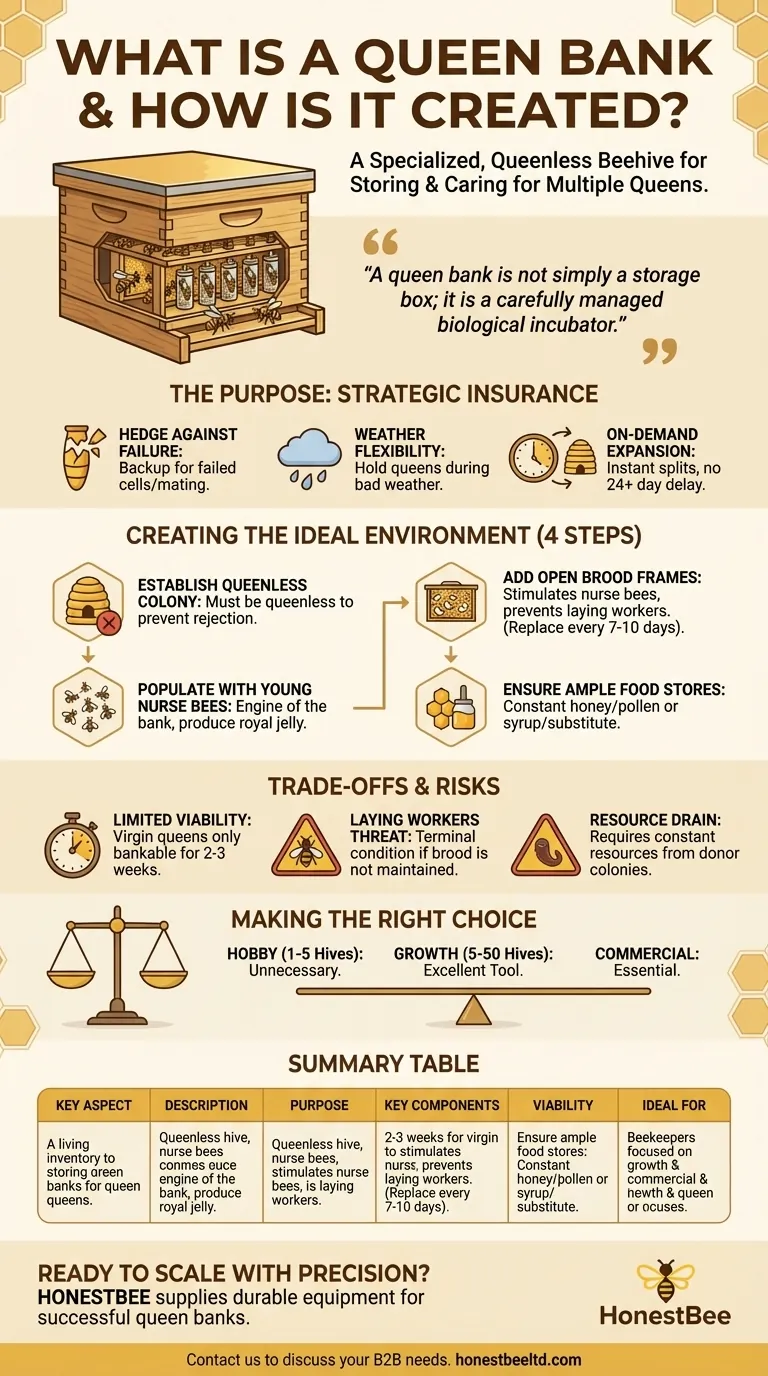
In short, a queen bank is a specialized, queenless beehive created to store and care for multiple queens. It is populated with young nurse bees and contains frames of open brood, which stimulates the bees to feed the caged queens or developing queen cells. This system allows a beekeeper to hold queens in reserve, ready for introduction into other colonies.
A queen bank is not simply a storage box; it is a carefully managed biological incubator. It leverages the bees' instinct to nurture royalty, providing a strategic advantage for timing splits, replacing failed queens, and managing apiary growth.

The Purpose of a Queen Bank: Strategic Insurance
A queen bank serves as a living inventory of one of your most valuable assets. It transforms queen management from a reactive process into a proactive strategy.
Hedging Against Failure
Not all queen cells are viable, and not all virgin queens successfully mate. Banking extra queens or cells ensures you have immediate replacements available without losing weeks of colony progress.
Gaining Weather Flexibility
A queen's mating flight is highly dependent on good weather. If a queen emerges during a long period of rain and cold, a queen bank allows you to safely hold her until conditions improve for her nuptial flight.
Enabling On-Demand Expansion
With ready-to-go queens, you can make splits or requeen failing hives at the optimal moment. This eliminates the 24+ day delay required to raise a new queen from an egg, preventing significant breaks in the colony's brood cycle.
Creating the Ideal Banking Environment
The success of a queen bank hinges on creating a very specific social environment that mimics a hive that is desperately trying to raise a new monarch.
Step 1: Establish a Queenless Colony
This is the non-negotiable first step. The presence of a laying queen's pheromones would cause the bees to reject and kill any other queens or queen cells you introduce. A queen bank must be and remain queenless.
