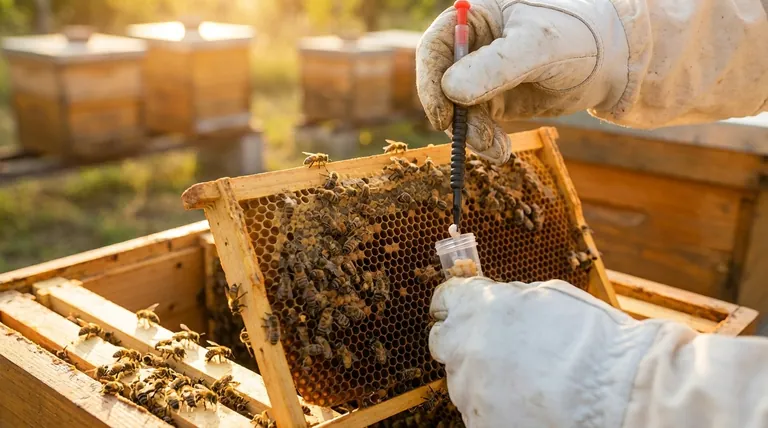
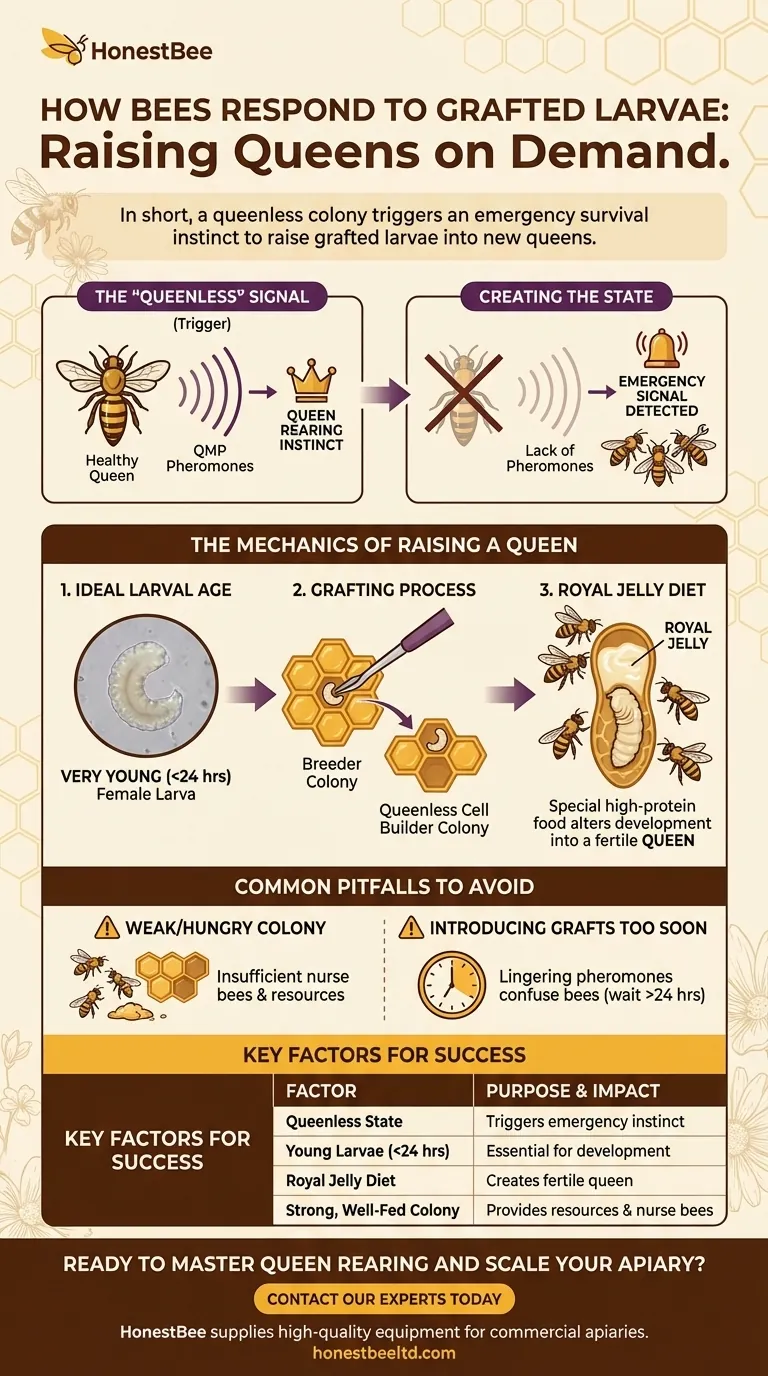
In short, a bee colony will raise grafted larvae into new queens. For this to occur, the colony must be in a "queenless" state, meaning the worker bees perceive that their existing queen is missing or failing. This triggers an emergency survival instinct to create a replacement.
The core principle is that beekeepers can leverage the honeybee's natural emergency response. By creating a queenless environment and providing suitable young larvae through grafting, we can direct the colony's instinct to produce new queens on demand.

