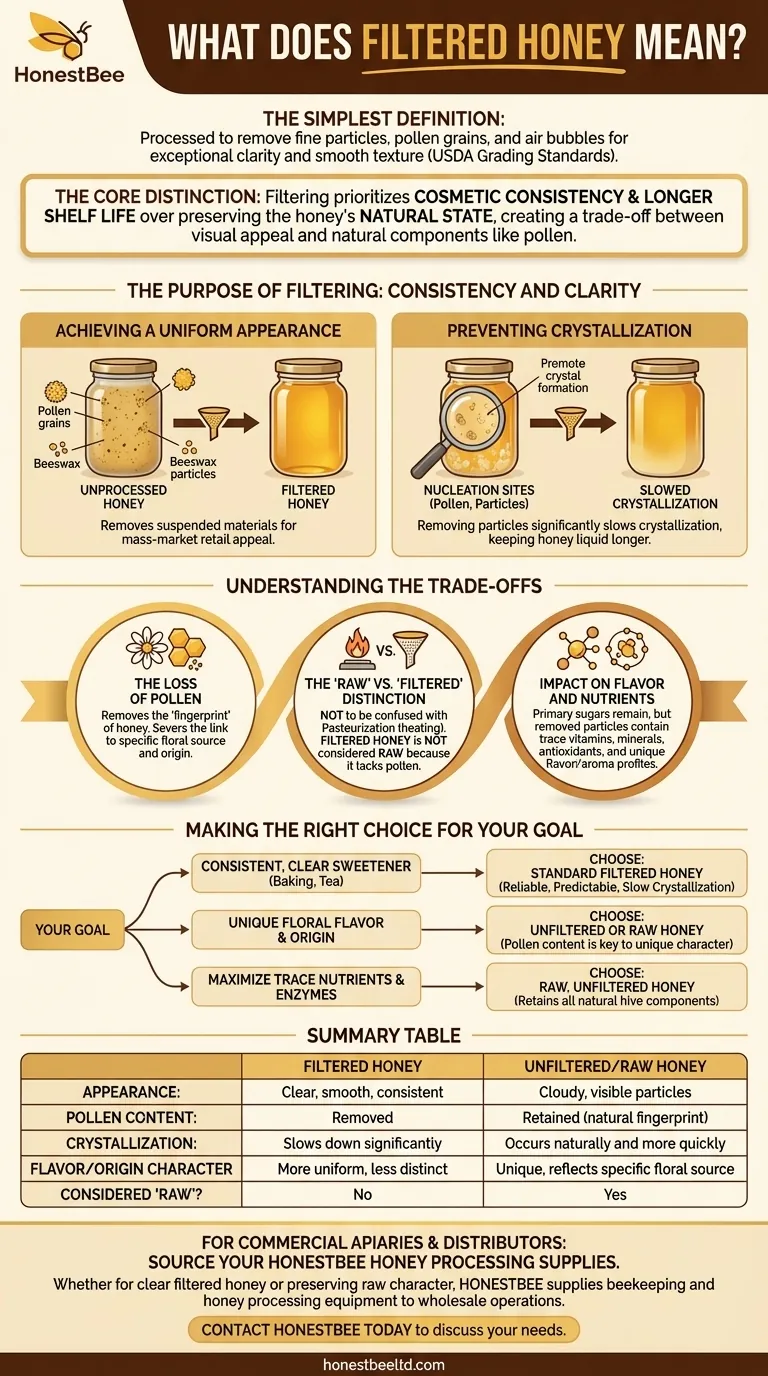
In the simplest terms, filtered honey is honey that has been processed to remove fine particles, pollen grains, and air bubbles. According to USDA Grading Standards, this process is designed to create a product that is exceptionally clear and smooth in texture.
The core distinction to understand is that filtering prioritizes cosmetic consistency and a longer shelf life over preserving the honey's natural, unadulterated state. This creates a clear trade-off between visual appeal and the retention of natural components like pollen.

The Purpose of Filtering: Consistency and Clarity
The primary driver behind filtering honey is commercial appeal. A uniform, clear product is often what mainstream consumers expect to see on the shelf.
