First and foremost, your wax cappings are a valuable secondary harvest, not waste. After extraction, these cappings can be processed to separate the remaining honey from the pure beeswax, which can then be rendered into clean blocks for use in a wide range of products, from candles and cosmetics to new hive foundations.
The core task after honey extraction is to separate the residual honey from the wax. The method you choose—washing, melting, or letting the bees clean it themselves—depends on your goals for efficiency, purity, and effort.

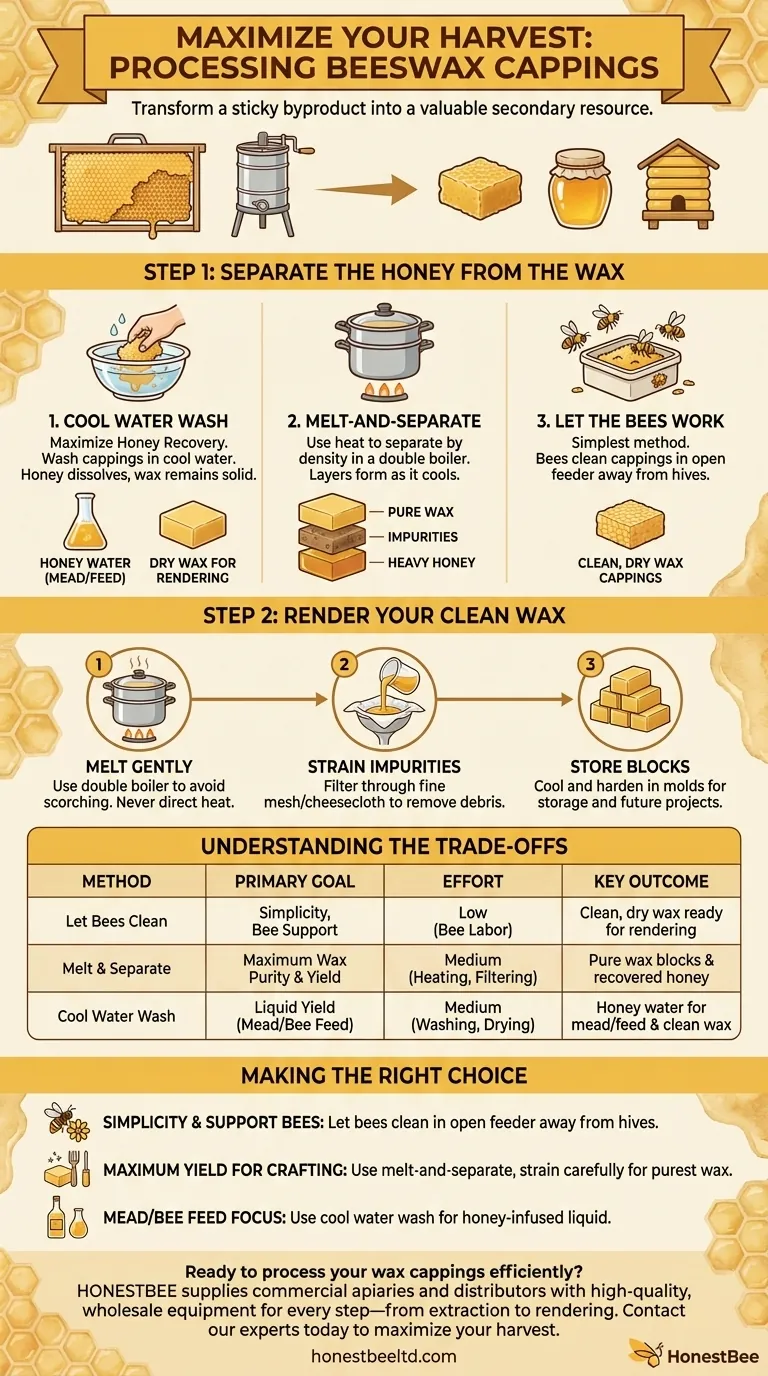
Step 1: Separate the Honey from the Wax
"Wet" cappings are a sticky mixture of beeswax and honey. The first and most critical step is to separate these two valuable products. You have three primary options.
Option 1: Washing with Cool Water
This method is excellent for maximizing honey recovery. By washing the cappings in cool or room-temperature water, the honey dissolves into the water without melting the wax.
The resulting sweet liquid, often called "honey water" or mead wash, can be used to make mead or fed back to the bees. The clean wax can then be dried and stored for rendering.
