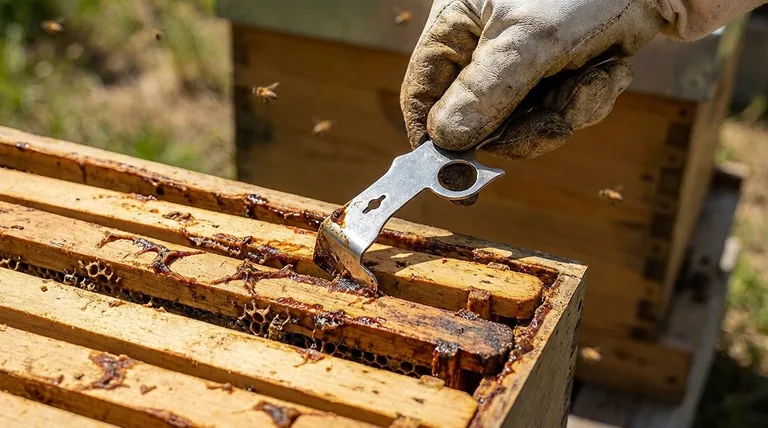
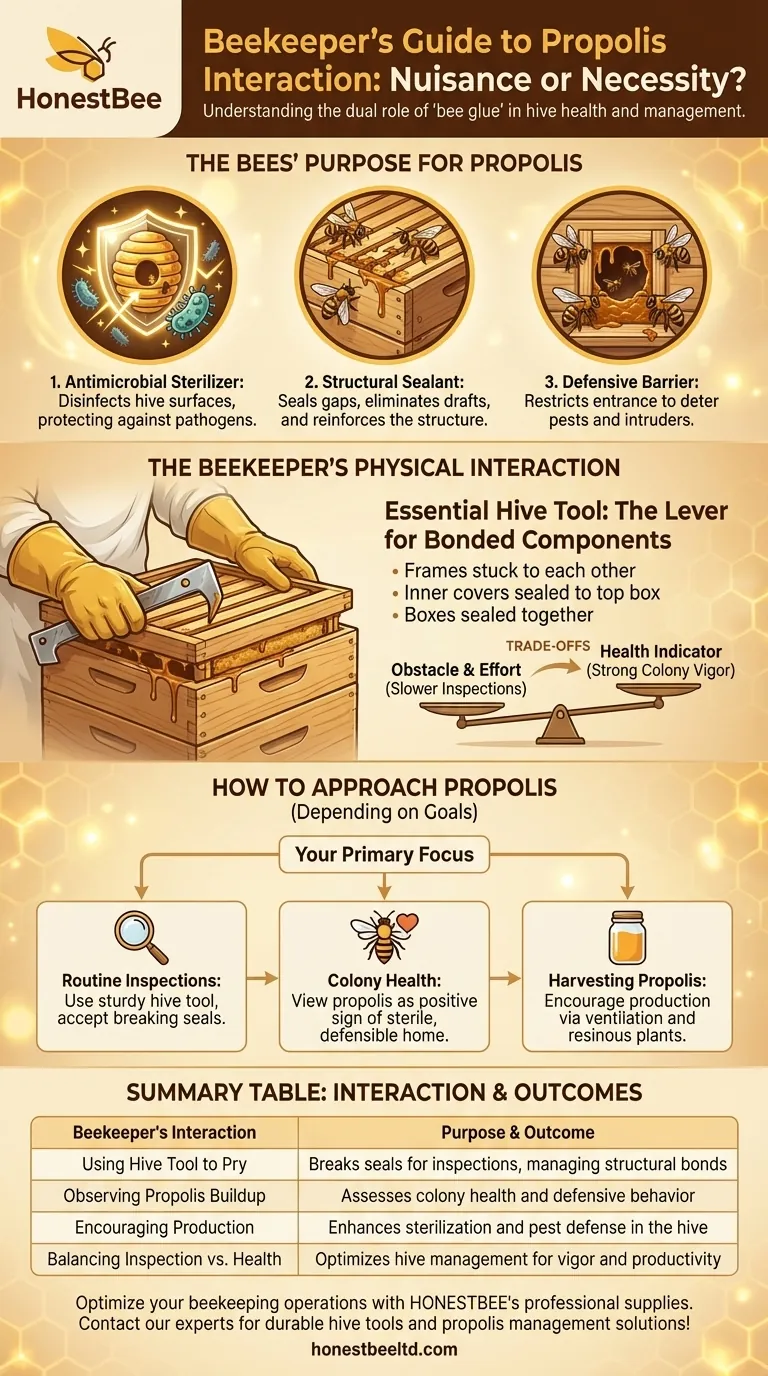
From a beekeeper's perspective, propolis is both a structural nuisance and a powerful indicator of colony health. The most direct interaction involves using a hive tool to physically pry apart hive components like frames, boxes, and covers that bees have sealed together with this sticky, resinous substance.
