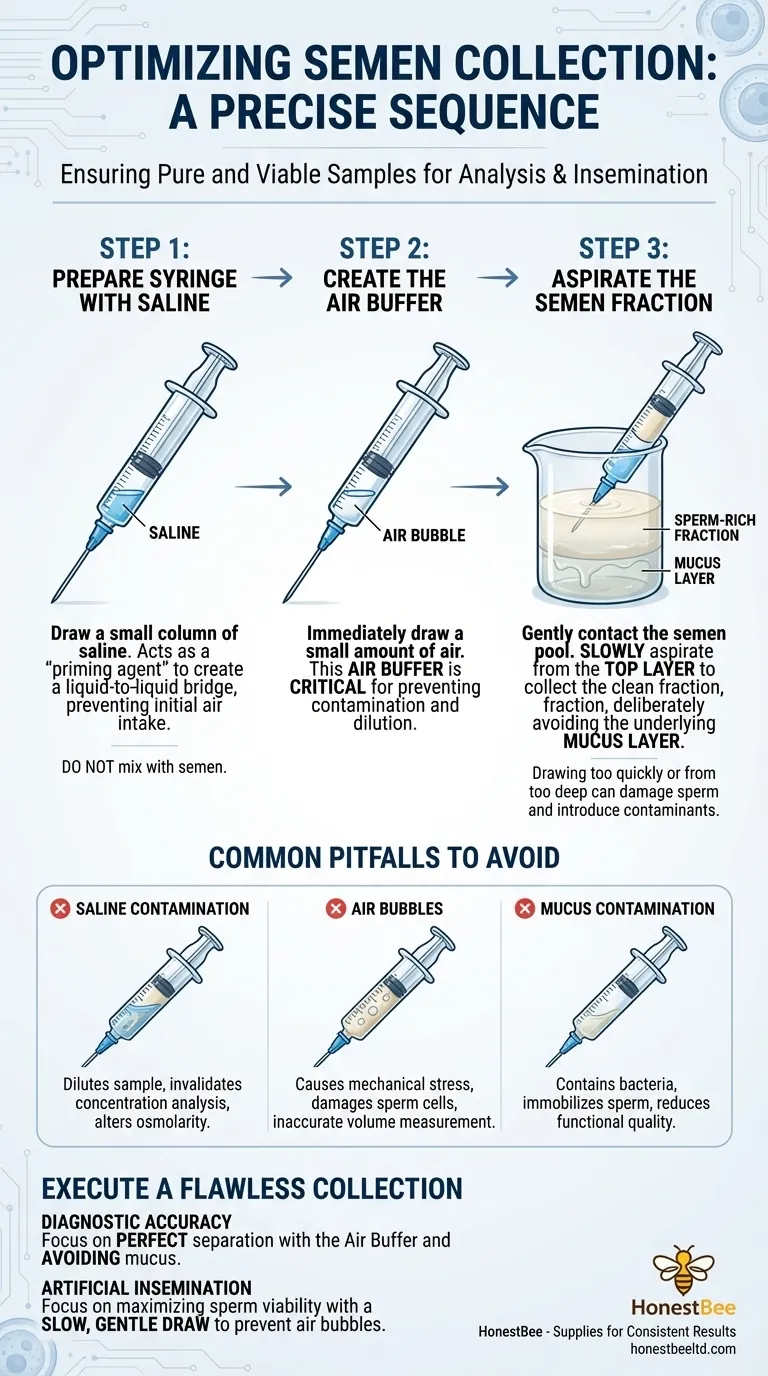
To ensure proper semen collection for each load, you must follow a precise sequence. First, draw a small column of saline into the syringe, followed immediately by an air bubble to act as a separator. When collecting, make gentle contact with the semen pool using the saline at the tip, avoid the underlying mucus layer, and draw the semen in slowly and carefully to prevent aspirating any additional air.
The core challenge in semen collection is not simply gathering a sample, but preserving its integrity. The key is to use a buffered collection technique—employing saline and air as strategic barriers—to protect the semen from contamination and physical damage.

The Goal: A Pure and Viable Sample
Proper collection technique is fundamental to the value of any semen sample. Whether for diagnostic analysis or for artificial insemination, the goal is to obtain a sample that is a true representation of the ejaculate, free from contaminants and cellular damage.
Every step in the collection process is designed to mitigate a specific risk. Deviating from the procedure can introduce variables that compromise the results.
