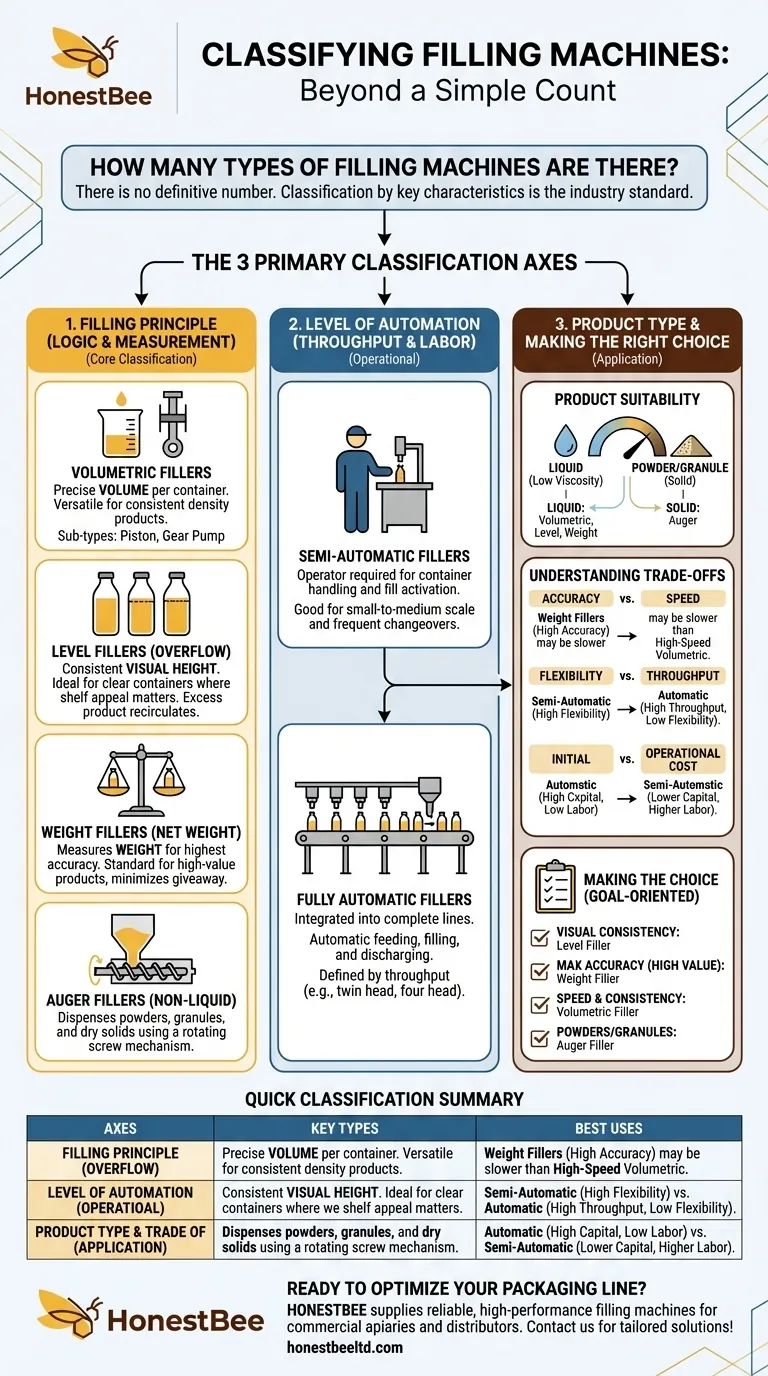
There is no definitive number of filling machine types. Instead of a simple count, the industry classifies equipment based on several key characteristics, which often overlap. Understanding these categories is far more useful than searching for a specific number.
The most effective way to understand filling machines is not by counting them, but by classifying them along three primary axes: their filling principle, their level of automation, and the type of product they are designed to handle.

The Core Classification: Filling Principle
The most fundamental way to categorize a filling machine is by the logic it uses to measure the product. This technical principle dictates the machine's accuracy, speed, and suitability for different products.
Volumetric Fillers
Volumetric fillers dispense a precise volume of product into each container. They are highly versatile and common.
These machines work by trapping a specific volume of product in a chamber (like a cylinder or a gear pump) and then discharging it.
They are ideal for products with a consistent density, as the filled volume will always be the same. The reference to volumetric linear filling machines falls into this category.
Level Fillers
Level fillers, also known as overflow fillers, fill each container to the same visual height.
