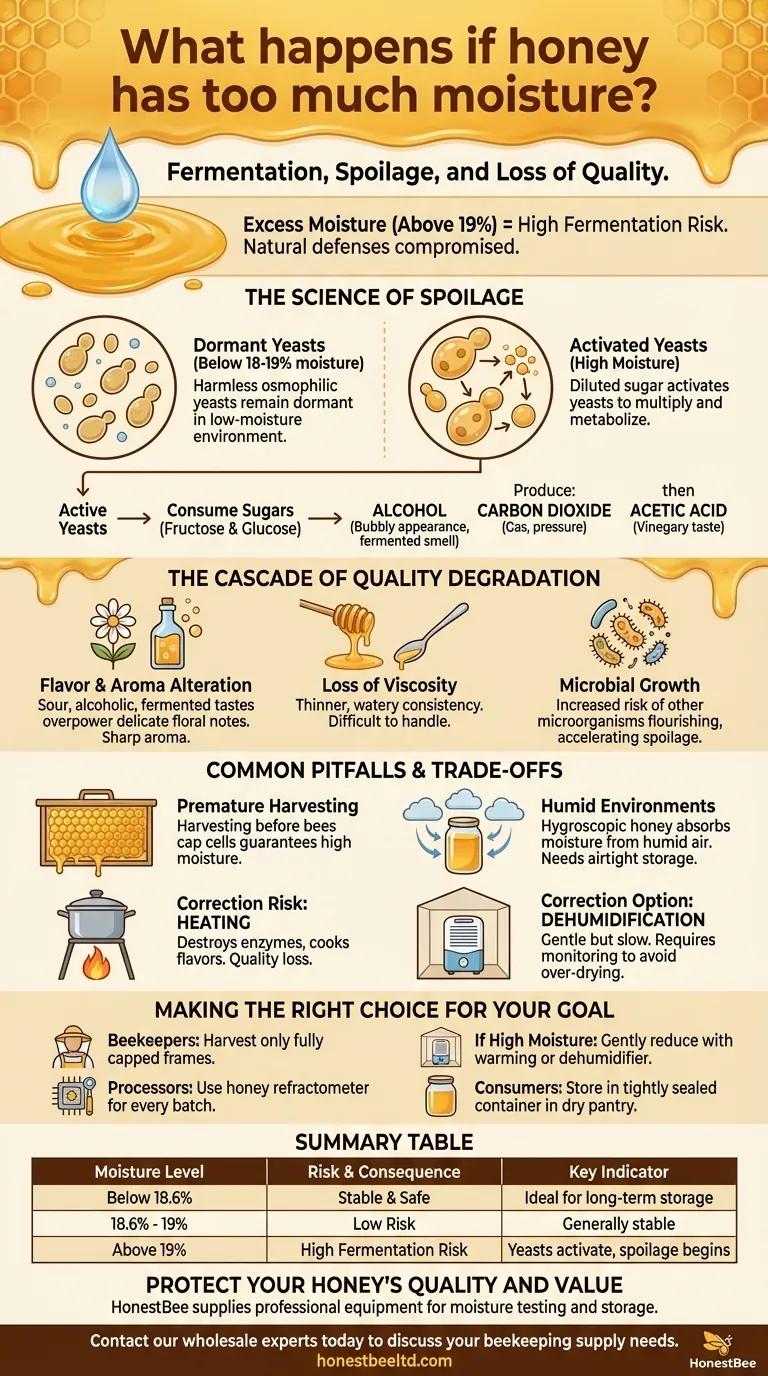
When honey contains excess moisture, it becomes highly susceptible to fermentation by naturally present yeasts. This process spoils the honey, altering its flavor, aroma, and texture, which significantly reduces its quality, value, and shelf life. The industry standard considers honey with a moisture content above 19% to be at high risk for this type of degradation.
Honey's remarkably long shelf life is due to its low water content, which creates an environment where microbes cannot thrive. Introducing excess moisture compromises this natural defense, turning a stable product into a perishable one.

The Science of Spoilage: Why Moisture Matters
The stability of honey is a delicate balance. Its low moisture and high sugar concentration create osmotic pressure that is inhospitable to most microorganisms. When this balance is disturbed, a chain reaction of spoilage begins.
Activating Dormant Yeasts
All raw honey contains natural, sugar-tolerant yeasts (known as osmophilic yeasts). At low moisture levels—typically below 18-19%—these yeasts remain dormant and harmless.
When the water content rises, it effectively dilutes the sugar concentration. This provides the yeasts with the water they need to become active, multiply, and begin metabolizing the honey's natural sugars.
