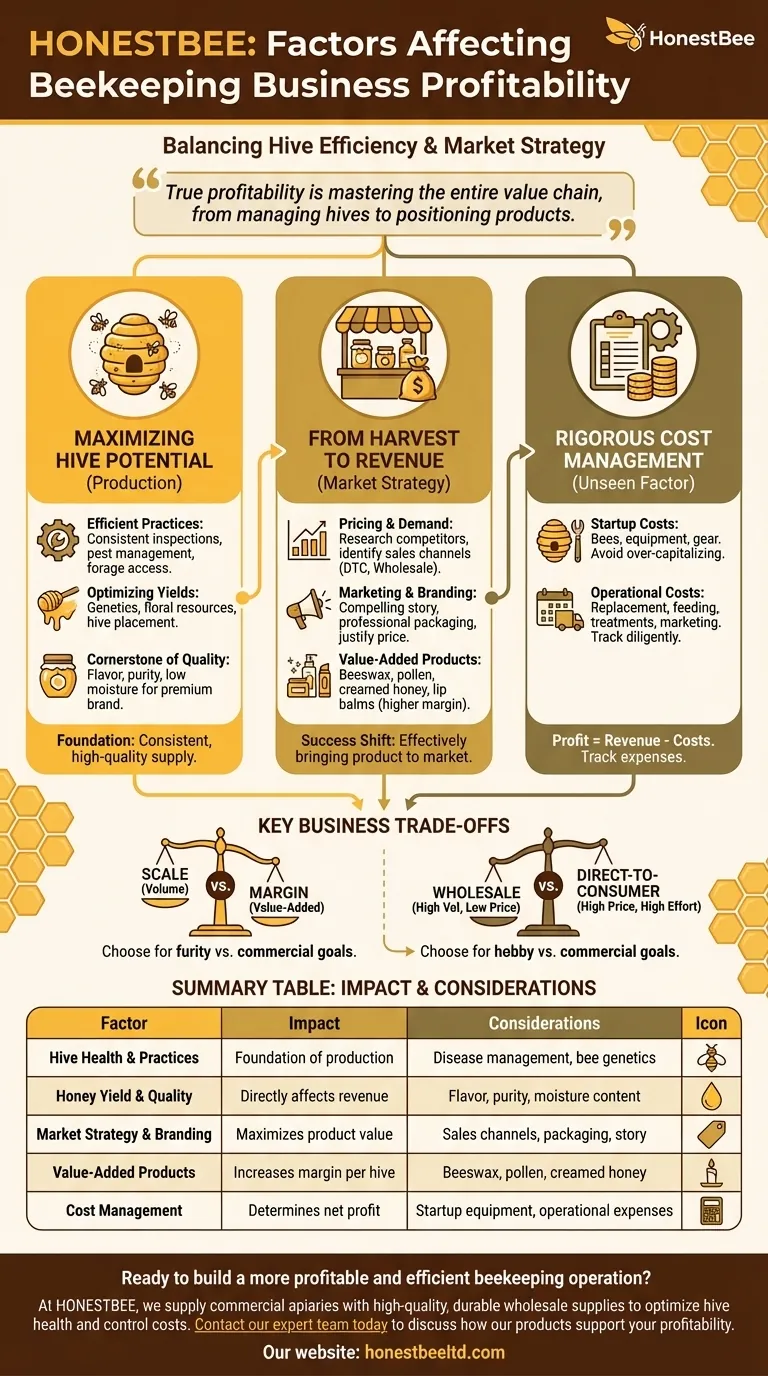
The profitability of a beekeeping business is determined by a direct relationship between your operational efficiency at the hive and your strategic execution in the marketplace. Key factors include your beekeeping practices, honey yields and quality, market pricing, cost management, your ability to create value-added products, and effective branding.
True profitability in beekeeping is not just about producing honey; it's about mastering the entire value chain, from managing healthy, productive hives to strategically positioning your products in a competitive market.

Maximizing Your Hive's Potential (Production)
The foundation of any profitable beekeeping operation is the health and productivity of the bees themselves. Without a consistent, high-quality supply, no amount of marketing can create a sustainable business.
The Impact of Efficient Practices
Effective beekeeping is a science and an art. It involves consistent hive inspections, proactive disease and pest management (like Varroa mites), and ensuring your colonies have access to sufficient forage and water. Efficient practices reduce colony loss and increase the productivity of each hive.
Optimizing Honey Yields
Yield is a primary driver of revenue. It is influenced by factors like bee genetics, local floral resources, weather patterns, and hive placement. Strong, healthy colonies will always produce more honey than weak ones.
