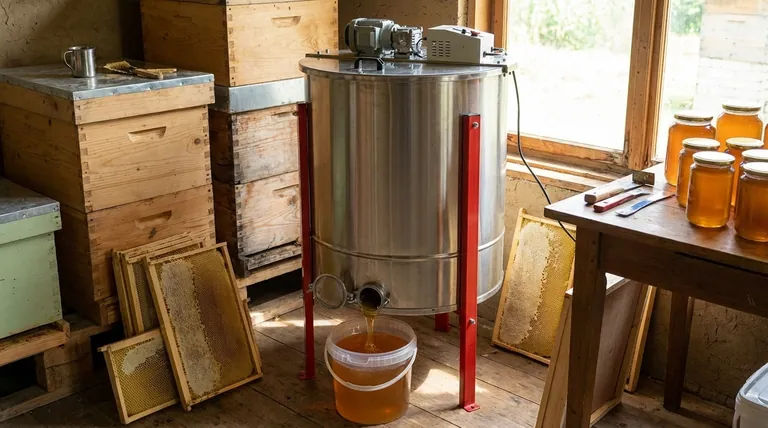
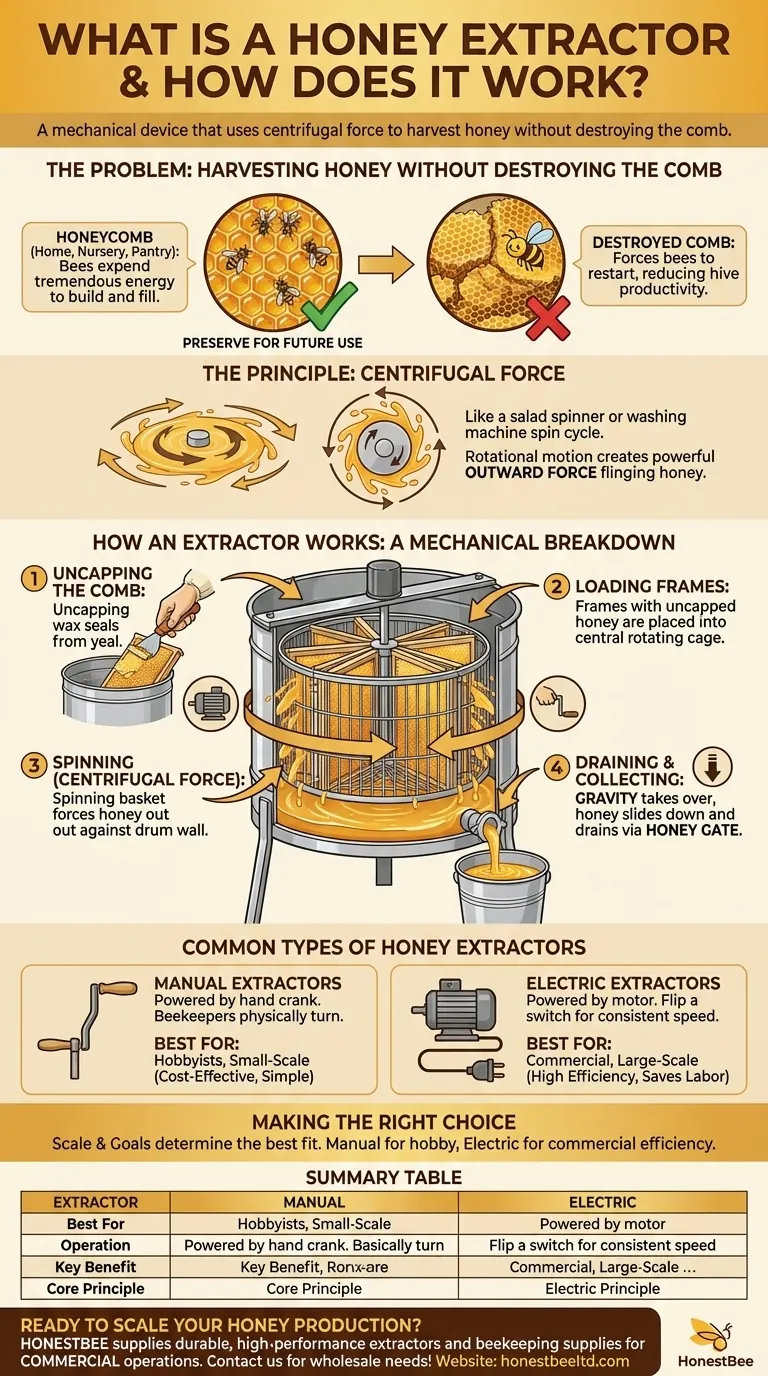
A honey extractor is a mechanical device used in beekeeping to remove honey from honeycomb frames. It operates using centrifugal force to spin honey out of the wax cells without destroying the comb itself. This allows beekeepers to harvest the honey efficiently while returning the intact combs to the hive for the bees to reuse.