The Fermentation Process
Once active, the yeasts consume the honey's simple sugars (fructose and glucose). This metabolic process produces byproducts, primarily alcohol and carbon dioxide.
The presence of alcohol gives the honey a "bubbly" appearance and a distinct fermented or sour smell. Over time, this alcohol can further convert into acetic acid, lending a vinegary taste that renders the honey unpalatable.
The Cascade of Quality Degradation
Excess moisture doesn't just cause one problem; it triggers a series of issues that collectively ruin the honey.
Flavor and Aroma Alteration
The most immediate and noticeable impact is on flavor. The delicate floral and sweet notes of the honey are overpowered by sour, alcoholic, or fermented tastes. The aroma will shift from pleasant to sharp and vinegary.
Loss of Viscosity
Higher water content makes honey thinner and more watery. This change in viscosity is often perceived as a sign of low quality and can make the honey difficult to handle and package properly.
Microbial Growth and Spoilage
While yeast fermentation is the primary concern, other microorganisms might also find the higher-moisture environment more suitable for growth, accelerating spoilage and reducing the honey's safety and stability.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
Managing honey's moisture content involves navigating several challenges, from harvesting to storage. Understanding the pitfalls is key to preventing spoilage.
The Pitfall of Premature Harvesting
A primary cause of high moisture is harvesting honey before the bees have finished their work. Bees dehydrate nectar by fanning their wings over the honeycomb, and they seal the cell with a wax cap only when the moisture content is ideally low.
Harvesting frames with a large percentage of uncapped cells almost guarantees the honey will have a high moisture content and be unstable.
The Challenge of Humid Environments
Honey is hygroscopic, meaning it will absorb moisture from the surrounding air. If honey is extracted, processed, or stored in a humid environment without an airtight seal, its water content can increase over time.
The Risk of Correction Methods
While you can reduce moisture, the methods involve trade-offs. Heating honey can evaporate water, but applying too much heat will destroy its beneficial enzymes and delicate flavors, effectively "cooking" it and reducing its quality.
Using a dehumidifier in a sealed, warm room is a gentler but much slower alternative that requires careful monitoring to avoid over-drying the honey.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your strategy for managing moisture depends on your role in the honey's journey from hive to table.
- If you are a beekeeper: Your primary focus should be harvesting fully capped frames, which is the most reliable natural indicator of low-moisture, stable honey.
- If you are a honey processor: Invest in a honey refractometer to accurately test the moisture content of every batch before bottling to ensure quality control.
- If your honey tests high for moisture: Gently reduce it using a controlled warming unit or a dehumidifier in a sealed room, and re-test to confirm you've reached a stable level (below 19%).
- If you are a consumer: Store your honey in a tightly sealed container in a dry pantry to protect it from absorbing ambient moisture.
Ultimately, controlling moisture is the single most important factor in preserving the value, stability, and unique character of your honey.
Summary Table:
| Moisture Level | Risk & Consequence | Key Indicator |
|---|---|---|
| Below 18.6% | Stable & Safe | Ideal for long-term storage |
| 18.6% - 19% | Low Risk | Generally stable |
| Above 19% | High Fermentation Risk | Yeasts activate, spoilage begins |
Protect Your Honey's Quality and Value
For commercial apiaries and distributors, honey spoilage due to excess moisture means lost revenue and damaged reputation. HONESTBEE supplies the professional-grade equipment you need to prevent this, including honey refractometers for precise moisture testing and storage solutions to maintain ideal conditions.
Ensure every batch meets the highest quality standards. Contact our wholesale experts today to discuss your beekeeping supply needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Precision Honey Refractometer Instrument for Quality Assessment
- Professional Thermostatic Conical Honey Melter
- HONESTBEE 3-Frame Manual Acrylic Honey Extractor
- 8-Frame Electric Self-Reversing Honey Extractor Spinner for Commercial Honey Extraction Equipment
- Honey Concentrating Vacuum Heating Thickening Machine Dehumidifier for Honey
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a honey refractometer in beekeeping? Ensure Harvest Quality and Prevent Fermentation
- How is a manual refractometer used to determine honey quality? Essential Moisture Control for Commercial Beekeeping
- Why is a refractometer necessary for determining the moisture content and quality grade of honey? Ensure Market Success
- What is the principle and importance of using a refractometer for honey moisture? Ensure Quality & Prevent Fermentation
- What should be considered regarding the measurement range of a honey refractometer? Ensure Peak Honey Quality



