The "Queenless" Signal: Triggering the Instinct
The entire process hinges on making a colony believe it needs a new monarch. This is not a conscious decision by the bees but an instinctive reaction to specific chemical signals.
The Role of Queen Pheromones
A healthy, laying queen constantly produces a complex chemical cocktail known as Queen Mandibular Pheromone (QMP). This pheromone spreads throughout the hive via contact between bees.
The presence of QMP signals to the entire colony that a viable queen is present and all is well. This suppresses the queen-rearing instinct in worker bees and also prevents their own ovaries from developing.
Creating the Queenless State
When a beekeeper removes the queen, the flow of her pheromones ceases. Within hours, the colony detects this absence.
This lack of QMP is the critical trigger. It signals an emergency and compels the nurse bees to initiate the process of raising new queens to ensure the colony's survival.
The Mechanics of Raising a Queen
Once the emergency is declared, the worker bees get to work immediately, and the grafted larvae become the focus of their efforts.
The Importance of Larval Age
Worker bees know they cannot turn an old larva or a pupa into a queen. They must start with a very young female larva, ideally one that is less than 24 hours old.
Grafting is simply the manual process of selecting these perfectly-aged larvae from a desirable "breeder" queen's colony and moving them into the queenless "cell builder" colony.
The Power of Royal Jelly
Upon accepting a grafted larva, the nurse bees begin constructing a special, oversized cell that hangs vertically—the queen cell.
They then feed the larva an exclusive, high-protein diet of royal jelly. This special food is what fundamentally alters the larva's development, switching its genetic path from becoming a worker to becoming a fully developed queen.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Success in queen rearing is not guaranteed. It requires understanding the biological needs of the colony and avoiding common mistakes.
A Weak or Hungry Colony
A colony with a small population, especially one with few young nurse bees, will struggle to raise quality queens. These young bees are the ones that produce the royal jelly.
Similarly, a colony without adequate pollen and nectar stores will not have the resources to invest in queen rearing. Proper feeding is crucial.
Introducing Grafts Too Soon
If you introduce grafted larvae immediately after removing the queen, the acceptance rate can be low. Lingering pheromones can confuse the bees.
It is best to wait at least a few hours, and often up to 24 hours, to ensure the colony is definitively in a queenless state and ready to accept the new larvae.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding this behavior allows beekeepers to manage and propagate their colonies effectively.
- If your primary focus is to raise new queens: Ensure your cell-builder colony is strong, well-fed, and definitively queenless for several hours before introducing the grafts.
- If your primary focus is to prevent swarming: Regularly check for natural queen cells, as their presence indicates the colony is preparing to create a new queen for swarming, not as an emergency.
- If your primary focus is simply understanding bee biology: Recognize that queen rearing is a powerful survival instinct triggered entirely by the absence of the queen's chemical signals.
By understanding and leveraging this natural emergency response, beekeepers can effectively propagate new, healthy queens for their apiaries.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Purpose & Impact |
|---|---|
| Queenless State | Triggers the colony's emergency instinct to raise a new queen. |
| Young Larvae (<24 hrs) | Essential for successful development into a queen; older larvae are rejected. |
| Royal Jelly Diet | Special food that alters larval development to create a fertile queen. |
| Strong, Well-Fed Colony | Provides the necessary nurse bees and resources for high-quality queen rearing. |
Ready to Master Queen Rearing and Scale Your Apiary?
Successfully grafting larvae and managing queenless colonies requires the right tools and equipment. HONESTBEE supplies commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with high-quality, wholesale-focused supplies—from grafting tools to full hive management systems.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our products can support your queen-rearing operations and improve your propagation success rates.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Black 2 Pack Beekeeper Queen Grafting Tool for Bee Queen Larva Transferring Needle
- Plastic Chinese Queen Grafting Tool for Bee Queen Rearing
- HONESTBEE Advanced Ergonomic Stainless Steel Hive Tool for Beekeeping
- Professional 3-Bar Frame Grip with Integrated Hive Tool
- No Grafting Queen Rearing Kit: System for Royal Jelly Production and Queen Rearing
People Also Ask
- What are the steps involved in using a queen grafting tool? A Guide to Successful Queen Rearing
- Why is a Chinese-style Grafting Needle used for honey bee larvae? Expert Tools for High-Success Queen Rearing
- How do wooden bars function within a grafting frame? Enhancing Queen Rearing Efficiency and Larval Survival
- Why does placing the grafting frame in the center of the beehive help? Boost Queen Rearing Success
- What should be done with extra queens from grafting? A Strategic Guide for Apiary Management
- What is the function of grafting tools in the production of virgin honeybee queens? Enhancing Larval Acceptance
- Why are specialized wooden rounding rods used in queen rearing? Master Precision Molding for High Acceptance Rates
- How do queen rearing frames and grafting needles function together? Master the Doolittle Method for High-Quality Queens



















