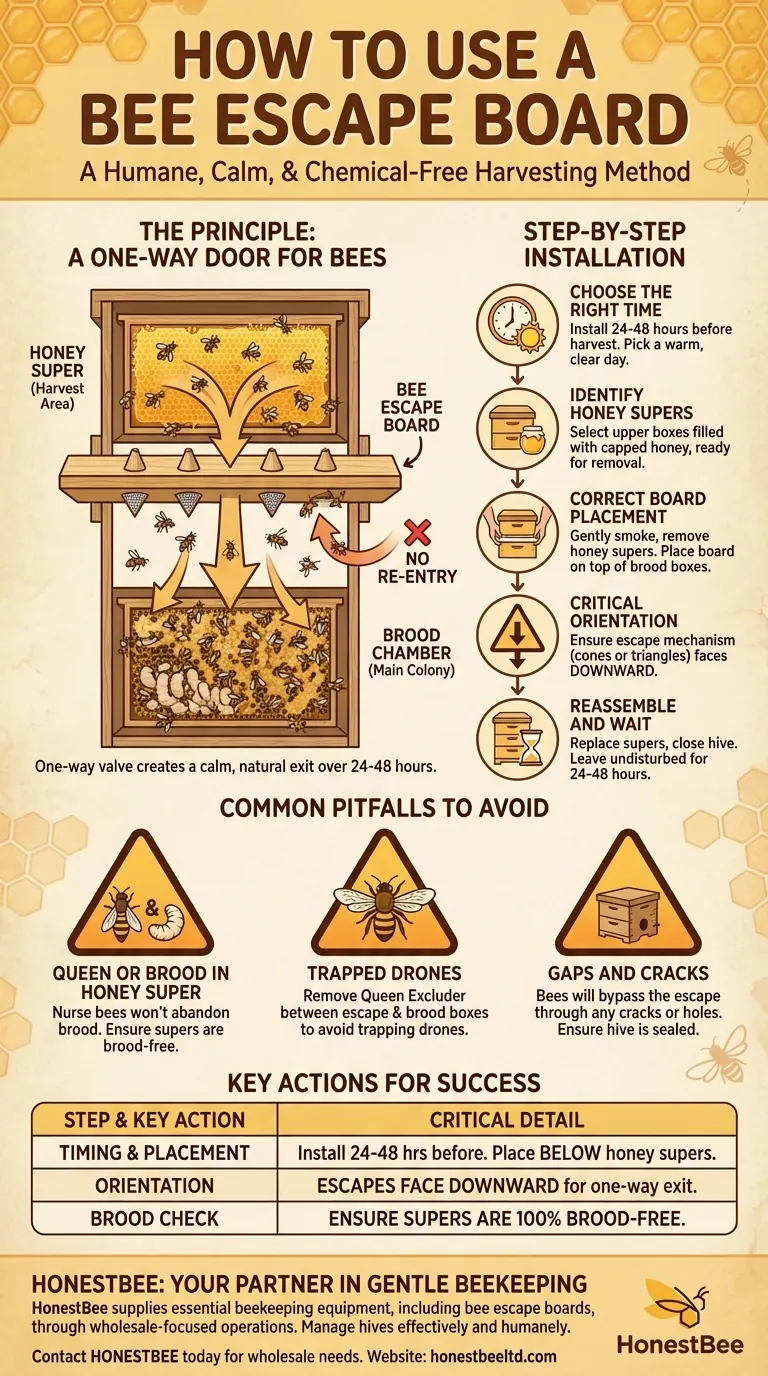
To use a bee escape board, you place it directly beneath the honey supers you intend to harvest and above the lower hive bodies or brood boxes. The board must be oriented correctly, with the side featuring the screened triangle or cone escapes facing downward, into the main part of the hive. This allows bees to leave the honey super but prevents them from re-entering.
The core principle of a bee escape board is to create a one-way exit for bees. This simple device humanely clears the honey supers over 24-48 hours, enabling a calm, chemical-free harvest without the need for excessive smoke.

The Principle: How a Bee Escape Works
A One-Way Door for Bees
A bee escape board is essentially an inner cover fitted with one or more one-way valves. Bees in the upper honey supers can easily navigate down through these escapes to join the main colony below.
However, the design of the escapes makes it nearly impossible for them to find their way back up into the supers.
The Goal: A Bee-Free Honey Super
By installing the board and waiting a day or two, the beekeeper allows the natural movement of the colony to do the work. The honey supers become progressively empty of bees, leaving only the honey ready for extraction.
