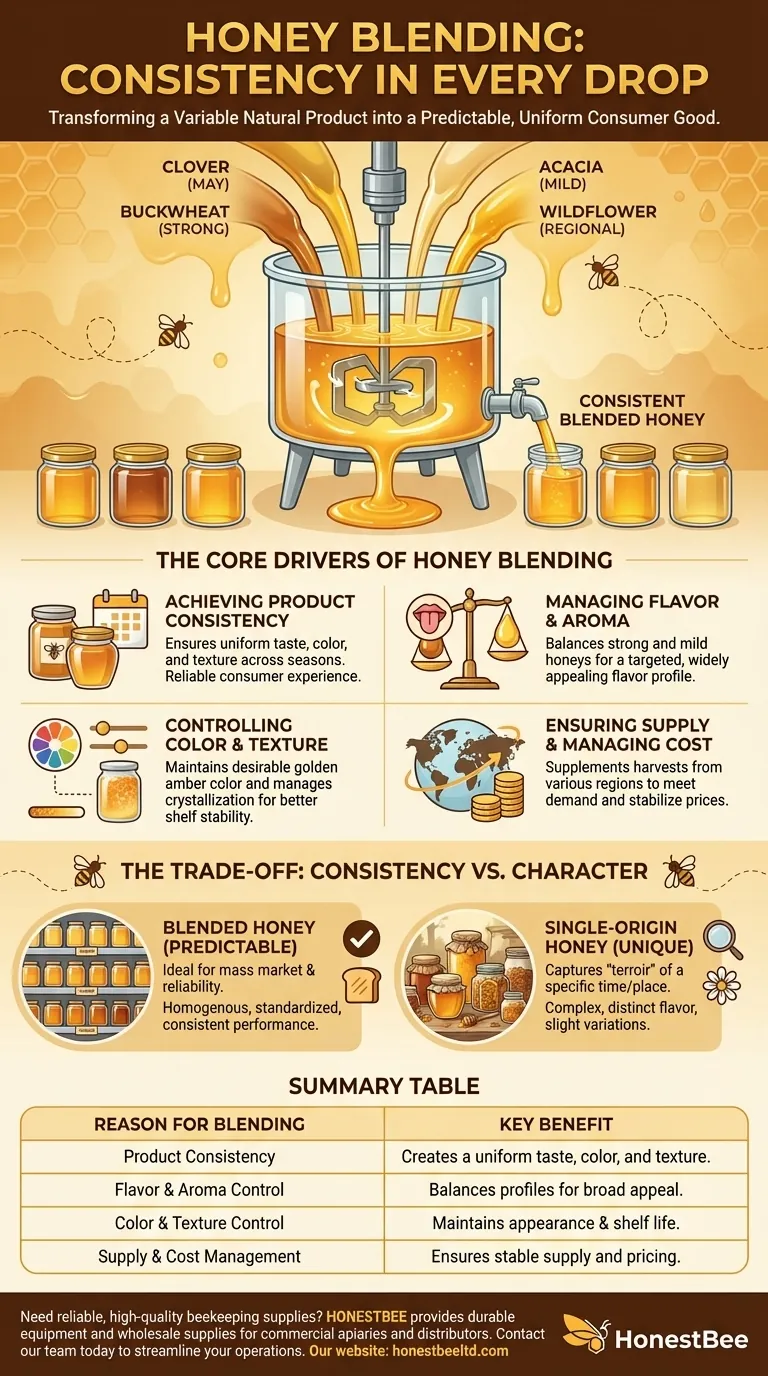
At its core, honey blending is the process of mixing honeys from different floral or geographical origins. This is done primarily by commercial producers to create a final product with a consistent flavor, color, and texture that consumers can rely on, jar after jar.
The central purpose of honey blending is to transform a variable, natural product into a predictable, uniform consumer good. It prioritizes consistency over the unique character of single-origin honey.

