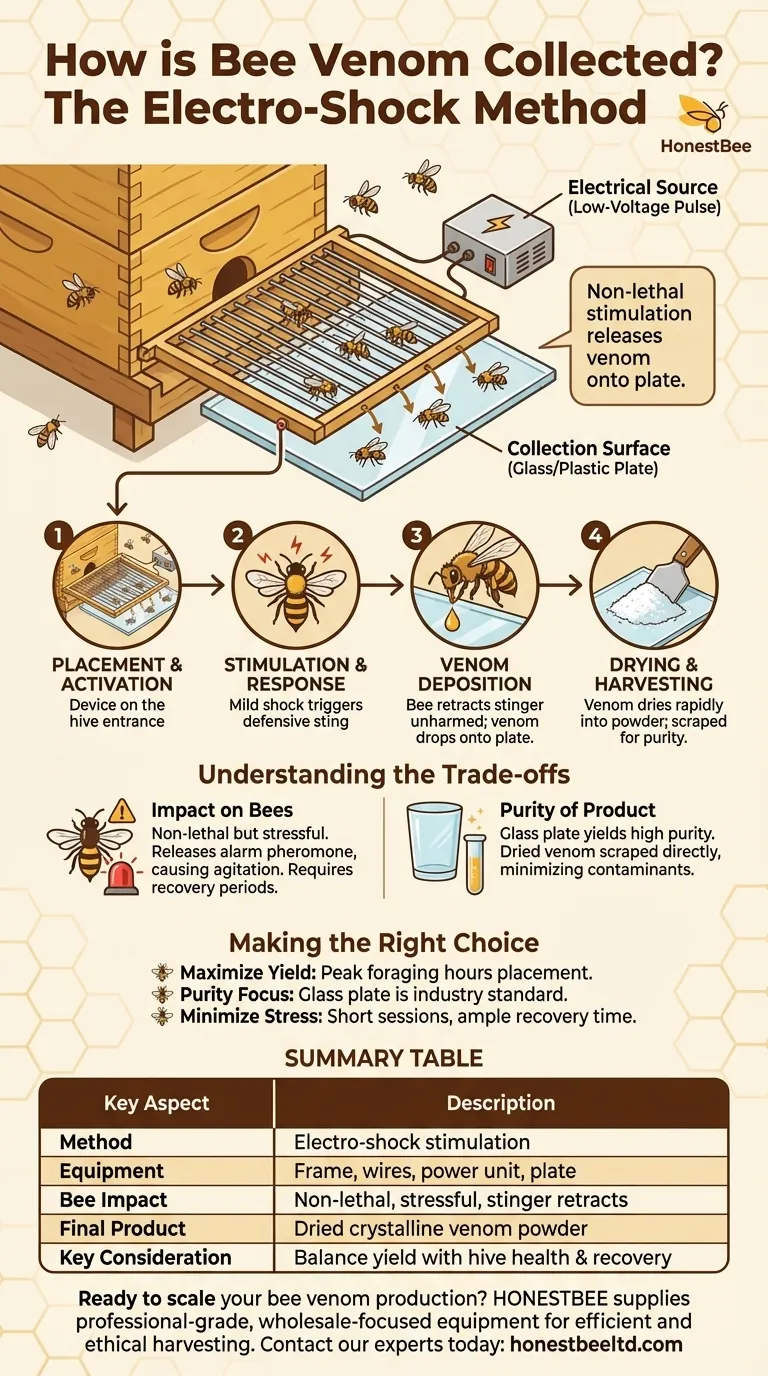
The electro-shock method for collecting bee venom operates by using a specialized frame placed at the hive entrance. This device generates a mild electrical current that stimulates bees to sting a collection surface, releasing their venom without being harmed in the process. The venom then dries on a glass or plastic plate and is later harvested.
The electro-shock method is an industry standard designed to be both efficient and non-lethal to the bees. It leverages the honeybee's natural defensive instinct in a controlled manner, allowing for the collection of pure, high-quality venom which is then harvested as a dry powder.
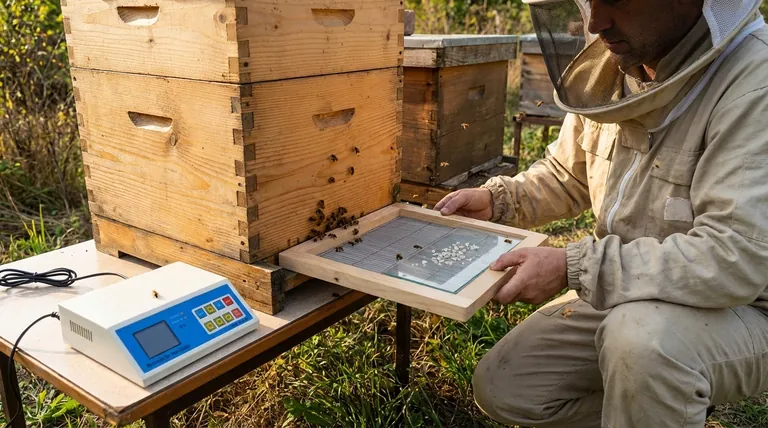

The Mechanics of the Collection Device
To understand the process, we must first look at the components of the specialized equipment used. The system is simple but highly effective.
