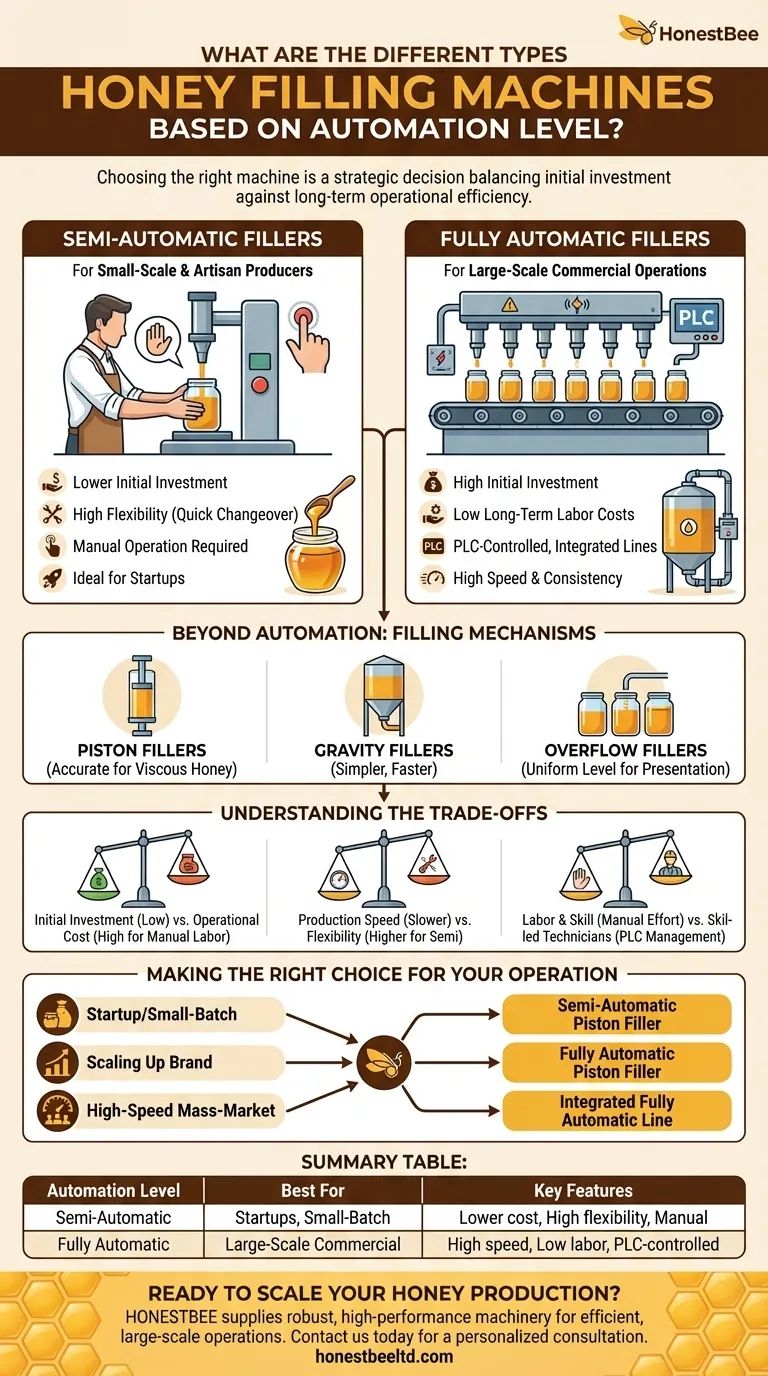
Choosing the right honey filling machine is a critical decision that hinges on your production scale. The primary distinction is between semi-automatic and fully automatic systems, where the core difference lies in the level of manual labor required to operate the equipment and the overall output capacity.
Your choice isn't just about automation; it's a strategic decision balancing your initial investment against long-term operational efficiency. The right machine aligns with your current production volume while providing a clear path for future growth.

The Two Levels of Automation
The most fundamental way to classify honey filling machines is by their degree of automation. This determines the machine's speed, cost, and labor requirements.
Semi-Automatic Fillers: For Small-Scale & Artisan Producers
Semi-automatic machines require an operator to manually place containers under the fill head and then activate the filling cycle. They may also need to move the filled containers to a capping station by hand.
These systems are the entry point for most small businesses and artisan producers. They offer a significant step up from manual filling without the high cost of a fully automated line.
Their main advantage is a lower initial investment and greater flexibility for handling various container sizes and shapes with minimal changeover.
Fully Automatic Fillers: For Large-Scale Commercial Operations
Fully automatic systems are integrated production lines that require minimal human intervention. Conveyors move containers into place, sensors trigger the fill, and the filled containers are automatically moved to the next station, such as capping and labeling.
