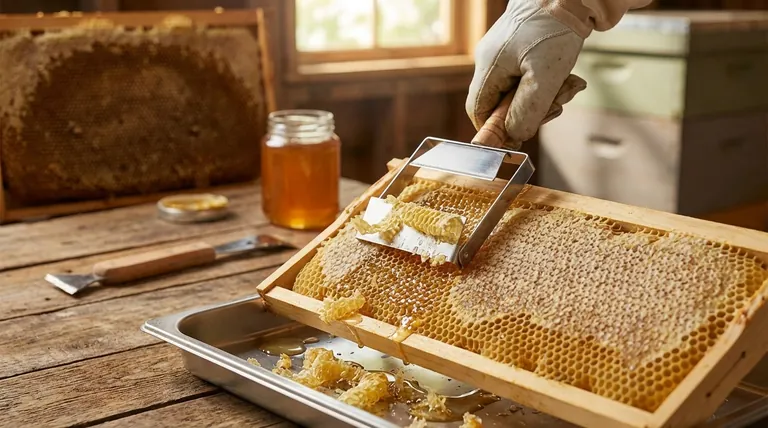
In the world of beekeeping, wax cappings are the fresh, thin layers of beeswax that honey bees build to seal and protect fully ripened honey within the cells of a honeycomb. Before a beekeeper can extract the liquid honey, these protective caps must be carefully sliced or scraped off. This makes the collection of cappings an essential and valuable step in any honey harvest.
Wax cappings are not merely a barrier to be removed; they are the purest and newest beeswax in the hive. Understanding how to properly collect and process them unlocks a second valuable harvest of premium beeswax right alongside your honey.

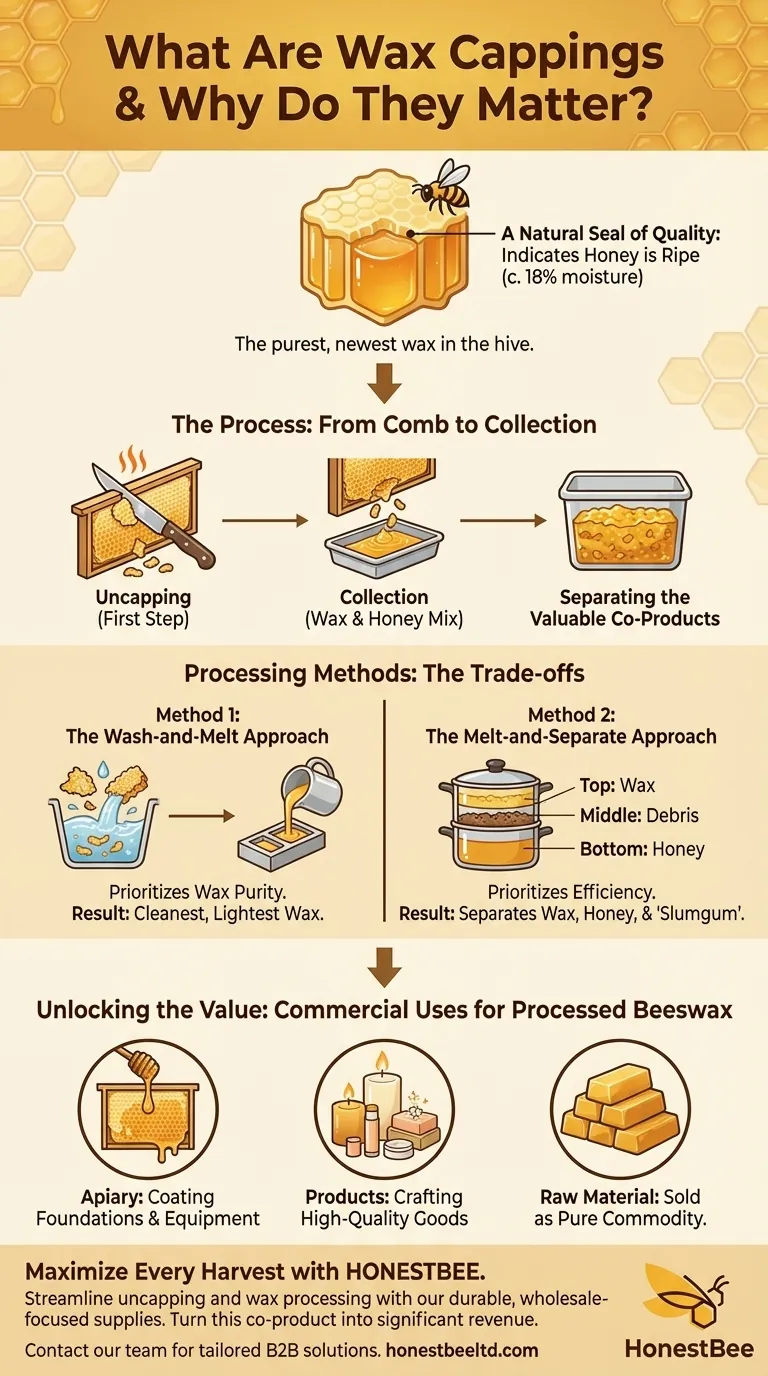
The Role of Cappings in the Hive and Harvest
A Natural Seal of Quality
Bees are meticulous. They only seal a cell of honey with a wax capping once the honey has been fanned down to the perfect moisture content, typically around 18%. A fully capped frame is therefore a visual confirmation for the beekeeper that the honey is ripe, mature, and ready for harvest.