Achieving a Uniform Appearance
Unprocessed honey naturally contains a variety of suspended materials. These include tiny grains of pollen, small particles of beeswax, and even propolis.
Filtering removes these elements, transforming a potentially cloudy liquid into the crystal-clear, golden product many people associate with honey. This consistency is highly valued for mass-market retail.
Preventing Crystallization
The fine particles suspended in unfiltered honey, especially pollen grains, act as nucleation sites. These are points where the natural sugars in honey can begin to form crystals.
By removing these particles, producers significantly slow down the crystallization process. This keeps the honey in a liquid state for much longer on the shelf, which is a major commercial advantage.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While filtering creates a visually stable product, this process is not without consequences. The choice to filter involves a direct trade-off that impacts the final character of the honey.
The Loss of Pollen
Pollen is one of the most significant components removed during filtration. While not a major source of nutrition, pollen is the "fingerprint" of honey.
It allows experts (and laboratories) to trace the honey back to its specific floral source and geographical origin. Removing it severs this link to its provenance.
The "Raw" vs. "Filtered" Distinction
It's important not to confuse filtering with pasteurization (heating), though they are often done together in large-scale processing.
Raw honey is by definition unfiltered and unpasteurized. Because filtering removes a key natural component (pollen), honey that has undergone this process is not considered raw.
Impact on Flavor and Nutrients
The primary nutritional profile of honey comes from its sugars and is largely unaffected by filtering.
However, the pollen and propolis particles that are removed do contain trace amounts of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Their removal can also subtly alter the complex flavor and aroma profile that makes honey from a specific floral source unique.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice between filtered and unfiltered honey should be guided by your specific priorities and what you value most in the product.
- If your primary focus is a consistent, clear sweetener for baking or tea: Standard filtered honey is a reliable and predictable choice that will not crystallize quickly.
- If your primary focus is experiencing a unique floral flavor and origin: Choose unfiltered or raw honey, as the pollen content is a key part of its unique character.
- If your primary focus is maximizing potential trace nutrients and enzymes: Raw, unfiltered honey is the best option, as it retains all the natural components from the hive.
Ultimately, understanding what "filtered" means empowers you to choose the honey that perfectly aligns with your needs.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Filtered Honey | Unfiltered/Raw Honey |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Clear, smooth, consistent | May be cloudy with visible particles |
| Pollen Content | Removed | Retained (acts as a natural fingerprint) |
| Crystallization | Slows down significantly | Occurs naturally and more quickly |
| Flavor/Origin Character | More uniform, less distinct | Unique, reflects specific floral source |
| Considered "Raw"? | No | Yes |
For Commercial Apiaries & Distributors: Source Your Honey Processing Supplies from HONESTBEE
Whether your operation focuses on producing clear, shelf-stable filtered honey or aims to preserve the unique character of raw honey, having the right equipment is crucial. HONESTBEE supplies beekeeping and honey processing supplies and equipment to commercial apiaries and beekeeping equipment distributors through our wholesale-focused operations.
We provide the reliable tools you need to meet market demands with confidence.
Contact HONESTBEE today to discuss your equipment needs and streamline your honey production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 0.5T Capacity Honey Dehumidifier Dryer with Vacuum Heating and Thickening Filtering Machine
- Economy Honey Homogenizer Mixer and Melting Machine for Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE 72 Frame Industrial Electric Honey Extractor for Beekeeping
- HONESTBEE 3-Frame Manual Acrylic Honey Extractor
- 10L Stainless Steel Electric Honey Press Machine
People Also Ask
- What principle does the honey vacuum thickener use to concentrate honey? Preserve Quality with Low-Temperature Evaporation
- Why is the use of dry sieves and storage containers critical? Prevent Honey Fermentation and Spoilage
- What are some methods to prevent fermentation in high-moisture honey? Protect Your Honey's Quality and Value
- Why is industrial-grade dehumidification equipment essential for producing commercial-standard honey? Expert Insights
- How does the internal ventilation management of a beehive affect the efficiency of honey dehydration?



