These machines are designed for high-volume, continuous production. They use advanced PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) systems to manage the entire process with high speed and precision.
While they require a significant upfront investment, they dramatically reduce long-term labor costs and ensure a highly consistent and efficient output for large-scale operations.
Beyond Automation: Understanding the Filling Mechanism
Just as important as the automation level is the mechanism the machine uses to dispense the honey. This choice is driven by honey's viscosity and your accuracy requirements. Both semi-automatic and fully automatic machines can utilize these mechanisms.
Piston Fillers: The Standard for Viscous Honey
Piston fillers are the most common and effective choice for honey. They use a cylinder and piston to draw in a precise volume of product and then dispense it into the container.
This method is extremely accurate and repeatable, making it ideal for a thick, viscous product like honey where consistent fill volumes are crucial for profitability and labeling compliance.
Gravity and Overflow Fillers: For Speed and Presentation
Gravity fillers rely on the weight of the honey in a holding tank above the filling nozzles. This is a simpler, often faster method but can be less accurate for very thick products.
Overflow fillers fill each container to the exact same level, regardless of minor variations in container volume. This creates a uniform, visually appealing product line, which is important for retail presentation on a shelf.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a machine involves balancing competing priorities. Being aware of these trade-offs is key to making an informed decision.
Initial Investment vs. Operational Cost
A semi-automatic machine has a low upfront cost but carries higher long-term operational costs due to the continuous need for manual labor.
A fully automatic machine is the inverse. It demands a high initial investment but significantly lowers per-unit labor costs, offering a better return on investment at high production volumes.
Production Speed vs. Flexibility
Fully automatic lines are built for speed and consistency, but changing over to a different jar size or product can be more time-consuming.
Semi-automatic systems are inherently slower but offer superior flexibility. An operator can switch between filling jars, bottles, or even small honey sticks with relative ease.
The Human Factor: Labor and Skill
Semi-automatic fillers reduce the physical strain of manual filling but still require a dedicated operator for every step of the process.
Fully automatic lines reduce the need for manual laborers but create a need for more highly skilled technicians who can operate, maintain, and troubleshoot the sophisticated PLC-controlled equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
The best machine is the one that aligns with your specific business goals, budget, and production volume.
- If you are a startup or small-batch producer: A semi-automatic piston filler offers the best balance of affordability, accuracy for a viscous product, and flexibility for various containers.
- If you are scaling up production for a growing brand: A fully automatic piston filler is the logical next step to increase output, reduce labor costs, and ensure brand consistency.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, mass-market manufacturing: An integrated, fully automatic line is essential for maximizing efficiency and achieving the lowest possible cost per unit.
Ultimately, a clear understanding of your production targets and growth strategy will guide you to the correct equipment investment.
Summary Table:
| Automation Level | Best For | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Semi-Automatic | Startups, Small-Batch Producers | Lower initial cost, High flexibility, Manual operation |
| Fully Automatic | Large-Scale Commercial Operations | High speed, Low labor cost, PLC-controlled, Integrated lines |
Ready to Scale Your Honey Production?
Choosing the right filling machine is a strategic investment in your business's future. HONESTBEE supplies commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the robust, high-performance machinery needed for efficient, large-scale operations.
We understand the unique challenges of honey production. Our experts can help you select the perfect semi-automatic or fully automatic system to meet your volume, accuracy, and budget requirements.
Contact HONESTBEE today for a personalized consultation and discover how our wholesale-focused solutions can boost your productivity and profitability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Economy Small Honey Filling Machine Honey Bottle Filler Packaging Machine
- Small Honey Filling Machine Sachet Packing Equipment Single Nozzle
- Commercial Rotary Honey Filling Machine for Production
- Precision Automated Packaging Turntable Honey Spoon Filling Sealing Packing Machine
- Double Wall Honey Heating Stirring Homogenizer Mixing Machine with Various Capacity
People Also Ask
- How do automated honey filling lines ensure commercial value? Boost Your Honey Brand's Competitiveness and ROI
- What function do automated Honey-filling Machines serve? Boost Commercial Honey Quality and Brand Consistency
- What technical advantages do automatic honey-filling machines provide? Elevate Your Production Standards
- Why is high-cleanliness honey extraction and filling machinery essential for atmospheric metal tracing? Guide to Data Integrity
- What criteria should be evaluated when selecting a honey filling machine? Top Tips for Maximum Efficiency
- Why are professional honey filling machinery and specialized storage consumables vital? Ensure Quality & Scalability
- What advanced equipment is available for professional honey bottling? Optimize Your Production and Quality Control
- What role does an industrial-grade honey filling machine play in maintaining the stability of medicinal honey?



















