In short, beeswax is a biological substance secreted from specialized glands on a worker bee's abdomen. The bee then processes these secretions with its legs and mouthparts to create a malleable building material for constructing the honeycomb.
Beeswax production is not a passive byproduct but a deliberate, energy-intensive manufacturing process. It is undertaken by specific bees at a specific age, only when the collective hive perceives a need for new construction.

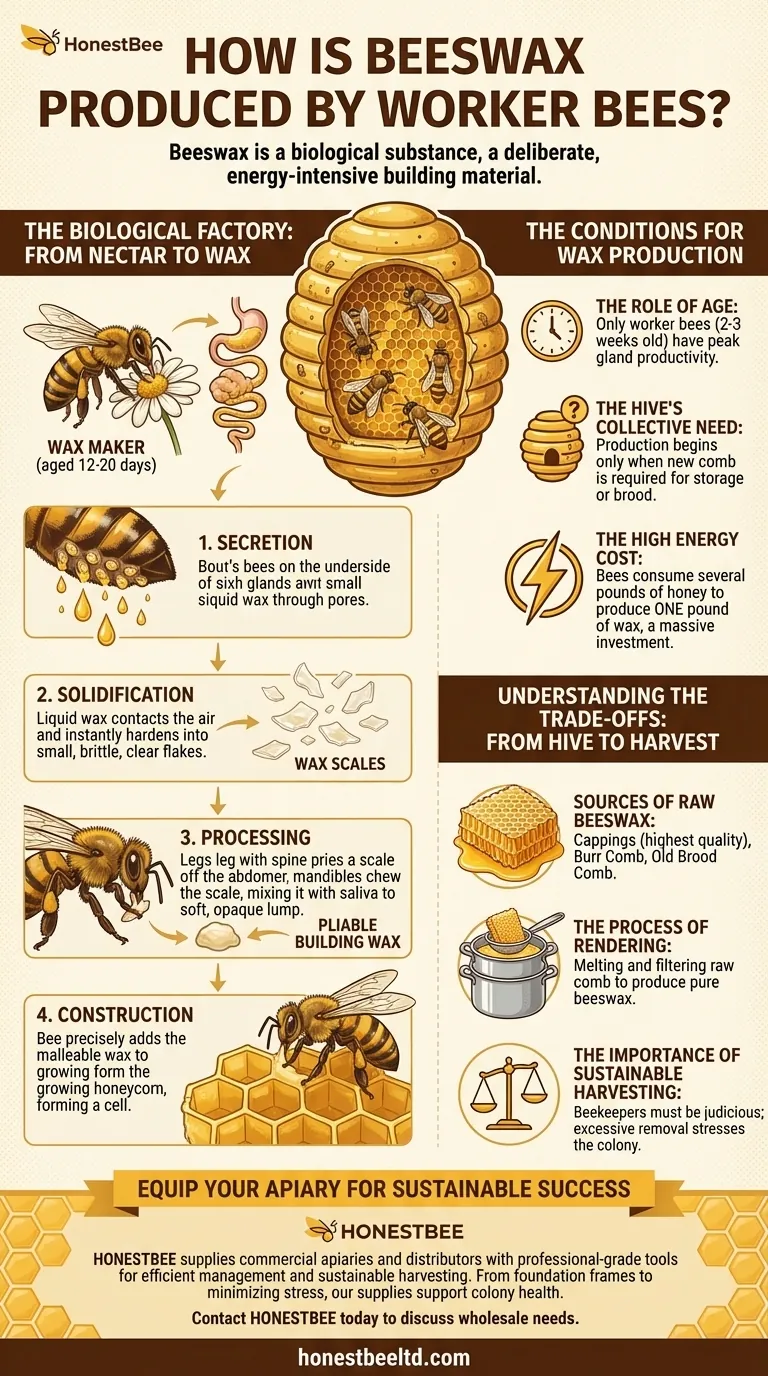
The Biological Factory: From Nectar to Wax
The creation of beeswax is a fascinating biological process that converts the colony's food stores into the very structure of its home. It is a highly specialized task performed by a distinct group of bees.
Specialized Glands on the Abdomen
Beeswax originates from four pairs of specialized glands located on the underside of a young worker bee's abdomen. These glands are most developed and productive in bees that are between 12 and 20 days old.
Secretion and Scale Formation
The glands convert sugars from honey into a liquid wax, which is then secreted through small pores. Upon contact with the air, this liquid hardens almost instantly into small, clear, and brittle flakes known as wax scales.
Chewing Wax into a Building Material
The worker bee uses a specialized spine on its middle leg to pry the hardened scale off its abdomen. It then passes the scale forward to its mandibles, or mouthparts.
