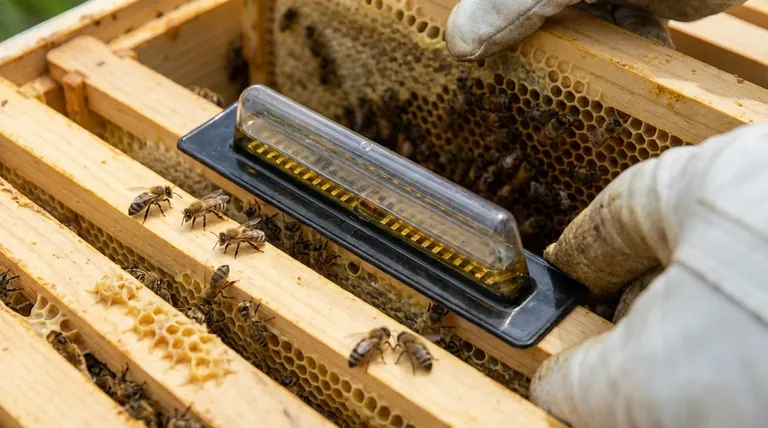
The most effective methods for killing small hive beetles are mechanical in-hive traps that use mineral oil or diatomaceous earth to capture and kill the pests. These traps are designed to be placed where beetles naturally congregate—either between frames or under a screened bottom board—and work by exploiting the beetles' instinct to hide from the bees.
While traps are a critical tool for reducing beetle populations, they are a reactive measure. The most definitive and sustainable strategy for controlling small hive beetles is to proactively maintain a strong, populous, and healthy bee colony that can effectively police its own hive.

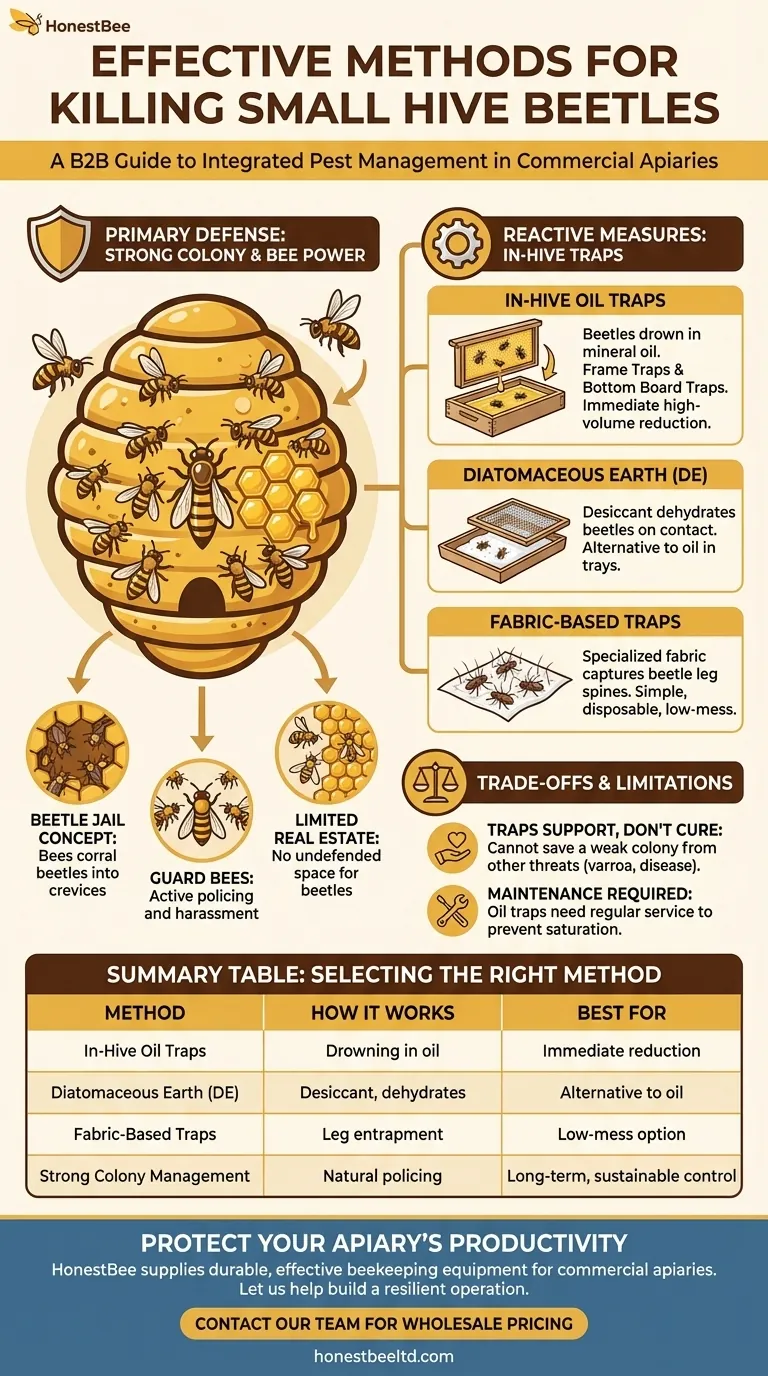
The Foundation: Why a Strong Colony Is Your Best Defense
Before deploying any trap, you must understand that small hive beetles (SHB) are primarily a secondary pest. They thrive by exploiting weakness. A powerful colony is, and always will be, the number one defense mechanism.