The Core Drivers of Honey Blending
Understanding why producers blend honey reveals the difference between mass-market products and artisanal ones. Each reason addresses a specific challenge in bringing a natural product to a large-scale audience.
Achieving Product Consistency
Honey is a natural product, and its characteristics vary dramatically based on the season, weather, and the specific flowers bees visit. Blending allows producers to smooth out these natural variations. By mixing different batches, they can ensure the jar of clover honey you buy in December tastes exactly like the one you bought in May.
Managing Flavor and Aroma
Not all honey is created equal in taste. Some, like buckwheat honey, are strong and robust, while others, like acacia, are incredibly mild. A master blender can skillfully combine these to create a balanced, targeted flavor profile that appeals to the widest possible audience.
Controlling Color and Texture
Consumers have expectations for what honey should look and feel like. Blending helps maintain a specific, desirable color (e.g., a classic golden amber) and viscosity. It's also used to manage the rate of crystallization, a natural process that blending can help control for better shelf stability.
Ensuring Supply and Managing Cost
A single floral source might have a poor harvest one year due to drought or other environmental factors. Blending allows producers to supplement their supply with honey from other regions or even countries. This practice ensures they can meet market demand and helps keep the final price stable for consumers.
The Trade-off: Consistency vs. Character
The decision to blend honey creates a fundamental trade-off between a predictable product and a unique one. Neither approach is inherently "better," but they serve entirely different purposes.
The Predictability of Blended Honey
For large-scale food production or for a consumer who wants a reliable sweetener, blended honey is ideal. It delivers a homogenous, standardized product that performs consistently in recipes and always tastes the same on your toast. This is its primary strength.
The Uniqueness of Single-Origin Honey
Single-origin, unblended honey is the opposite. It captures the unique essence of a specific time and place—the "terroir" of its environment. Its flavor profile is a direct reflection of the local flora. This honey offers complexity and character, but it will have slight variations from one harvest to the next, which is part of its appeal to enthusiasts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice between blended and single-origin honey depends entirely on what you value in the product.
- If your primary focus is consistency and a predictable taste: Blended honey from a major brand is engineered to deliver exactly that experience reliably and affordably.
- If your primary focus is experiencing unique flavors and supporting local apiaries: Seek out single-origin, raw honeys to explore the distinct taste profiles created by specific ecosystems.
Ultimately, understanding why honey is blended empowers you to choose the product that perfectly suits your palate and purpose.
Summary Table:
| Reason for Blending | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Product Consistency | Creates a uniform taste, color, and texture across batches. |
| Flavor & Aroma Control | Balances strong and mild honeys for a targeted, appealing profile. |
| Color & Texture Control | Maintains a specific appearance and manages crystallization. |
| Supply & Cost Management | Ensures stable supply and pricing despite seasonal variations. |
Need reliable, high-quality beekeeping supplies for your honey production? Whether you're a commercial apiary focused on consistency or a distributor sourcing for the market, HONESTBEE provides the durable equipment and wholesale supplies you need to succeed. Contact our team today to discuss your requirements and streamline your operations.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Professional Thermostatic Conical Honey Melter
- 10L Stainless Steel Electric Honey Press Machine
- HONESTBEE 72 Frame Industrial Electric Honey Extractor for Beekeeping
- Honey Concentrating Vacuum Heating Thickening Machine Dehumidifier for Honey
- 8-Frame Electric Self-Reversing Honey Extractor Spinner for Commercial Honey Extraction Equipment
People Also Ask
- What equipment is commonly used for heating and processing honey? Essential Tools for Every Beekeeper
- What is the effect of heating on honey? Preserve Quality with Controlled Warming
- Why is it important to heat honey slowly and evenly? Preserve Flavor, Nutrients & Value
- What are the negative effects of overheating honey? Preserve Your Honey's Natural Quality
- Is it safe to heat crystallized honey? Restore Your Honey's Liquid State Safely



