By chewing the scale and mixing it with saliva, the bee transforms the brittle flake into a pliable, opaque, and workable construction material. This finished wax is then meticulously applied to build or repair the hive's iconic hexagonal honeycomb cells.
The Conditions for Wax Production
Bees do not produce wax constantly. Its creation is a carefully regulated activity, triggered by specific conditions within the hive and requiring a significant investment of resources.
The Role of Age
The "wax-maker" phase in a worker bee's life is temporary. The wax glands are at their peak productivity when a bee is roughly two to three weeks old. After this, the glands begin to atrophy as the bee transitions to other duties, such as foraging.
The Hive's Collective Need
Wax production begins only when the colony needs to build new comb for honey storage or for the queen to lay eggs. This collective "decision" ensures the bees do not waste precious energy and resources creating wax that isn't needed.
The High Energy Cost
Producing wax is one of the most energy-intensive tasks a bee can perform. It is estimated that bees must consume several pounds of honey to produce a single pound of wax. This high cost underscores why production is so tightly controlled.
Understanding the Trade-offs: From Hive to Harvest
Humans have collected beeswax for millennia, but this process involves understanding where the wax comes from and the impact of its removal.
Sources of Raw Beeswax
Beekeepers collect wax from several sources. The highest quality wax often comes from cappings, the thin layer of wax used to seal ripened honey in the comb. Other sources include burr comb (excess comb built in irregular places) and old, dark brood comb that is being retired.
The Process of Rendering
Raw comb collected from a hive contains impurities like honey, pollen, and debris. Rendering is the process of melting and filtering the raw comb to produce clean, pure beeswax. This is often done with water in a double boiler or a solar melter, where the lighter wax separates from the water and debris as it cools.
The Importance of Sustainable Harvesting
Because bees expend so much energy to produce wax, beekeepers must be judicious in how much they harvest. Removing too much comb, especially from a young or weak colony, can place significant stress on the bees, forcing them to divert energy from other vital tasks to rebuild their home.
Applying This Knowledge
Understanding the lifecycle of beeswax provides a deeper appreciation for both the material and the organism that creates it.
- If your primary focus is beekeeping: Recognize that a colony's ability to draw comb is a key indicator of its health and access to resources, and harvest wax sustainably.
- If your primary focus is using beeswax: Understand that wax from cappings is often considered the purest, while wax from old brood comb may be darker and retain more hive aromas.
- If your primary focus is general knowledge: Appreciate that beeswax is a deliberately manufactured building material, representing a massive energy investment for the colony.
Understanding this intricate process reveals beeswax not as a simple byproduct, but as the very architecture of the honey bee colony.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Actor | Key Action | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Secretion | Worker Bee (12-20 days old) | Wax glands convert honey sugars into liquid wax. | Liquid wax is secreted. |
| 2. Solidification | Air | Liquid wax contacts air. | Liquid hardens into brittle wax scales. |
| 3. Processing | Worker Bee's legs & mandibles | Bee pries off scale, chews it with saliva. | Brittle scale becomes pliable building wax. |
| 4. Construction | Worker Bee | Bee applies malleable wax to the comb. | New hexagonal honeycomb cells are built. |
Equip Your Apiary for Sustainable Success
Understanding the immense energy bees invest in wax production highlights the need for high-quality, durable equipment that supports colony health. HONESTBEE supplies commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the reliable tools needed for efficient hive management and sustainable wax harvesting.
From foundation frames that encourage straight comb to harvesting tools that minimize colony stress, our wholesale-focused operations ensure you get the professional-grade supplies your business depends on.
Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss your wholesale needs and discover how our equipment can contribute to the success and sustainability of your beekeeping operations.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Beeswax Melter for Candle Making Honey Bee Wax Melter
- Steam Beeswax Melter Wax Warmer for Wax Processing
- Professional Stainless Steel Wax Melter for Beekeeping and Crafts
- Electric Flatting and Embossing Machine with Tray for Beekeeping
- Electric Beeswax Flat Sheet Machine with Operating Tray for Wax Processing
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of high-resolution fixed IP cameras in automated bee colony monitoring?
- Why is the implementation of sustainable harvesting tools critical for ecological protection in honey production?
- How do clean, new beehives support the process of colony expansion and artificial swarming? Boost Growth and Hygiene
- What role do industrial-grade sound intensity sensors play in beehive behavior analysis? Predicting Swarms & Queen Loss
- Why do Precision Apiculture Systems require high-capacity batteries and dual-battery power rotation schemes?
- How does sunlight exposure influence honey bee colony health? Optimize Hive Placement for Maximum Productivity
- Why is the configuration of standardized beehives critical? Ensure Precise Data in Bee Foraging Research
- How are portable electronic platform scales or hanging scales utilized to measure honey bee colony productivity?



















