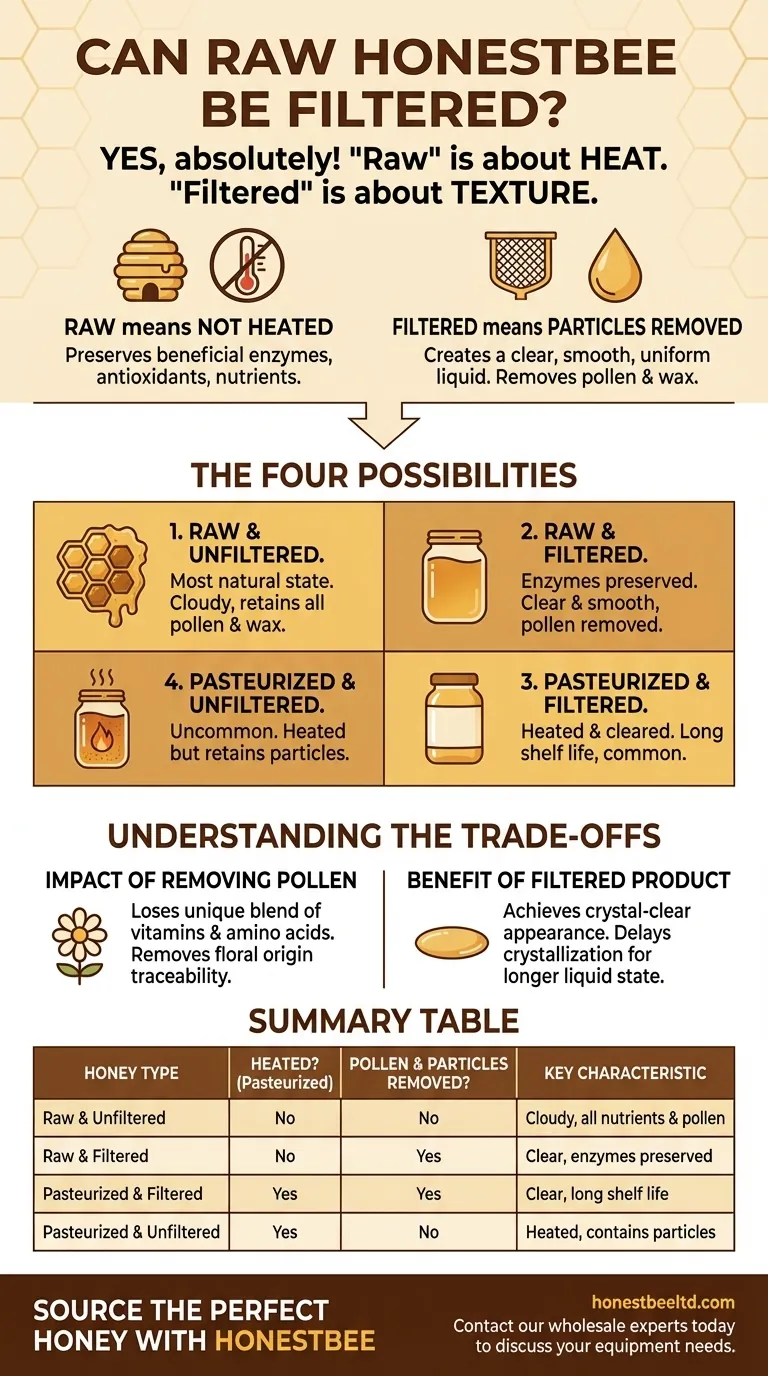
Yes, raw honey can absolutely be filtered. The term "raw" refers to whether the honey has been heated (pasteurized), while "filtered" refers to whether physical particles like pollen and wax have been removed. These are two separate processes, meaning you can have honey that is both raw and filtered.
The core distinction is simple: "raw" is about heat, and "filtered" is about texture. Understanding this difference is the key to knowing exactly what kind of honey you are buying.

Deconstructing the Labels: Raw vs. Filtered
To make an informed choice, it's crucial to understand what each term signifies independently. A jar of honey can be any combination of these two attributes.
What "Raw" Truly Means
"Raw" signifies that the honey has not been pasteurized. This means it hasn't been heated to high temperatures that can destroy the beneficial enzymes, antioxidants, and other delicate nutrients naturally present.
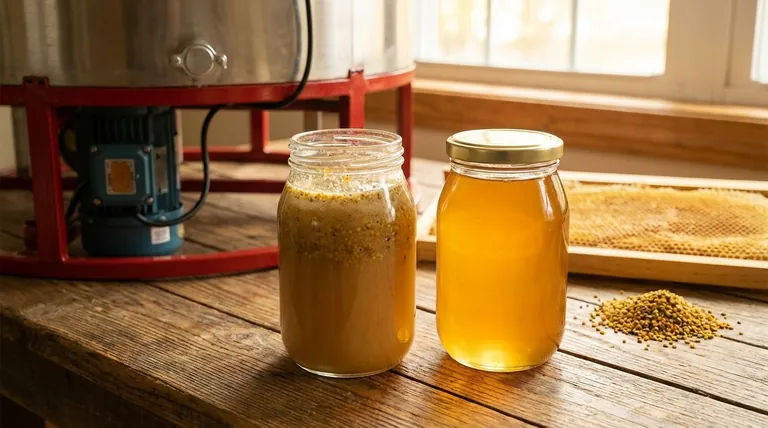
Raw honey is essentially honey as it exists in the beehive, often only lightly strained to remove large debris like beeswax or dead bees.