The core function of a honey extractor is to separate liquid honey from the delicate wax comb. By spinning frames at high speed, it automates a critical step in honey harvesting, making the process faster and preserving the bees' valuable comb for future use.

The Problem: Harvesting Honey Without Destroying the Comb
To understand the extractor's value, it's essential to recognize the problem it solves. Bees expend a tremendous amount of energy to produce the wax and construct the intricate hexagonal cells that form their comb.
Why Preserving the Comb is Crucial
The wax comb is the bee colony's home, nursery, and pantry. Destroying it during a honey harvest forces the bees to start from scratch.
By preserving the comb, beekeepers give their colonies a significant head start. The bees can immediately begin refilling the empty cells with new honey, leading to a more productive and healthy hive.
The Principle of Centrifugal Force
A honey extractor works on the same principle as a salad spinner or the spin cycle of a washing machine.
When the frames are spun rapidly, the rotational motion creates a powerful outward force. This centrifugal force flings the liquid honey from the open cells against the inner wall of the extractor's drum.
How an Extractor Works: A Mechanical Breakdown
While designs vary, all honey extractors share a few fundamental components that work together to accomplish this task.
Key Components
An extractor consists of a large, cylindrical drum, typically made of stainless steel or plastic. Inside, a rotating basket or cage is designed to hold several honeycomb frames.
This central basket is connected to a mechanism—either a hand crank or an electric motor—that spins it. At the bottom of the drum is a honey tap or gate for draining the collected honey.
The Extraction Process
First, the beekeeper uses a special tool to uncap the wax seals on the honeycomb cells. The frames are then placed into the extractor's basket.
As the basket spins, honey is forced out and splatters against the interior drum wall. Gravity then takes over, causing the honey to slide down the wall and pool at the bottom of the extractor.
Once the process is complete, the beekeeper opens the honey gate to drain the pure, filtered honey into buckets or other containers for bottling. The empty, undamaged combs are then returned to the bees.
Common Types of Honey Extractors
The primary distinction between extractors lies in how they are powered. This choice directly impacts the efficiency and scale of the honey harvesting operation.
Manual Extractors
A manual extractor is powered by a hand crank. The beekeeper must physically turn the crank to generate the centrifugal force needed to spin the frames.
These are excellent for hobbyists with a small number of hives, offering a cost-effective and simple solution for honey harvesting.
Electric Extractors
An electric extractor uses a motor to spin the basket, automating the most labor-intensive part of the process.
With the flip of a switch, the motor spins the frames at a consistent, high speed. This significantly reduces physical effort and is far more efficient for beekeepers managing multiple colonies.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting an extractor depends entirely on the scale of your beekeeping and your personal goals.
- If your primary focus is hobby beekeeping with a few hives: A manual extractor is a practical and economical choice that achieves the core goal of preserving your combs.
- If your primary focus is efficiency or commercial-level production: An electric extractor is a necessary investment that dramatically reduces labor and speeds up your harvest.
Ultimately, the honey extractor is a cornerstone of modern beekeeping that enables a sustainable and productive relationship between the beekeeper and the hive.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Manual Extractor | Electric Extractor |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | Hobbyists, Small-Scale Beekeepers | Commercial Apiaries, Large-Scale Operations |
| Operation | Hand-Cranked | Motor-Driven |
| Key Benefit | Cost-Effective, Simple to Use | High Efficiency, Saves Labor & Time |
| Core Principle | Centrifugal Force | Centrifugal Force |
Ready to scale your honey production? For commercial apiaries and distributors, the right equipment is key to efficiency and profitability. HONESTBEE supplies durable, high-performance honey extractors and a full range of beekeeping supplies through our wholesale-focused operations. Let us help you equip your business for success—contact our team today to discuss your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 8-Frame Electric Self-Reversing Honey Extractor Spinner for Commercial Honey Extraction Equipment
- HONESTBEE 3-Frame Manual Acrylic Honey Extractor
- Electric 8 Frame Honey Spinner Extractor Equipment for Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE 72 Frame Industrial Electric Honey Extractor for Beekeeping
- 2 Frame Stainless Steel Manual Honey Spinner Extractor for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- What operational benefits do motorized honey extractors provide? Scale Your Harvest Efficiency
- What are the core functions of an industrial 12-frame honey extractor? Boost Efficiency and Hive Resource Conservation
- Why is a centrifugal honey extractor considered core equipment? Boost Your API's Efficiency and Yield
- What makes automated honey extractors adaptable to different beekeeping needs? Precision Tuning for Commercial Success
- How does a honey extractor contribute to the honey harvesting process? Maximize Your Yield and Preserve Bees' Energy



