Step 1: Preparing the Syringe with Saline
The first step is to draw a small amount of saline into the syringe. This is not meant to be mixed with the semen.
The saline acts as a "priming" agent. A tiny drop at the syringe tip helps create a liquid-to-liquid bridge when you make contact with the semen pool, preventing the immediate intake of air.
Step 2: Creating the Air Buffer
Immediately after drawing the saline, you must draw a small amount of air into the syringe. This creates a visible air space or bubble.
This air buffer is the most critical element for preventing contamination. It serves as a physical barrier that separates the main saline column from the semen sample you are about to collect, ensuring the sample is not diluted or chemically altered.
Step 3: Aspirating the Semen Fraction
With the syringe prepared, the final step is the collection itself. Position the syringe tip so it just touches the surface of the semen pool.
Gently submerge the tip and begin to draw the semen into the syringe slowly and steadily. It is crucial to aspirate from the top layer of the sample.
The goal is to collect the clean, sperm-rich fraction while deliberately avoiding the viscous, underlying mucus layer, which can trap and immobilize sperm. Drawing slowly also prevents the accidental intake of air bubbles, which can damage sperm cells.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Understanding what can go wrong is as important as knowing the correct procedure. Each common mistake directly impacts the quality of the sample.
The Risk of Saline Contamination
If you forget to create the air buffer between the saline and the semen, you will dilute your sample.
This dilution alters sperm concentration, which invalidates any subsequent analysis of sperm count or density. It can also change the sample's osmolarity, potentially shocking and damaging the sperm cells.
The Danger of Air Bubbles
Aspirating the sample too quickly or failing to keep the syringe tip submerged will introduce air bubbles into the semen column.
These bubbles cause mechanical stress and shearing forces that can damage or kill sperm cells, reducing motility and viability. They also make it impossible to measure the collected volume accurately.
The Problem with Mucus Contamination
Collecting from too deep within the sample pool risks drawing in the gelatinous mucus fraction.
Mucus can contain bacteria, cellular debris, and substances that immobilize sperm. Its presence renders a sample suboptimal for both analysis and insemination, as it drastically reduces the functional quality of the spermatozoa.
Executing a Flawless Collection
Your specific goal will determine which aspect of the procedure is most critical.
- If your primary focus is diagnostic accuracy: Strict separation is paramount, so perfecting the use of the air buffer and completely avoiding the mucus layer is essential for a representative sample.
- If your primary focus is artificial insemination: Maximizing sperm viability is key, so your technique must prioritize a slow, gentle draw that avoids creating any air bubbles within the semen column.
Mastering this multi-step technique transforms semen collection from a routine task into a precise scientific procedure.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Purpose | Critical Detail |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Draw Saline | Create liquid bridge | Prevents initial air intake |
| 2 | Draw Air Bubble | Create separation barrier | Prevents saline dilution of sample |
| 3 | Aspirate Semen | Collect sperm-rich fraction | Draw slowly from top layer, avoid mucus |
Ensure every sample collection is a success. For commercial apiaries and distributors, reliable equipment is as crucial as precise technique. HONESTBEE supplies the durable, precision beekeeping supplies and equipment you need for consistent results in breeding and hive management. Contact our experts today to discuss wholesale solutions for your operation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Professional Galvanized Hive Strap with Secure Locking Buckle for Beekeeping
- Metal Queen Bee Excluder for Beekeeping
- Wooden Queen Bee Excluder for Beekeeping
- Plastic Beekeeping Honey Bee Larvae Grafting Tools for Queen Rearing and Chinese Grafting
- Premium Wood Framed Metal Wire Queen Bee Excluder
People Also Ask
- How does the quality of queen bees impact the productivity and economic viability of a commercial apiary? Guide to Yield
- What are the benefits of artificial insemination in beekeeping? Unlock Precision Genetics for Superior Bee Health
- What is the role of a high-precision micro-syringe in drone semen collection? Mastering Precision Breeding
- What challenges does the use of artificial insemination equipment pose to honeybee colonies? Balancing Breeding & Vigor
- Why is a stereo microscope necessary for the artificial insemination of queen bees? Achieve Surgical Precision
- What is the role of artificial insemination equipment in bee genetic improvement programs? Master Precision Breeding
- How are capillary tubes utilized for the cross-regional transport of honeybee semen? Secure Your Genetic Exchange
- How should the syringe tip be maintained during semen collection? Prevent Sample Dilution and Osmotic Shock



