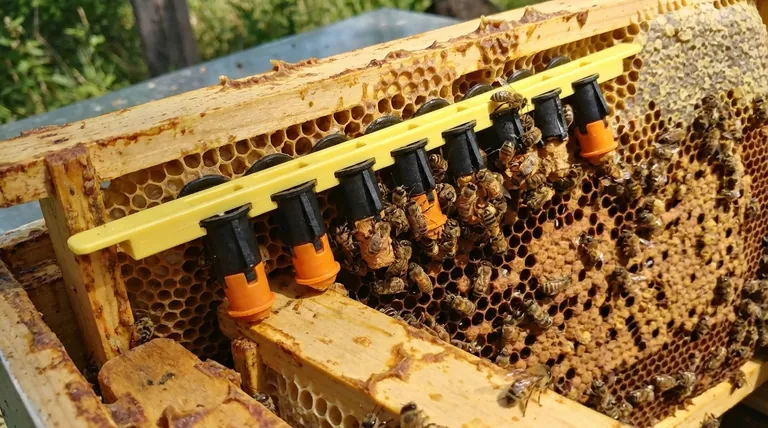
Step 2: Populate with Young Nurse Bees
Young bees, or nurse bees, are the engine of the bank. They are the ones who produce royal jelly and will instinctively feed the developing queen cells or caged queens through the screen. A good method is to shake bees from frames of open brood from several strong hives.
Step 3: Add Frames of Open Brood
A frame containing eggs and young larvae is the "magnet" that holds the bank together. The pheromones from this open brood signal to the nurse bees that there is work to do, stimulating their glands and preventing them from becoming laying workers. This frame must be replaced every 7-10 days.
Step 4: Ensure Ample Food Stores
Supporting numerous queens is resource-intensive. The bank must have constant access to frames of pollen and honey or be fed a steady supply of 1:1 sugar syrup and a pollen substitute.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
While powerful, a queen bank is a delicate system that requires consistent management and awareness of its limitations.
Limited Viability Window
A queen bank is not a long-term solution. Ripe queen cells must be used shortly after emerging. Virgin queens can only be "banked" for about two to three weeks before their mating success and future laying potential begin to decline significantly.
The Constant Threat of Laying Workers
If you fail to regularly add a new frame of open brood, the colony's queenless state will eventually trigger some worker bees to begin laying unfertilized (drone) eggs. This is a terminal condition for the colony if not caught very early.
It's a Resource Drain
A queen bank is a parasite on your apiary. It requires a constant influx of resources—bees, brood, and food—from your other healthy, productive colonies. This can weaken donor hives if not managed with care.
Making the Right Choice for Your Apiary
Whether you need a queen bank depends entirely on the scale and goals of your beekeeping operation.
- If your primary focus is hobby beekeeping (1-5 hives): A dedicated bank is likely unnecessary. Focus on timing your splits to use queen cells immediately after they are capped.
- If your primary focus is growth and expansion (5-50 hives): A small bank in a 5-frame nucleus box is an excellent tool for managing queens for requeening and making splits efficiently.
- If your primary focus is commercial queen rearing: Large, multi-story queen banks are an essential and non-negotiable piece of equipment for managing inventory and fulfilling customer orders.
By understanding how to create and manage this living reserve, you can shift from simply keeping bees to strategically directing their future.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | A living inventory of queens for strategic insurance and on-demand expansion. |
| Key Components | Queenless hive, young nurse bees, frames of open brood, ample food. |
| Viability Window | 2-3 weeks for virgin queens; not a long-term storage solution. |
| Ideal For | Beekeepers focused on growth (5-50+ hives) and commercial queen rearing. |
Ready to scale your beekeeping operation with precision?
A queen bank is a cornerstone of professional apiary management, allowing you to proactively replace failing queens and time your splits perfectly. For commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors, having the right supplies is just as critical as having the right strategy.
HONESTBEE supplies the durable, high-quality beekeeping equipment and supplies you need to build and maintain successful queen banks and thriving apiaries. Our wholesale-focused operations are designed to support your growth.
Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss your equipment needs and let us help you build a more resilient and productive beekeeping business.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- JZBZ Langstroth Queen Rearing Frame for Beekeeping
- Stainless Steel Queen Grafting Tool for Beekeeping and Bee Queen Grafting
- Professional Queen Catcher and Introduction Queen Cage
- Heavy Duty Stainless Steel Queen Bee Catcher Clip
- Stainless Steel Honey Bee Smoker Hive and Honeycomb Smoker for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- How long can a hive survive queenless? The Critical Countdown to Save Your Colony
- What is the purpose of queen rearing frames? Master Controlled Queen Production for Your Apiary
- How long does it take for a virgin queen to mate and start laying eggs? A Beekeeper's Timeline Guide
- Why is it difficult to purchase queens during the production season? The Seasonal Demand Spike Explained
- What are orientation flights for virgin queens? The Essential Guide to Queen Bee Navigation













