In short, pump-based honey filling systems are defined by their speed and suitability for high-volume production. Their primary advantages are fast, consistent filling rates ideal for large-scale, automated operations. The main disadvantage is a significantly higher initial investment compared to other filling methods.
Choosing a filling machine is less about which technology is "best" and more about aligning the machine's core strengths—speed, precision, or simplicity—with your specific production goals and budget.
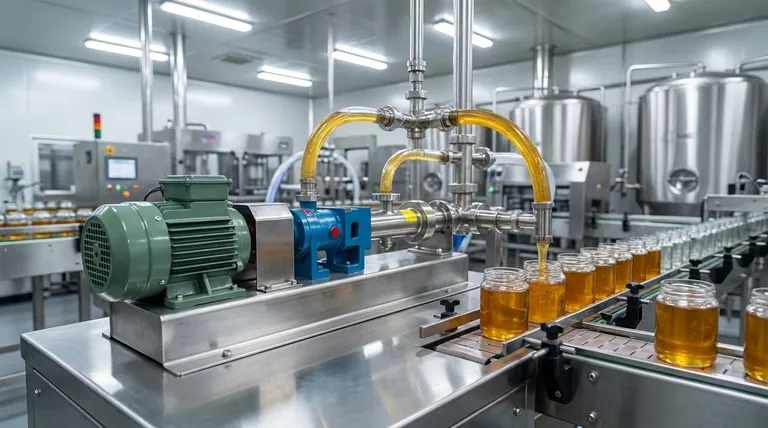

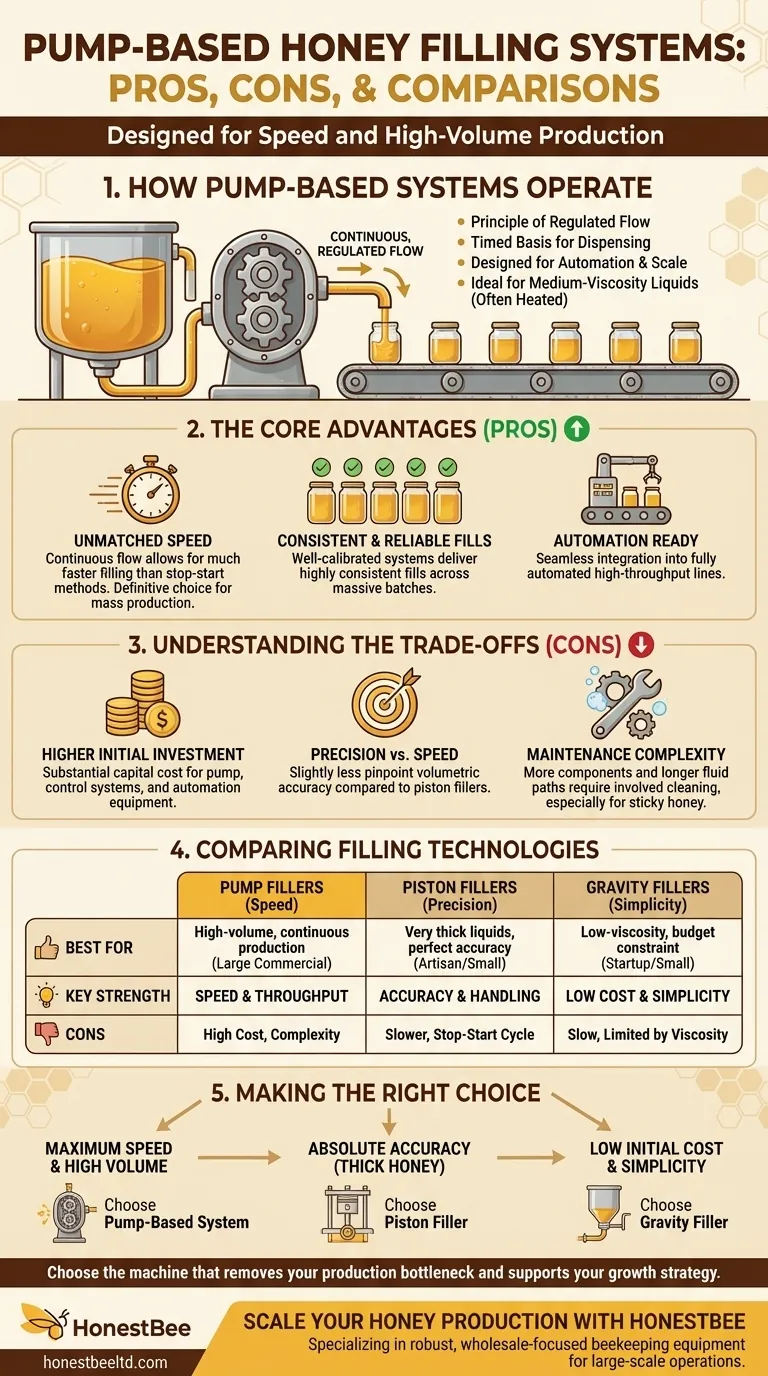
How Pump-Based Systems Operate
The Principle of Regulated Flow
Pump-based fillers work by using a pump (such as a lobe, gear, or progressive cavity pump) to create a continuous, regulated flow of honey. Unlike systems that measure a specific volume per cycle, pump fillers often operate on a timed basis—the pump runs for a set duration to dispense the target amount into each container.