A Calm Alternative
This method is a gentle alternative to using a bee brush, fume board with chemicals, or a bee blower. It significantly reduces stress on the colony and the beekeeper, leading to a much calmer harvesting experience.
Step-by-Step Installation
Choose the Right Time
Plan to install the bee escape board 24 to 48 hours before you intend to harvest the honey. Choose a warm, clear day when the bees are actively flying.
Identify the Honey Supers
First, identify the upper boxes (supers) filled with capped honey that you are ready to remove from the hive.
Correct Board Placement
Gently smoke the hive and remove the honey supers you plan to harvest, setting them aside temporarily. Place the bee escape board directly on top of the brood boxes or the lower supers that will remain with the hive.
Critical Orientation: Escapes Down
Ensure the side of the board with the escape mechanism (often a triangle-shaped screen or plastic cones) is facing downward. This orientation is critical for the one-way system to function correctly.
Reassemble and Wait
Place the honey supers you intend to harvest back on top of the bee escape board. Close up the hive and leave it undisturbed for 24 to 48 hours. When you return, the supers should be nearly free of bees.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Forgetting to Remove a Queen Excluder
If a queen excluder is left between the bee escape and the brood boxes below it, any drones in the honey super will become trapped, as they are too large to pass through either device. Always remove excluders from this area when using an escape board.
Queen or Brood in the Honey Super
The system will fail if the queen or any frames of brood (eggs and larvae) are present in the honey supers above the escape board. The nurse bees will not abandon the brood, defeating the purpose of the board. Always ensure your honey supers are free of brood before installation.
Gaps and Cracks in Equipment
Bees are resourceful. If there are any other cracks, holes, or entrances in the honey supers above the board, bees may use those to exit and re-enter, bypassing the escape mechanism entirely. Ensure your hive equipment is well-maintained and sealed.
Specific Hive Adjustments
For some hive types, like a Warre hive, you may need to ensure there is a complete seal around the board. This might involve modifying a separator canvas or creating a dedicated mounting board to prevent bees from simply walking around the escape.
Key Considerations for a Successful Harvest
- If your primary focus is a calm, stress-free harvest: Double-check that the board's escape mechanism is facing down and give the bees a full 48 hours to clear out.
- If your primary focus is efficiency: Before installing the board, ensure your honey supers are 100% free of brood, as this is the most common reason for failure.
- If your primary focus is preventing problems: Make sure your hive boxes are in good condition with no extra cracks or holes that could serve as an alternative entrance for the bees.
Using a bee escape board is a simple, effective technique that aligns with the principles of gentle beekeeping.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Critical Detail |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Timing | Install 24-48 hours before harvest. | Choose a warm, clear day. |
| 2. Placement | Place beneath honey supers, above brood boxes. | Remove any queen excluder first. |
| 3. Orientation | Ensure escape mechanism faces downward. | This creates the one-way exit. |
| 4. Wait | Leave hive undisturbed for 24-48 hours. | Supers will clear of bees naturally. |
| Pitfall | How to Avoid Failure | |
| Brood in supers | Ensure honey supers are 100% free of brood. | Nurse bees will not abandon brood. |
| Gaps in equipment | Check for and seal any cracks or holes in supers. | Prevents bees from bypassing the escape. |
Ready for a Calmer, More Efficient Harvest?
A bee escape board is a cornerstone of gentle, effective hive management. For commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors, having access to reliable, high-quality supplies is key to operational success.
HONESTBEE supplies the essential beekeeping equipment you need, including bee escape boards, through our wholesale-focused operations. We help you manage your hives more effectively and humanely.
Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss your wholesale supply needs and discover how our products can support your beekeeping success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Professional Durable Two-Piece Plastic Bee Escape
- Slatted Porter Style Bee Escape for Rapid Hive Clearing
- Circular Labyrinth Bee Escape for Efficient Hive Management
- HONESTBEE Multi Exit Plastic Bee Escape Board for Efficient Honey Harvesting
- HONESTBEE Wooden Bee Escape Board with Triangle Mesh Design for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- How does an escape board function as a bee removal tool during honey harvesting? Simplify Your Harvest Workflow
- What is the purpose of a bee escape board? A Gentle, Chemical-Free Way to Harvest Honey
- How does an escape board work? A Gentle, Bee-Friendly Method for Harvesting Honey
- How is an escape board constructed? A Guide to Gentle, Chemical-Free Honey Harvesting
- How can bees be cleared off honey supers in a Langstroth hive? Use a Gentle Bee Escape



















