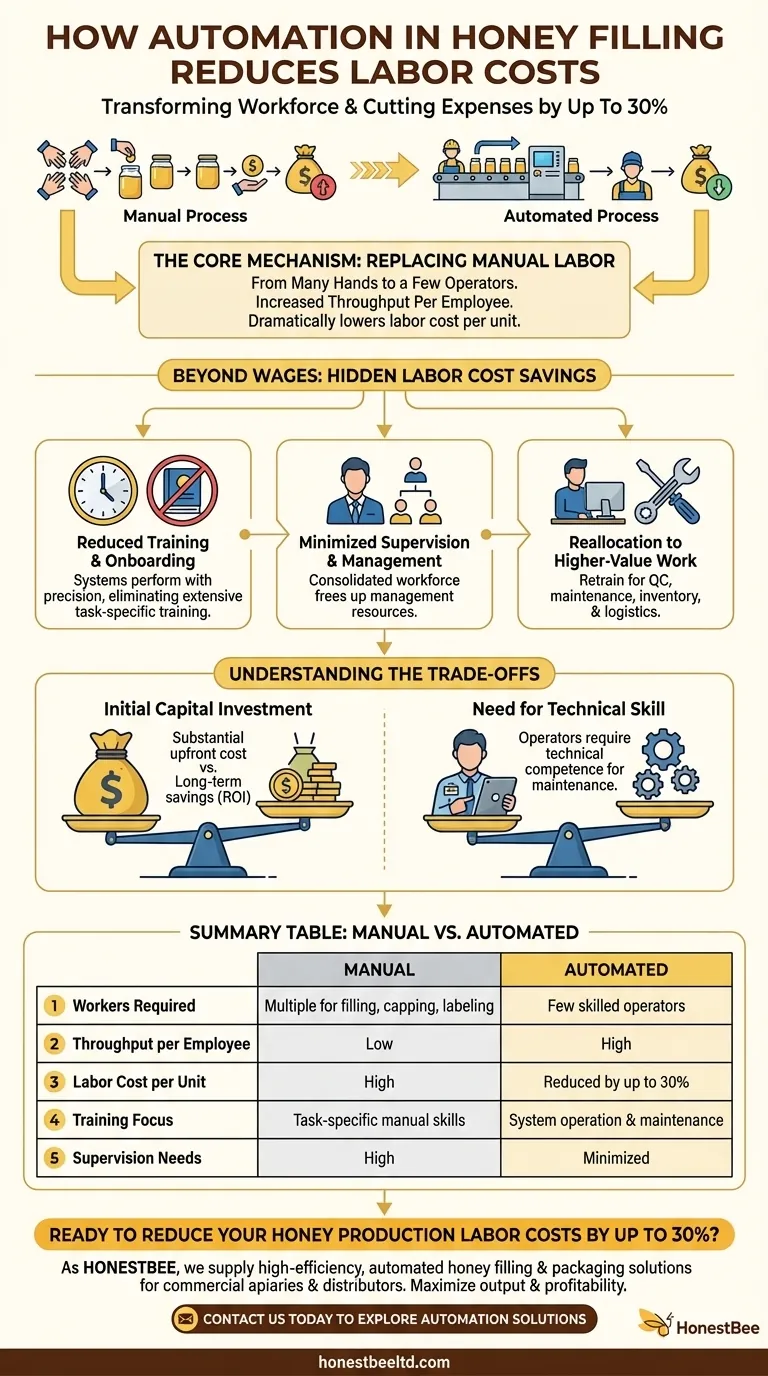
At its core, automation in honey filling reduces labor costs by replacing repetitive manual tasks with high-speed, consistent machine work. This fundamental shift means fewer workers are needed on the production line to fill, cap, and label jars, directly cutting down on wages and associated employment expenses, with potential labor cost reductions of up to 30%.
The primary value of automation is not just in reducing headcount, but in transforming the nature of your workforce—shifting human capital from tedious, low-skill tasks to higher-value roles that drive quality and growth.
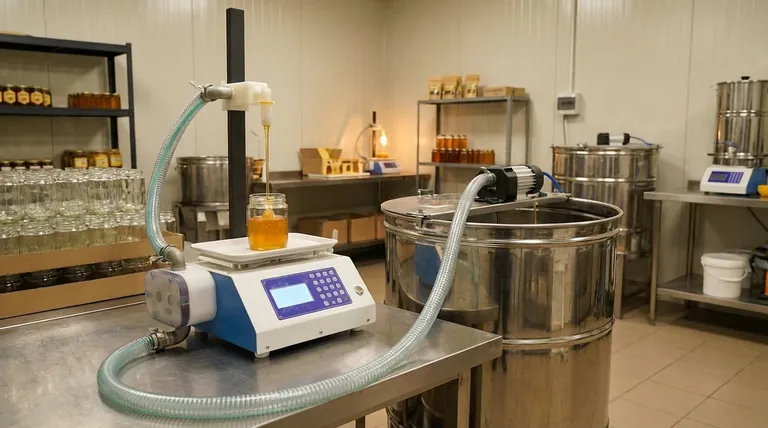

The Core Mechanism: Replacing Manual Labor
Automating the honey filling process fundamentally changes the production equation. Instead of relying on a team of people to perform each step, a single integrated system handles the most labor-intensive parts of the job.
