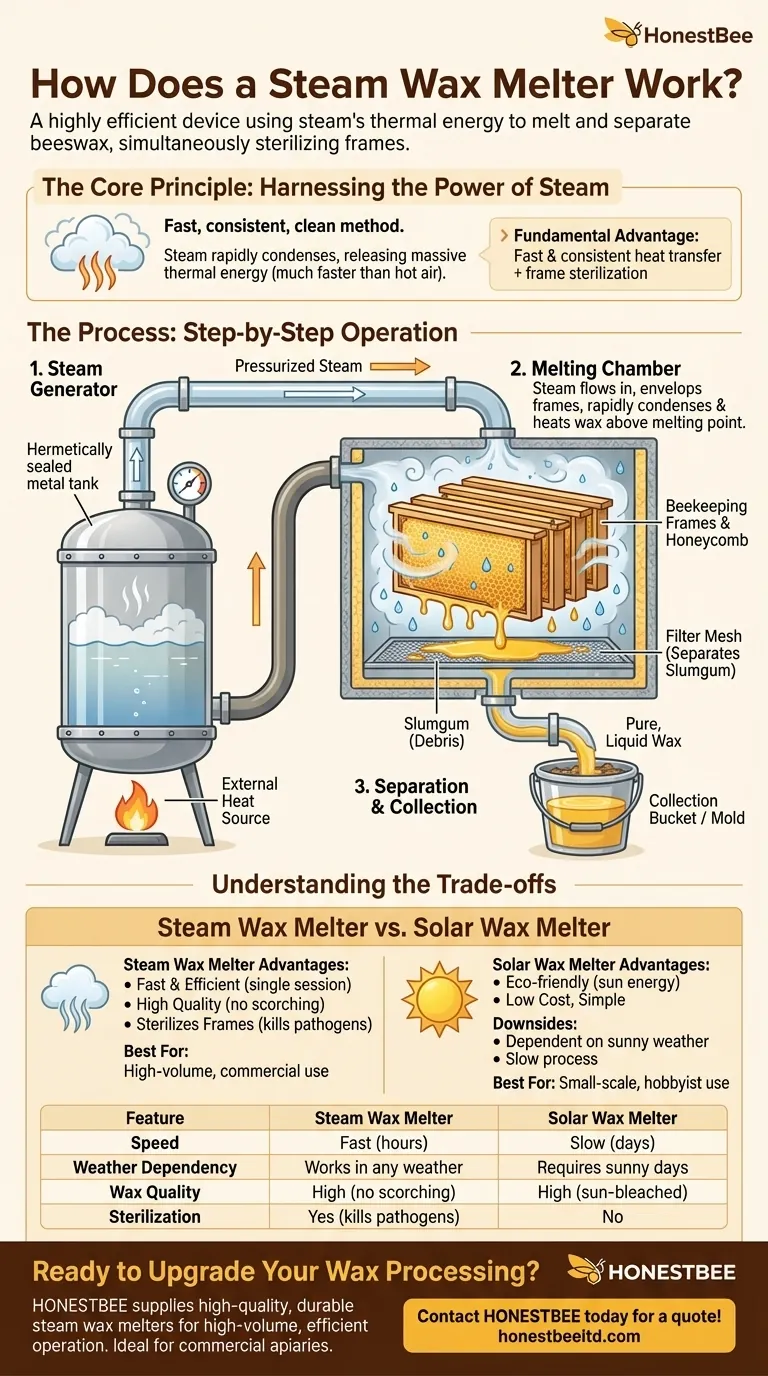
At its core, a steam wax melter is a highly efficient device that uses the thermal energy of hot steam to melt and separate beeswax from old honeycombs. It consists of two main parts: a sealed container to boil water and generate steam, and a separate, insulated chamber where the frames are placed. The steam is piped from the generator into the melting chamber, quickly heating the honeycomb to over 70°C, causing the wax to liquify and drain away for collection.
The fundamental advantage of a steam wax melter is its use of steam as a medium for heat transfer. This provides a fast, consistent, and clean method for rendering high-quality wax while simultaneously sterilizing the beekeeping frames.

The Core Principle: Harnessing the Power of Steam
Understanding how a steam wax melter operates comes down to appreciating the physics of steam. It's a far more effective method of heating than simply using dry heat.
The Steam Generator
The process begins with the steam generator. This is a hermetically sealed container, often a metal tank, that is filled approximately halfway with water.
Leaving ample space above the water is critical for vaporization. As the water is heated by an external source (like fire or an electric element), it boils and produces a large volume of steam, building pressure inside the sealed container.