Option 2: The Melt-and-Separate Method
This method uses heat to separate the components by density. Using a double boiler or a dedicated wax melter is essential to avoid scorching the wax.
As the cappings melt, three distinct layers will form as it cools. The pure, melted wax will float to the top and harden. The heavier honey will sink to the bottom, and a layer of impurities (sometimes called "slumgum") will get trapped in between. Once solid, you can easily remove the clean disc of wax.
Option 3: Letting the Bees Do the Work
For many hobbyists, this is the simplest method. You can place the wet cappings in an open container or feeder some distance away from your hives.
The bees will find this resource and carry all the remaining honey back to their hive, leaving you with perfectly clean, dry wax cappings that are ready for melting and processing. This also provides your colony with a valuable food source.
Step 2: Render Your Clean Wax
Once your wax is free of honey and dry, the next step is to render it—the process of melting and filtering it to remove impurities.
The Importance of a Double Boiler
Beeswax is flammable and can be easily scorched. Never melt it over direct heat. Always use a double boiler, which melts the wax gently with steam, or a dedicated, temperature-controlled wax melter.
Strain to Remove Impurities
As you melt the wax, you will notice debris like bee parts or pollen. To create a clean, high-quality product, you must strain the molten wax.
Pour the melted wax through several layers of cheesecloth or a dedicated fine-mesh filter into a heat-safe mold. Molds can be anything from silicone bread pans to dedicated beeswax block molds.
Storing for Future Use
Once the wax cools and hardens in the molds, you will have solid blocks of pure, clean beeswax. These blocks are easy to store in a cool, dark place and are ready for any project.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right method involves balancing effort, purity, and potential risks. Each approach has distinct advantages and disadvantages.
Effort vs. Purity
Washing and melting require more active work but give you complete control over the process, yielding both recovered honey and clean wax immediately. Letting the bees clean the cappings is the lowest-effort method but you forfeit the remaining honey.
Safety and Pest Management
Wet cappings left in the open will attract pests, from ants to wasps. If you are not giving them to your bees, they must be processed quickly or stored in a sealed, airtight container.
When letting your own bees clean the cappings, place the container at least 50-100 feet from your hives. Placing it too close can trigger a "robbing frenzy," where bees from different colonies fight over the resource, which can be destructive to weaker hives.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should align with your priorities as a beekeeper.
- If your primary focus is simplicity and supporting your bees: Let the bees clean the cappings in an open feeder away from the hives.
- If your primary focus is maximum yield for crafting: Use the melt-and-separate method, followed by careful straining to produce the purest wax blocks.
- If your primary focus is making mead or feeding bees liquid sugar: Use the cool water washing method to create a honey-infused liquid.
By properly processing your wax cappings, you transform a sticky byproduct into another valuable and rewarding resource from your hive.
Summary Table:
| Method | Primary Goal | Effort Level | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Let Bees Clean | Simplicity, Bee Support | Low | Clean, dry wax ready for rendering |
| Melt & Separate | Maximum Wax Purity/Yield | Medium | Pure wax blocks & recovered honey |
| Cool Water Wash | Liquid Yield (Mead/Bee Feed) | Medium | Honey water for mead/feed & clean wax |
Ready to process your wax cappings efficiently? HONESTBEE supplies commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors with the high-quality, wholesale-focused equipment needed for every step—from extraction to wax rendering. Contact our experts today to discuss how our products can help you maximize the value of your entire harvest.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Beeswax Melter for Candle Making Honey Bee Wax Melter
- Steam Beeswax Melter Wax Warmer for Wax Processing
- Professional Stainless Steel Wax Melter for Beekeeping and Crafts
- Honey Wax Separating Wax Press with Metal Screw Wax Separator Machine
- Electric Beeswax Flat Sheet Machine with Operating Tray for Wax Processing
People Also Ask
- What makes polyurethane foam environmentally friendly? The Surprising Benefits of a Durable, Inert Material
- What role do precision wax melting units and molds play? Professional Beeswax Processing & Crafting Guide
- How do water jacket melters function? Achieve Gentle, Scorch-Free Melting for Sensitive Materials
- What are the features of industrial wax melters? Unlock Precision Purity for Commercial Beeswax Production
- What happens to beeswax if it is heated beyond 170F? Prevent Irreversible Quality Loss and Darkening



