This mechanism is what makes them exceptionally fast. It allows for a non-stop, "on-the-fly" filling process that integrates seamlessly into a fully automated production line where containers are constantly moving.
Designed for Automation and Scale
You will almost always find pump fillers as part of a larger, automated system. Their design is inherently suited for high-throughput environments where minimizing downtime and maximizing the number of units filled per hour are the primary objectives.
They are particularly effective for medium-viscosity liquids. While honey is thick, many large-scale producers use gentle heating systems to slightly reduce its viscosity, making it flow more easily through the pump and tubing.
The Core Advantages of Pump Fillers
Unmatched Speed for High Volume
The single greatest advantage of a pump-based system is speed. Because they provide a continuous flow, they can fill containers much faster than the start-stop cycle of a piston filler. This makes them the definitive choice for businesses focused on mass production.
Consistent and Reliable Fills
While not always as volumetrically precise as a piston filler, a well-calibrated pump system delivers highly consistent fills. By precisely controlling the run time of the pump, it ensures that every jar receives the same amount of honey, maintaining product consistency across a massive batch.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
The Higher Initial Investment
The most significant drawback is cost. Pump-based systems, especially those integrated into a fully automated line, represent a substantial capital investment. This includes the pump itself, the control systems, conveyors, and other associated equipment.
Precision vs. Speed
Pump fillers excel at consistency but may offer slightly less pinpoint accuracy than a piston filler. A piston filler dispenses an exact, pre-measured volume from a cylinder, which is often considered the gold standard for precision. For very high-value products sold in small containers, this marginal difference in accuracy can be a critical factor.
Maintenance and Cleaning Complexity
An automated pump system has more complex components and longer fluid paths than simpler gravity or piston fillers. This can translate to more involved and time-consuming cleaning and maintenance procedures, which is a crucial consideration for facilities handling a natural, sticky product like honey.
How Pumps Compare to Other Filling Technologies
Pump Fillers vs. Piston Fillers
This is the most common comparison for honey producers. Piston fillers are champions of accuracy and are excellent for very thick, viscous liquids without needing heat. They are ideal for artisan producers or anyone prioritizing perfect volumetric fills over raw speed.
Pump fillers, in contrast, prioritize speed and throughput. They are the workhorses of large commercial operations where filling thousands of jars per hour is the goal.
Pump Fillers vs. Gravity Fillers
Gravity fillers are the simplest and most cost-effective option. They rely on the weight of the honey in an overhead tank to fill containers. This method works best for low-viscosity (runny or heated) honey and is suited for small-scale or startup operations where budget is a primary constraint.
A pump system is vastly faster and can handle higher viscosities than a gravity filler, but at a much higher cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
Choosing the correct technology requires a clear understanding of your business priorities.
- If your primary focus is maximum production speed and high volume: A pump-based filling system is the undisputed best choice for scaling your operation.
- If your primary focus is absolute filling accuracy, especially for thick honey: A piston filler will provide the precision and material handling you need.
- If your primary focus is low initial cost and operational simplicity: A gravity filler is the most practical entry point, provided your honey's viscosity is suitable.
Ultimately, the right machine is the one that removes your biggest production bottleneck and supports your growth strategy.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Pros of Pump Systems | Cons of Pump Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Unmatched for high-volume, continuous filling | - |
| Cost | - | High initial investment |
| Precision | Highly consistent fills | Slightly less accurate than piston fillers |
| Maintenance | - | More complex cleaning and upkeep |
| Best For | Large-scale, automated commercial apiaries | Smaller operations with budget constraints |
Scale your honey production with the right equipment.
Pump-based filling systems are the powerhouse for high-volume commercial apiaries and distributors. At HONESTBEE, we specialize in supplying robust, wholesale-focused beekeeping equipment that meets the demands of large-scale operations.
Let us help you choose the perfect filling machine to eliminate bottlenecks and maximize your output. Contact our experts today for a tailored solution that drives your growth.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Honey Convey Pump Screw Honey Pump for Viscous Liquid
- 10L Stainless Steel Electric Honey Press Machine
- Stainless Steel Manual Honey Press with Guard for Pressing Honey and Wax
- Electric Honey Press Machine for Squeezing Honey Comb Press Equipment
- Easy Use Manual Stainless Steel Honey Press for Honey Comb
People Also Ask
- What is the process for harvesting honey from a Kenya Top-Bar Hive? Master the Crush and Strain Method
- What is a stainless steel screw honey pump used for? A Guide to Gentle, Efficient Honey Transfer
- What voltage options are available for stainless steel screw honey pumps? Choose the Right Power for Your Scale
- How does a stainless steel screw honey pump operate? A Guide to Gentle, High-Quality Honey Transfer
- How do professional honey processing tools improve industrial efficiency? Boost Your Apiary's Scalability



