The First Step in Honey Extraction
There is no way to extract honey from a sealed frame without first removing the cappings. The process, known as "uncapping," is a mandatory first step. This is why harvesting beeswax is considered an integral and unavoidable part of harvesting honey.
Why Cappings Produce "Premium" Wax
The wax used for cappings is newly produced by the bees specifically for this purpose. Unlike older comb wax that may have been used for raising brood (young bees) and can become darkened over time, capping wax is clean, pure, and light in color, making it the most desirable wax in the hive.
The Process: From Comb to Collection
Uncapping the Honeycomb
Beekeepers typically use a specialized tool to remove the cappings. This is often a heated "hot knife" that melts through the wax cleanly, but serrated knives or pronged "uncapping scratchers" also work.
Separating Honey from Wax
As the cappings are sliced off, they fall into a collection tray. This initial collection is a mixture of wax and a significant amount of residual honey. The next step is to separate the two valuable products.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Processing Your Cappings
Once collected, the honey-laden cappings must be processed. There are two primary methods, each with its own advantages.
Method 1: The Wash-and-Melt Approach
This method prioritizes wax purity. The cappings are first washed in cold or lukewarm water, which dissolves and rinses away the honey without significantly affecting the wax. After being thoroughly dried, the clean wax is gently melted, strained through cheesecloth to remove impurities, and poured into molds to cool into solid blocks.
Method 2: The Melt-and-Separate Approach
This method prioritizes efficiency. The entire mixture of wax and honey is gently heated together in a double boiler. As the mixture melts and then cools, it naturally separates into three distinct layers:
- Top Layer: The lighter melted wax floats to the top and hardens as it cools.
- Bottom Layer: The heavier honey settles at the bottom.
- Middle Layer: A thin layer of impurities and hive debris, often called "slumgum," forms between the wax and honey.
Once solid, the block of clean wax can be easily lifted off.
Unlocking the Value: What to Do with Processed Beeswax
Cleaned and rendered beeswax from cappings is a valuable commodity with numerous uses.
For the Apiary
Many beekeepers use the rendered wax to coat new plastic frames and foundations. This encourages the bees to accept the new equipment and begin building comb on it more quickly.
For Crafting and Products
The purity and pleasant scent of capping wax make it ideal for high-quality consumer products. Common uses include making candles, lip balms, soaps, lotions, and furniture polish.
As a Raw Material
Clean beeswax bricks are a product in their own right. They can be sold directly to other crafters, artisans, or cosmetic companies who value pure, natural beeswax.
Making the Right Choice for Your Harvest
How you handle your wax cappings depends on your equipment and your ultimate goal for the final products.
- If your primary focus is maximum honey yield: Allow the raw cappings to drip-drain through a strainer for 24-48 hours before processing the wax to recover every last drop of honey.
- If your primary focus is the purest possible wax: Use the "wash-and-melt" method to gently rinse the honey off before melting, which helps maintain the wax's light color and delicate aroma.
- If your primary focus is efficiency: Use the "melt-and-separate" method in a double boiler to process the honey and wax in a single, time-saving step.
Ultimately, treating wax cappings as a co-product, not a waste product, is a hallmark of a sustainable and resourceful beekeeper.
Summary Table:
| Wax Cappings Aspect | Key Information |
|---|---|
| Definition | Fresh, pure beeswax used by honey bees to seal ripened honey in comb cells. |
| Significance | Indicates honey is ripe (approx. 18% moisture) and ready for harvest. |
| Primary Processing Methods | Wash-and-Melt (for pure wax) or Melt-and-Separate (for efficiency). |
| Value & Uses | Coating foundations, crafting candles/balms/soaps, or selling as a raw material. |
Maximize the value of every harvest with HONESTBEE.
As a commercial apiary or beekeeping equipment distributor, you understand that efficiency and product quality are paramount. The premium beeswax from your wax cappings is a valuable asset. HONESTBEE supplies the durable, wholesale-focused beekeeping supplies and equipment you need to streamline your uncapping and wax processing, helping you turn this co-product into significant additional revenue.
Let's discuss how our solutions can enhance your operation's productivity and profitability. Contact our expert team today for wholesale pricing and tailored equipment recommendations.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Stainless Steel Dual Blade Uncapping Plane
- Extra Wide Stainless Steel Honey Uncapping Fork with Scraper Beekeeping Tool
- Professional Wide Blade Honey Scraper for Beekeeping and Honey Processing
- Professional Extra-Wide Uncapping Fork with Bent Tines for Beekeeping
- Professional Long-Handled Silicone Honey Scraper for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- What are the drawbacks of using an electric knife for uncapping honey frames? Cost and Power Constraints Explained
- How do specialized honey knives contribute to sustainable harvesting? Protect Your Brood and Boost Yields
- What is the function of an uncapping knife in the honey extraction process? Unlock Efficiency and Preserve Comb Integrity
- What is a decapping knife used for in beekeeping? Essential Tools for Efficient Honey Harvesting
- What is an uncapping plane, and how does it differ from an electric knife? Precision vs. Speed for Beekeepers



