The Melting Chamber
The second key component is the melting chamber or tank. This insulated box is designed to hold the beekeeping frames, either stacked or placed in a basket.
The chamber has an inlet for the steam hose and an outlet at the bottom for the melted wax to drain. Insulation is key to retaining heat and ensuring the process is efficient.
Heat Transfer and Melting
A hose connects the steam generator to the melting chamber. As pressure builds, hot steam flows through the hose and fills the chamber, enveloping the frames.
When the steam contacts the cooler surfaces of the honeycomb and frames, it rapidly condenses back into water, releasing a massive amount of thermal energy. This process is much faster and more thorough than heating with hot air, quickly raising the wax temperature above its melting point.
Separation and Collection
As the wax melts, it drips down from the combs. The liquid wax passes through a filter mesh or screen located at the bottom of the chamber.
This filter separates the pure wax from "slumgum"—the residue of old cocoons, pollen, and other debris. The filtered liquid wax then accumulates on a pallet and flows out through a drain tap into a prepared mold or collection bucket.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, a steam wax melter is one of several options available to a beekeeper. Its advantages and disadvantages become clear when compared to other methods, like a solar melter.
Key Advantages of Steam
A steam melter offers significant benefits, particularly for a serious beekeeper. The process is fast and efficient, allowing you to process many frames in a single session, regardless of the weather.
The resulting wax is very high quality and clean because the indirect heat from the steam prevents scorching or burning. A major secondary benefit is that the hot steam sterilizes the frames and woodenware, killing pathogens like American Foulbrood spores.
Potential Downsides
The primary trade-off is the need for an active heat source, which requires fuel or electricity and adds to the operational cost. The equipment is also more complex and generally more expensive than a simple solar melter.
The beekeeper must actively monitor the process, managing the heat source and ensuring the water level in the steam generator is sufficient.
Comparison to Solar Melters
A solar wax melter uses the sun's energy, making it environmentally friendly and free to operate. However, it is entirely dependent on sunny weather and works much more slowly.
Solar melters are excellent for small-scale operations or hobbyists, while steam melters are better suited for beekeepers who need to process large quantities of comb reliably and quickly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right wax rendering method depends entirely on the scale of your operation and your primary objectives.
- If your primary focus is speed and high-volume processing: A steam wax melter is the definitive choice for its efficiency and ability to work in any weather condition.
- If your primary focus is low cost and environmental impact: A solar wax melter is an ideal, simple solution for smaller apiaries with reliable access to sunlight.
- If your primary focus is equipment sterilization and wax quality: The steam melter holds an advantage, as the steam not only produces clean wax but also thoroughly sanitizes your frames.
Ultimately, understanding the mechanics of each tool empowers you to choose the one that best aligns with the needs of your apiary.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Steam Wax Melter | Solar Wax Melter |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Fast (hours) | Slow (days) |
| Weather Dependency | Works in any weather | Requires sunny days |
| Wax Quality | High (no scorching) | High (sun-bleached) |
| Sterilization | Yes (kills pathogens) | No |
| Best For | High-volume, commercial use | Small-scale, hobbyist use |
Ready to upgrade your wax processing? For commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors, HONESTBEE supplies high-quality, durable steam wax melters designed for high-volume, efficient operation. Our wholesale-focused operations ensure you get the reliable equipment you need to maximize your wax yield and maintain hive health.
Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss your needs and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Beeswax Melter for Candle Making Honey Bee Wax Melter
- Steam Beeswax Melter Wax Warmer for Wax Processing
- Professional Stainless Steel Wax Melter for Beekeeping and Crafts
- Electric Flatting and Embossing Machine with Tray for Beekeeping
- Honey Wax Separating Wax Press with Metal Screw Wax Separator Machine
People Also Ask
- How does a solar melter work to process beeswax? The Eco-Friendly Way to Pure Wax
- What are the key functions of large heated water tanks in beeswax cleaning? Expert Purification Strategies
- What features ensure the efficiency of the Solar Wax Melter? Maximize Your Wax Yield with Superior Heat Control
- How does a solar wax melter use solar energy to melt wax? Harness Free Energy for Premium Beeswax
- What is the final step after straining the beeswax? Master the Art of Undisturbed Cooling
- How do wax melting and processing systems prevent Nosema? Stop Re-infection with High-Temp Thermal Sterilization
- What are the safety considerations when using a wax melter? Essential Guide to Burn and Hazard Prevention
- Can the Solar Wax Melter operate on partly cloudy days? Harness Solar Power Effectively



