Propolis, often called "bee glue," is a powerful antimicrobial resin bees use to sterilize and seal their hive. For the beekeeper, this means managing a substance that cements the hive together while also recognizing it as a vital component of colony health and defense.

The Purpose of Propolis in the Colony
Before understanding the beekeeper's actions, it's critical to understand the bees' intent. Propolis is not a random byproduct; it is a manufactured substance with several clear functions.
A Natural Sterilizer
Honey bees use propolis to coat the interior surfaces of the hive. Its potent antimicrobial properties create a sterile environment, effectively disinfecting the colony cavity and protecting it from pathogens.
A Structural Sealant
Bees are meticulous architects. They use propolis as a building material to seal cracks and gaps in the hive, eliminating drafts and reinforcing the structure.
A Defensive Barrier
To protect against intruders, bees use propolis to restrict or narrow the hive entrance. This makes the colony easier to defend against pests and robbing bees.
The Beekeeper's Physical Interaction
A beekeeper's work is made physically more demanding by the very substance that keeps the bees' home secure and clean.
The Essential Hive Tool
The single most common interaction with propolis involves the hive tool. This simple metal bar is used as a lever to pry apart and separate any components the bees have glued together.
Managing Bonded Components
Frames become stuck to each other and to the hive boxes. Inner covers are sealed to the top box, and boxes are sealed to the ones below them. Every inspection requires breaking these propolis seals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Working with propolis is a classic example of balancing the hive's needs with the beekeeper's management goals.
The "Glue" Problem
From a purely mechanical standpoint, propolis is an obstacle. It makes hive inspections slower and more difficult, requiring force that can disrupt the colony.
The Health Indicator
Conversely, a hive with abundant propolis is often a strong one. Its presence shows the colony is actively defending and sterilizing its home, which is a clear sign of a healthy, vigorous workforce.
Proactive Management
Some beekeepers may even encourage its production. By increasing ventilation or placing hives near resinous plants, a beekeeper can help bees access the materials needed to create more propolis, enhancing colony health.
How to Approach Propolis in Your Hives
Your interaction with propolis depends entirely on your immediate goal for the hive.
- If your primary focus is routine inspections: Always have a sturdy hive tool ready and accept that breaking propolis seals is a standard, necessary part of the process.
- If your primary focus is colony health: View the presence of propolis as a positive sign that your bees are actively maintaining a sterile and defensible home.
- If your primary focus is harvesting propolis: Consider management techniques that encourage its production, recognizing its value as a hive product.
Ultimately, working with propolis is a fundamental aspect of beekeeping that requires both physical effort and an appreciation for the colony's natural instincts.
Summary Table:
| Beekeeper's Interaction with Propolis | Purpose & Outcome |
|---|---|
| Using a Hive Tool to Pry Components | Breaks seals for inspections, managing structural bonds |
| Observing Propolis Buildup | Assesses colony health and defensive behavior |
| Encouraging Production (e.g., via ventilation) | Enhances sterilization and pest defense in the hive |
| Balancing Inspection vs. Health Goals | Optimizes hive management for vigor and productivity |
Optimize your beekeeping operations with HONESTBEE's professional supplies. As a trusted wholesale partner for commercial apiaries and distributors, we provide durable hive tools, protective gear, and equipment designed to handle propolis-rich hives efficiently. Enhance your colony health and productivity—contact our experts today to discuss bulk pricing and tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HONESTBEE Advanced Ergonomic Stainless Steel Hive Tool for Beekeeping
- Professional Multi-Function Stainless Steel Hive Tool
- HONESTBEE Premium Italian Style Hive Tool with Hardwood Handle
- HONESTBEE Professional Long Handled Hive Tool with Precision Cutting Blade
- Multi-Function Plier-Style Frame Grip Hive Tool
People Also Ask
- What is the significance of professional hive-making tools? Scale Your Stingless Bee Farm with Precision Equipment
- What are the primary functions of a stainless steel hive tool? Essential Equipment for Professional Beekeeping
- How does the hive splitting process contribute to colony management? Master Your Apiary Recovery Strategies
- Why is it important to compare the progress of different hives? A Beekeeper's Key Diagnostic Tool
- What is the hole in a hive tool for? A Multi-Tool for Apiary Repairs and Maintenance



