The Collector Frame
The core of the device is a frame, often the size of a standard hive frame, with a series of parallel wires stretched across it. This frame is placed directly in the path of the bees.
The Electrical Source
A power unit provides a low-voltage, pulsed electrical current to the wires. The current is mild enough to irritate the bees without causing injury.
The Collection Surface
Beneath the grid of wires sits a collection plate. This is most commonly a sheet of glass, though thin plastic membranes can also be used. This is the surface the bees will walk on and ultimately sting.
The Step-by-Step Collection Process
The collection process is systematic, relying on predictable bee behavior when faced with a mild threat.
Placement and Activation
The entire apparatus is typically placed at the entrance of the beehive. As forager bees return to the hive, they must walk across the device. Once activated, the wires deliver the mild shock.
Stimulation and Response
The electrical sensation agitates the bees. Their natural defensive instinct is to sting the source of the irritation, which in this case is the collection plate directly beneath their feet.
Venom Deposition
Crucially, because the bee stings a hard, smooth surface like glass, its barbed stinger cannot get stuck. The bee deposits a droplet of venom and then retracts its stinger, allowing it to fly away unharmed.
Drying and Harvesting
Bee venom is approximately 88% water and dries very rapidly when exposed to air. On the collection plate, it turns into a whitish, crystalline substance. After the collection period is over and the device is removed, this dried venom is carefully scraped off the plate.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While effective, this method is not without its implications for the colony. Objectivity requires we acknowledge them.
Impact on the Bees
The method is designed to be non-lethal. However, the process is stressful for the colony. When a bee stings, it releases an alarm pheromone which signals a threat to other bees, causing widespread agitation and defensiveness in the hive.
Purity of the Product
Using a glass collection plate results in extremely pure venom, as it can be scraped off without contaminants. The alternative mentioned in some methods, using absorbent tissues, requires a secondary extraction step with distilled water, which can introduce complexities.
Frequency of Collection
Because of the stress it induces, venom collection cannot be performed constantly on the same hive. Beekeepers must allow for a recovery period to ensure the long-term health and productivity of the colony.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Applying this method effectively requires aligning your technique with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is maximizing yield: Place the collector at the hive entrance during peak foraging hours to ensure the maximum number of bees cross the device.
- If your primary focus is venom purity: A glass collection plate is the industry standard and the superior choice, as the dried venom can be harvested directly with a scraper.
- If your primary focus is minimizing hive stress: Limit collection sessions to short durations (e.g., 20-30 minutes) and provide ample recovery time between harvests from the same colony.
Ultimately, the electro-shock method represents a sophisticated balance between harvesting a valuable natural product and preserving the health of the honeybee colony.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Method | Electro-shock stimulation |
| Primary Equipment | Collector frame with wires, power unit, glass/plastic plate |
| Bee Impact | Non-lethal but stressful; bee stings plate and retracts stinger unharmed |
| Final Product | Dried, crystalline venom powder |
| Key Consideration | Balance yield with hive health; requires recovery periods between collections |
Ready to scale your bee venom production or start your own operation?
HONESTBEE supplies commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the professional-grade, wholesale-focused supplies needed for efficient and ethical harvesting. From durable collector frames to reliable power units, our equipment is designed for maximum yield and minimal hive stress.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our wholesale solutions can support your commercial beekeeping goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Full Set Beekeeping Electronic Bee Venom Collector Machine Device for Bee Venom Collecting
- 8-Frame Electric Self-Reversing Honey Extractor Spinner for Commercial Honey Extraction Equipment
- HONESTBEE 6 Frame Three Use Electric Honey Extractor for Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE 72 Frame Industrial Electric Honey Extractor for Beekeeping
- 40 Frame Commercial Electric Honey Extractor for Beekeeping
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of an electric stimulus bee venom collection device? Optimize Your Venom Yield Safely
- How do electronic bee venom collectors ensure efficient harvesting? Maximize Pharmaceutical Purity with Pulse Technology
- Why is specialized hardware necessary for inflammatory disease treatments? Master Pure Bee Venom Extraction
- How does an electric shock collector function to harvest bee venom without harming bees? Safe Extraction Guide
- What is the function of an electronic pulse bee venom collector? Boost Revenue Without Harming Your Colony



