This method is perfect for transparent containers where a consistent appearance on the retail shelf is critical. Any excess product is returned to the supply tank.
While the visual fill level is identical, the actual volume may vary slightly if the containers themselves have minor inconsistencies.
Weight Fillers
Net weight fillers measure the weight of the product as it enters the container, providing the highest level of accuracy.
These systems use a scale or load cell to ensure the precise amount of product is dispensed, regardless of temperature, viscosity, or density changes.
They are the standard for high-value products where minimizing waste and ensuring precise dosage is paramount. The "electronic liquid filling machines" mentioned in the references often use this principle.
Other Principles
For non-liquid products, other principles are used. The most common is the auger filler, which uses a rotating screw to dispense powders, granules, and other dry solids.
A Practical Distinction: Level of Automation
The next layer of classification is operational. This determines the machine's throughput, labor requirements, and integration into a production line.
Semi-Automatic Fillers
On a semi-automatic machine, an operator is required to place the containers, activate the fill cycle, and then remove the filled containers.
These machines offer a significant upgrade in speed and consistency over manual filling and are ideal for small-to-medium scale production or lines with frequent product changeovers.
Fully Automatic Fillers
Fully automatic fillers are integrated into a complete packaging line with conveyors. They automatically handle container feeding, filling, and discharging without operator intervention.
Machines in this category are defined by their throughput. Designations like twin head, four head, or eight head simply refer to the number of nozzles filling containers simultaneously, directly impacting the line's overall speed.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a filling machine involves balancing competing priorities. There is no single "best" type; there is only the best fit for a specific application.
Accuracy vs. Speed
Weight fillers offer the highest accuracy but can sometimes be slower than high-speed rotary volumetric fillers. The value of the product being lost in giveaways must be weighed against the need for maximum throughput.
Flexibility vs. Throughput
Semi-automatic systems are highly flexible and can often handle a wide range of container sizes and products with minimal changeover time. In contrast, a high-speed automatic line is optimized for one container and product, offering massive throughput at the cost of flexibility.
Initial Cost vs. Operational Cost
The capital investment for a fully automatic line is substantial. However, it dramatically reduces long-term labor costs and can reduce product waste through higher accuracy, providing a return on investment over time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your product and business objectives will determine the correct technology.
- If your primary focus is visual consistency in clear bottles: A level filler is the most practical and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is maximizing accuracy for a high-value liquid: A net weight filler is the industry standard for minimizing product giveaway.
- If your primary focus is high-speed production of a consistent liquid: A volumetric filler (like a piston or pump filler) provides an excellent balance of speed and accuracy.
- If your primary focus is handling powders, spices, or granules: An auger filler is the specialized tool designed for that job.
Ultimately, selecting the right machine begins with a clear understanding of your product, your container, and your operational goals.
Summary Table:
| Classification | Key Types | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Filling Principle | Volumetric, Level, Weight, Auger | Liquids, powders, high-value products |
| Automation Level | Semi-Automatic, Fully Automatic | Small batches, high-speed production |
| Product Type | Liquid, Powder, Granule | Based on viscosity and packaging needs |
Ready to optimize your packaging line? HONESTBEE specializes in supplying durable, high-performance filling machines and beekeeping equipment to commercial apiaries and distributors. Our wholesale-focused operations ensure you get reliable equipment that boosts efficiency and accuracy. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs and receive a tailored solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Pneumatic Double Nozzle Honey Filling Bottling Packaging Machine
- Pneumatic Paste Filling Machine Bottling Packaging Machine Single Nozzle
- Semi-Automatic Pneumatic Bottle Capping Machine by HONESTBEE
- Professional Durable Customizable Blister Packing Machine
- Semi Automatic Round Bottle Labeling Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the functional benefits of using automated honey filling machines? Optimize Your Honey Supply Chain Efficiency
- How does the implementation of high-precision honey filling and sealing machinery affect honey product value?
- What tools are used to measure honey viscosity during the filling process? Optimize Your Honey Filling Line
- Why is advanced Honey Packaging Technology essential for commercial honey? Secure Quality and Brand Value
- What are the features and uses of a Honey Filling Machine? Optimize Your Apiary Production Efficiency
- How do automated honey filling lines ensure commercial value? Boost Your Honey Brand's Competitiveness and ROI
- How does high-precision filling equipment ensure quality and efficiency? Optimize Your Honey Packaging Performance
- What competitive advantages do automated filling and packaging machines provide in honey processing? Scale Your Business


