What "Filtered" Truly Means
"Filtered" is a physical process that removes fine particles. This is done by passing the honey through a filter to create a clear, smooth, and uniform liquid.
This process removes things like honeycomb bits, propolis, and, most notably, grains of pollen.
The Four Possibilities
This leaves us with four potential types of honey you might encounter:
- Raw and Unfiltered: The most natural state. It is not heated and contains all its natural pollen and wax particles.
- Raw and Filtered: This honey is not heated, preserving its enzymes, but has had pollen and other fine particles removed for clarity.
- Pasteurized and Filtered: The most common type found in major supermarkets. It is heated and filtered for a long shelf life and a perfectly clear appearance.
- Pasteurized and Unfiltered: An uncommon combination, but possible. The honey is heated but retains its solid particles.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between filtered and unfiltered raw honey involves a direct trade-off between aesthetic preference and nutritional completeness.
The Impact of Removing Pollen
Filtering almost always removes the pollen naturally present in the honey. While not a major source of nutrients in the grand scheme, pollen is valuable for two key reasons.
First, it contains a unique blend of vitamins and amino acids. Second, pollen is the primary way to trace honey's floral and geographical origin, verifying its source.
The Benefit of a Clear Product
The primary reason to filter honey is to achieve a crystal-clear appearance and a perfectly smooth texture. Many consumers prefer this look.
Additionally, removing the fine particles that act as "seeds" for crystallization helps the honey remain liquid for longer.
The Cloudy but Complete Alternative
Unfiltered honey retains all of its natural components. The suspended pollen and bits of wax make it appear cloudy or opaque.
This type of honey is favored by those who want the full spectrum of compounds the hive has to offer and appreciate the more complex texture and faster crystallization.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your ideal honey depends entirely on your priorities. By understanding the terminology, you can select the product that best aligns with your needs.
- If your primary focus is maximum nutritional benefit and traceability: Choose raw, unfiltered honey to ensure all natural components, including pollen, are present.
- If your primary focus is a smooth texture without sacrificing enzymes: Choose raw, filtered honey for a clear liquid that has not been damaged by heat.
- If your primary focus is consistency and a long-lasting liquid sweetener: Standard pasteurized and filtered honey offers the longest shelf stability and clearest look.
Ultimately, choosing your honey is about deciding what you value most: the complete, natural product or the refined, clear liquid.
Summary Table:
| Honey Type | Heated? (Pasteurized) | Pollen & Particles Removed? | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Raw & Unfiltered | No | No | Cloudy, retains all nutrients & pollen |
| Raw & Filtered | No | Yes | Clear, smooth, enzymes preserved |
| Pasteurized & Filtered | Yes | Yes | Clear, long shelf life, common in stores |
| Pasteurized & Unfiltered | Yes | No | Uncommon; heated but contains particles |
Source the Perfect Honey for Your Customers
As a commercial apiary or distributor, understanding these nuances is key to stocking the right products. HONESTBEE supplies the high-quality beekeeping supplies and equipment you need to produce and process honey exactly to your specifications, whether you aim for raw, filtered, or any combination.
Let us help you meet market demand with confidence. Contact our wholesale experts today to discuss your equipment needs and sourcing strategy.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HONESTBEE 72 Frame Industrial Electric Honey Extractor for Beekeeping
- Plastic Honey Gate Spout with Wing Nut for Beekeeping Honey Bucket
- 10L Stainless Steel Electric Honey Press Machine
- Electric Honey Press Machine for Squeezing Honey Comb Press Equipment
- 6 Frame Manual Stainless Steel Honey Extractor Beekeeping Equipment
People Also Ask
- How is raw honey filtered? A Guide to Clean, Natural Honey Production
- What role does low-damage filtration equipment play in the processing of honey and propolis? Preserve Bioactive Integrity
- Why is a 0.5 mm aperture stainless steel sieve required for honey sample pretreatment? Ensure Accurate Lab Analysis
- How does honey filtering and storage equipment affect market value? Maximize Profits with Single-Origin Quality
- Why is honey pollen filtration equipment regulated? Protect Your Trade Integrity & Traceability
- Why is the implementation of mechanized Honey Filtering Machines necessary? Scale Your Honey Quality and Production
- How does high-precision honey filtration and clarification equipment contribute to the value of commercial honey products?
- Why is filtering honey an important step in honey processing? Ensure Purity, Clarity & Marketability



