From Many Hands to a Few Operators
A manual production line requires multiple people for distinct tasks: one to place jars, another to fill them, a third to cap, and several more to apply labels.
An automated system consolidates these functions. It requires only a few skilled operators to oversee the entire process, from loading empty jars to packing the finished product.
Increased Throughput Per Employee
With automation, a small team can produce a significantly higher volume of finished goods in the same amount of time.
This dramatic increase in efficiency means your labor cost per unit plummets, making your operation more profitable and scalable.
Beyond Wages: The Hidden Labor Cost Savings
The most obvious savings come from a reduced payroll, but automation impacts labor costs in several other crucial, often overlooked, ways.
Reduced Training and Onboarding
Training new employees for consistent manual filling and labeling is time-consuming and costly. Automated systems perform these tasks with precision every time.
This eliminates the need for extensive task-specific training, allowing you to focus onboarding on system operation and safety protocols instead.
Minimized Supervision and Management
A larger manual workforce requires more supervisors to manage workflow, ensure quality, and maintain productivity.
By consolidating the workforce into a few skilled operators, the need for direct line supervision decreases significantly, freeing up management resources.
Reallocation to Higher-Value Work
Reducing the need for manual fillers and labelers allows you to reallocate those team members to more strategic roles.
Former line workers can be retrained for quality control, machine maintenance, inventory management, or logistics—tasks where human oversight and problem-solving create more value.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the labor savings are significant, adopting automation is a strategic decision that involves clear trade-offs. It is not a universally perfect solution.
Initial Capital Investment
Automated filling and labeling machinery requires a substantial upfront capital investment. This cost must be weighed against the projected long-term labor savings to calculate a return on investment (ROI).
Need for Technical Skill
The remaining workforce will require a different skill set. Operators must be trained to manage, troubleshoot, and maintain the machinery, which often demands a higher level of technical competence than manual labor.
How to Apply This to Your Operation
Choosing to automate is about aligning your investment with your business goals and operational scale.
- If your primary focus is artisanal quality on a small scale: The direct labor of manual filling may be a part of your brand identity and cost structure, making full automation unnecessary.
- If your primary focus is scaling a growing business: Automation is the clearest path to reducing per-unit labor costs and meeting increasing demand without exponentially growing your workforce.
- If your primary focus is competing in a large commercial market: High-speed automation is a fundamental requirement to achieve the efficiency and low production costs needed to remain competitive.
Ultimately, investing in automation is an investment in operational efficiency that strategically reduces your reliance on manual labor costs.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Manual Process | Automated Process |
|---|---|---|
| Workers Required | Multiple for filling, capping, labeling | Few skilled operators |
| Throughput per Employee | Low | High |
| Labor Cost per Unit | High | Reduced by up to 30% |
| Training Focus | Task-specific manual skills | System operation & maintenance |
| Supervision Needs | High | Minimized |
Ready to reduce your honey production labor costs by up to 30%?
As HONESTBEE, we specialize in supplying commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with high-efficiency, automated honey filling and packaging solutions through our wholesale-focused operations. Our systems are designed to minimize your labor expenses while maximizing your output and profitability.
Contact us today to explore how our automation solutions can transform your operation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Semi Automatic Small Honey Bottle Filling Machine Honey Filler
- Fully Automatic Honey Filling Packaging Machine for Processing Line
- Manual Honey Filling Machine Bottling Machine for Honey
- Automatic Honey Filling and Filtering Machine for Beekeeping Bottle Filling
- Double Nozzle Small Honey Filling Machine Honey Sachet Packing Packaging Equipment
People Also Ask
- What technical advantages do precision honey filling machines provide? Scaling Your Honey Brand for Global Export
- What are the benefits of a honey packaging machine's design? Boost Efficiency & Protect Product Quality
- What advantages do industrial honey-filling machines offer? Boost Throughput and Precision for Commercial Beekeeping
- What is the function of an automatic honey-filling machine in maintaining export-grade quality?
- When is a pump filling machine the ideal choice for filling honey? Boost Efficiency and Scalability for Your Apiary
- What are the main processes of a sachet filling and packing machine? Streamline Your Packaging Line
- What are the common causes of product leakage from a filling machine? Expert Tips to Fix Seals & Nozzle Alignment
- What are VFFS and HFFS bagging machines? Choose the Right Packaging Automation for Your Product



