The Cornerstone of Quality
Honey quality—defined by its flavor, color, moisture content, and purity—directly impacts the price you can command. Producing a high-quality, unadulterated product is essential for building a premium brand and securing customer loyalty.
From Harvest to Revenue (Market Strategy)
Once you have a quality product, your success shifts to how effectively you can bring it to market. Many beekeepers focus solely on production, but market strategy is where profit is truly realized.
Understanding Market Demand and Pricing
Your local market dictates the baseline price for honey. Researching competitors, understanding consumer preferences (e.g., raw vs. processed honey), and identifying sales channels like farmers' markets, local retailers, or online stores are critical first steps.
The Power of Marketing and Branding
Branding is what separates your honey from others on the shelf. A compelling brand story, professional packaging, and consistent marketing help you connect with customers, justify a higher price point, and build a recognizable business.
Expanding Revenue with Value-Added Products
Relying solely on honey sales limits your revenue potential. Value-added products like beeswax candles, lip balms, pollen, or creamed honey can significantly increase your profit margins per hive, as they command much higher prices for the same base resource.
The Unseen Factor: Rigorous Cost Management
Profit is simply revenue minus costs. A failure to accurately track and control expenses is one of the fastest ways for a beekeeping business to become unsustainable, no matter how much honey you sell.
Controlling Initial Startup Costs
The primary startup costs include bees, hive components (boxes, frames), protective gear, and extraction equipment. Buying equipment strategically and starting with a manageable number of hives can prevent you from over-capitalizing early on.
Managing Ongoing Operational Costs
Operational costs are recurring and include replacing equipment, supplementary feeding, disease treatment, packaging, marketing expenses, and travel. Diligently tracking these expenses is non-negotiable for understanding your true profitability.
Understanding Key Business Trade-offs
Every business decision involves a trade-off. Recognizing these is crucial for making informed choices that align with your goals.
Scale vs. Margin
You can grow your business by adding more hives (increasing scale) or by creating more value-added products from your existing hives (increasing margin). Scaling requires more labor and land, while focusing on margin requires more processing and marketing effort.
Wholesale vs. Direct-to-Consumer
Selling wholesale to a packer or retailer offers high volume and less marketing effort but yields the lowest price per pound. Selling directly to consumers at a farmers' market or online offers the highest price but requires a significant investment in time, marketing, and customer service.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
Your strategic focus should align directly with the scale and goals of your beekeeping business.
- If your primary focus is a small-scale hobby or side business: Concentrate on maximizing direct-to-consumer sales and creating high-margin, value-added products.
- If your primary focus is building a full-time commercial operation: Your success will depend on achieving operational efficiency, managing costs rigorously, and securing stable wholesale or large-scale retail contracts.
Ultimately, a profitable beekeeping business is one that balances the art of beekeeping with the discipline of sound business management.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Profitability | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Hive Health & Practices | Foundation of production | Disease management, bee genetics, forage availability |
| Honey Yield & Quality | Directly affects revenue | Flavor, purity, moisture content for premium pricing |
| Market Strategy & Branding | Maximizes product value | Sales channels (DTC vs. wholesale), packaging, story |
| Value-Added Products | Increases margin per hive | Beeswax candles, pollen, creamed honey, lip balms |
| Cost Management | Determines net profit | Startup equipment, operational expenses, labor |
Ready to build a more profitable and efficient beekeeping operation?
At HONESTBEE, we supply commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the high-quality, durable supplies needed to optimize hive health, increase yields, and control costs. Our wholesale-focused operations ensure you get the reliable equipment your business depends on.
Contact our expert team today to discuss how our products can support your path to greater profitability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Heart-Shaped Comb Honey Frame and Honeycomb Cassette
- Professional Queen Catcher and Introduction Queen Cage
- Plastic Honey Gate Spout with Wing Nut for Beekeeping Honey Bucket
- JZBZ Langstroth Queen Rearing Frame for Beekeeping
- 10L Stainless Steel Electric Honey Press Machine
People Also Ask
- What is a benefit of storing honey-laden frames? A Strategic Food Source for Spring Colony Survival
- How much honey from a full frame? Maximize Your Harvest with the Right Frame Size
- How are standard honey bee frames used as a measurement tool? Quantify Colony Strength with Precision
- How much honey can one medium frame yield? Unlock the Secrets to Maximizing Your Harvest
- What are honey super frames and what foundation options are available? Choose the Best Support for Your Bees



