The Role of "Bee Power"
A hive with a large population of bees has the workforce needed to manage pests. These "guard" bees will actively chase beetles, harass them, and prevent them from accessing brood or food stores.
The "Beetle Jail" Concept
Bees instinctively corral SHB into small cracks and crevices, effectively creating "jails" where the beetles are trapped. Most commercial traps are designed to mimic these jails, tricking beetles into a space from which they cannot escape.
Limiting Beetle Real Estate
A strong colony can defend every corner of its hive. A weak colony in a large hive leaves undefended space where beetles can hide, reproduce, and overwhelm the bees. Never give your bees more space than they can patrol.
Primary Trapping Methods: How to Kill Small Hive Beetles
Traps are an essential part of an integrated pest management plan, especially for managing heavy beetle loads. They support the bees' natural defensive behaviors.
In-Hive Oil Traps
These are the most common and widely effective traps. Beetles, fleeing from bees, fall into the trap and drown in the oil.
- Frame Traps: These small, reusable plastic traps hang between frames in the brood box.
- Bottom Board Traps: These are larger trays or pans placed under a screened bottom board. They can capture a very high number of beetles.
Diatomaceous Earth (DE)
As an alternative to oil, food-grade diatomaceous earth can be placed in bottom board traps. DE is a desiccant composed of fossilized algae with microscopic sharp edges. It works by absorbing the oils and fats from a beetle's exoskeleton, causing it to dehydrate.
Fabric-Based Traps
Some traps use disposable, single-use sheets made of a specific fabric. When beetles run across the cloth, their leg spines get caught in the fibers, permanently trapping them. These are often placed on the hive floor or on top of the inner cover where beetles congregate.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No single method is a silver bullet. Effective control requires understanding the limitations of your chosen tools.
Traps Support, They Don't Cure
A hive that is already weak from disease, a poor queen, or varroa mites will not be saved by beetle traps alone. Traps reduce the beetle population, giving a struggling colony a better chance, but they do not solve the root cause of the weakness.
The Mess and Maintenance Factor
Oil traps require regular service. If neglected, the oil can become saturated with dead beetles, creating a bridge for new beetles to escape. Spilling oil inside a hive can be messy and harmful to bees if not done carefully.
The Question of "Natural" Remedies
While some beekeepers experiment with essential oils or beneficial nematodes, their effectiveness for in-hive control is less documented and reliable than mechanical traps. Beneficial nematodes, for instance, are applied to the soil outside the hive to kill beetle larvae pupating in the ground, not the adult beetles inside the hive.
Making the Right Choice for Your Hive
Your strategy should be dictated by your immediate goal and long-term philosophy.
- If your primary focus is immediate infestation control: Deploy in-hive oil traps or DE trays immediately to reduce the adult beetle population and alleviate pressure on the bees.
- If your primary focus is long-term, sustainable management: Concentrate on hive husbandry—ensure a strong queen, manage varroa mites, and only provide as much hive space as your bees can actively defend.
- If your primary focus is a simple, low-mess approach: Consider fabric-based traps, as they are disposable and do not involve oils or powders.
Ultimately, effective beetle control is a key component of holistic hive management that empowers your bees to defend themselves.
Summary Table:
| Method | How It Works | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| In-Hive Oil Traps | Beetles drown in mineral oil after being chased by bees. | Immediate, high-volume beetle reduction. |
| Diatomaceous Earth (DE) | A desiccant that dehydrates and kills beetles on contact. | An alternative to oil in bottom board traps. |
| Fabric-Based Traps | Beetles' legs get caught in specialized fibers, trapping them. | A simple, low-mess, disposable option. |
| Strong Colony Management | A populous hive naturally polices and contains beetle populations. | Long-term, sustainable, and proactive control. |
Protect Your Apiary's Productivity and Health
Effectively managing small hive beetles is critical for maintaining hive strength and honey production. HONESTBEE supplies the durable, effective beekeeping equipment and supplies that commercial apiaries and distributors rely on to implement these proven pest control strategies.
Let us help you build a more resilient operation. Contact our team today to discuss wholesale pricing on hive beetle traps and other essential equipment tailored for professional beekeepers.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Plastic Beetle Blaster Trap Beekeeping Tools and Supplies
- Removable Washable Hive Beetle Trap Attractants for Small Hive Beetles
- Professional Multi-Function Stainless Steel Hive Tool
- HONESTBEE Professional Long Handled Hive Tool with Precision Cutting Blade
- Wholesales Dadant Size Wooden Bee Hives for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- How do beetle blasters work to protect bee colonies? Effective IPM for Healthy Hives
- What is the recommended number of beetle traps per hive? Optimize Your Hive's Beetle Defense
- Where is the ideal placement for Beetle Blasters in a hive? Maximize Control with Strategic Positioning
- What should be avoided when installing Beetle Blasters in a hive? Avoid These 3 Costly Placement Mistakes
- What is the purpose of the small hive beetle tray? A Non-Chemical Pest Control Solution



















